Open-Source Purchase Order Systems: Options, When to Use, How to Deploy
Scale beyond open source, Hyperbots delivers AI-powered procurement efficiency, compliance, and lasting enterprise value.
Executive Summary
The digitization of procurement has shifted purchase order (PO) processes from paper and email to structured platforms that improve visibility, compliance, and efficiency. Many finance and procurement leaders, especially in mid-sized companies, initially consider adopting an open source purchase order system. These platforms promise flexibility, low upfront cost, and community-driven innovation.
Yet, the decision is not straightforward. While a purchase order management system open source can reduce licensing costs and provide basic functionality, enterprises often find limitations in scalability, compliance, and integration. As procurement matures, CFOs and Controllers must decide when a free electronic purchase order system suffices—and when investing in an advanced AI-powered solution like Hyperbots’ Procurement Co-pilot delivers exponentially higher ROI.
By the end, finance leaders will gain a clear framework for evaluating open source purchase order systems versus enterprise-grade AI solutions, and understand how Hyperbots is uniquely positioned to deliver transformational outcomes.
Why Purchase Order Automation Matters
For decades, purchase orders were managed through manual paperwork, phone calls, and emails. While effective for small operations, these approaches introduced inefficiencies, compliance risks, and errors. As organizations scaled, they realized that purchase order workflows directly affect:
Spend control: Preventing overspending and enforcing budget approvals.
Compliance: Ensuring regulatory adherence and audit readiness.
Vendor relationships: Faster PO approvals accelerate supplier trust and performance.
Operational efficiency: Reducing back-and-forth between procurement, finance, and vendors.
Today, an open source purchase order system is often the first step for mid-sized businesses seeking automation without the heavy price tag of enterprise software. However, the market has evolved. Enterprises now expect not only automation but also intelligence—predictive recommendations, anomaly detection, and end-to-end integration. This is where Hyperbots’ Procurement Co-pilot stands apart, delivering far more than traditional PO platforms.
Fundamentals of an Open Source Purchase Order System
Before diving into options and deployments, let’s define what makes an open source purchase order system distinct.
What Is an Open Source Purchase Order System?
An open source purchase order system is software that enables organizations to create, approve, track, and close purchase orders without licensing fees. The source code is openly available, allowing businesses to customize features, integrate with their existing ERP, or build unique workflows.
Key attributes include:
Free to use: No proprietary license fees.
Customizable: Developers can tailor workflows and reporting.
Community support: Updates, bug fixes, and plugins often come from a global community.
Transparency: Full visibility into the codebase for compliance and security audits.
Typical Features in an Open Source System
While functionality varies, most open-source purchase order management systems open source platforms include:
Basic PO creation and approval workflows
Vendor information storage
Budget or category tagging
Reporting dashboards
Limited integration with accounting systems
These features are sufficient for startups and small businesses, but often require significant IT involvement for customization and maintenance.
Open Source vs. Proprietary Purchase Order Systems
Choosing between open source and enterprise-grade proprietary systems requires understanding their trade-offs.
Advantages of Open Source
Cost savings: Avoids high licensing fees.
Flexibility: Custom code enables unique workflows.
No vendor lock-in: Organizations own their deployments.
Community innovation: Access to global developer contributions.
Limitations of Open Source
High IT dependency: Internal teams must handle updates, security, and integrations.
Limited compliance features: Audit trails, SOX readiness, and SLA monitoring are often absent.
Scalability challenges: Managing thousands of POs requires infrastructure scaling.
Fragmented support: Reliance on forums and communities instead of guaranteed SLAs.
By contrast, platforms like Hyperbots’ Procurement Co-pilot are designed for scale, compliance, and intelligence—providing end-to-end automation and auditability without overburdening IT.
Free and Community-Driven Options in Today’s Market
Organizations exploring an electronic purchase order system free from licensing costs often start with popular open source options.
Popular Open Source Purchase Order Systems
Odoo Procurement Module
A flexible ERP suite with procurement extensions.
Pros: Integrated with inventory, sales, and finance.
Cons: Requires paid enterprise support for advanced features.
ERPNext Procurement
Community-driven ERP system with strong customization capabilities.
Pros: Cloud and on-premise deployment.
Cons: Complex setup for large enterprises.
Dolibarr ERP & CRM
Lightweight ERP with procurement workflows.
Pros: Simple UI, free modules.
Cons: Limited reporting and automation.
inoERP
Open source ERP with supply chain focus.
Pros: Procurement and vendor modules included.
Cons: Small community, limited integrations.
Where Free Systems Work Best
A purchase order management system, open source, is often suitable when:
The organization is early-stage with low transaction volumes.
Budgets are limited, and licensing fees are prohibitive.
Internal IT teams are capable of managing updates and integrations.
Compliance requirements are minimal.
However, once procurement volumes cross thousands of POs annually, or when audit requirements intensify, organizations need more sophisticated solutions like Hyperbots’ AI Co-pilots.
When to Use an Open Source Purchase Order System
Not every organization should adopt open source procurement tools. The right choice depends on scale, compliance requirements, and long-term strategy.
Ideal Scenarios for Open Source PO Systems
Startups and small businesses managing <500 POs annually.
Non-profits and NGOs seeking low-cost digitalization.
IT-savvy teams who can customize and maintain the system.
Short-term pilots where open source is used to validate digital procurement before enterprise rollout.
When to Look Beyond Open Source
Mid-market and enterprise organizations requiring SLA-backed support.
CFOs demanding compliance, audit trails, and GL-coding recommendations.
Procurement leaders are seeking intelligent workflows like anomaly detection and budget control.
Finance teams are aiming for end-to-end automation across requisitions, approvals, invoices, and vendor management.
This is where Hyperbots’ Procurement Co-pilot delivers transformational outcomes. Unlike open source systems that focus on workflows, Hyperbots provides AI-driven intelligence and automation, a critical differentiator.
Deployment Best Practices for Open Source Purchase Order Systems
Deploying an open source purchase order system requires thoughtful planning. Unlike proprietary SaaS tools, where the vendor manages hosting, upgrades, and compliance, open source platforms shift much of the responsibility to internal teams.
Below are the best practices finance and procurement leaders should follow when considering deployment.

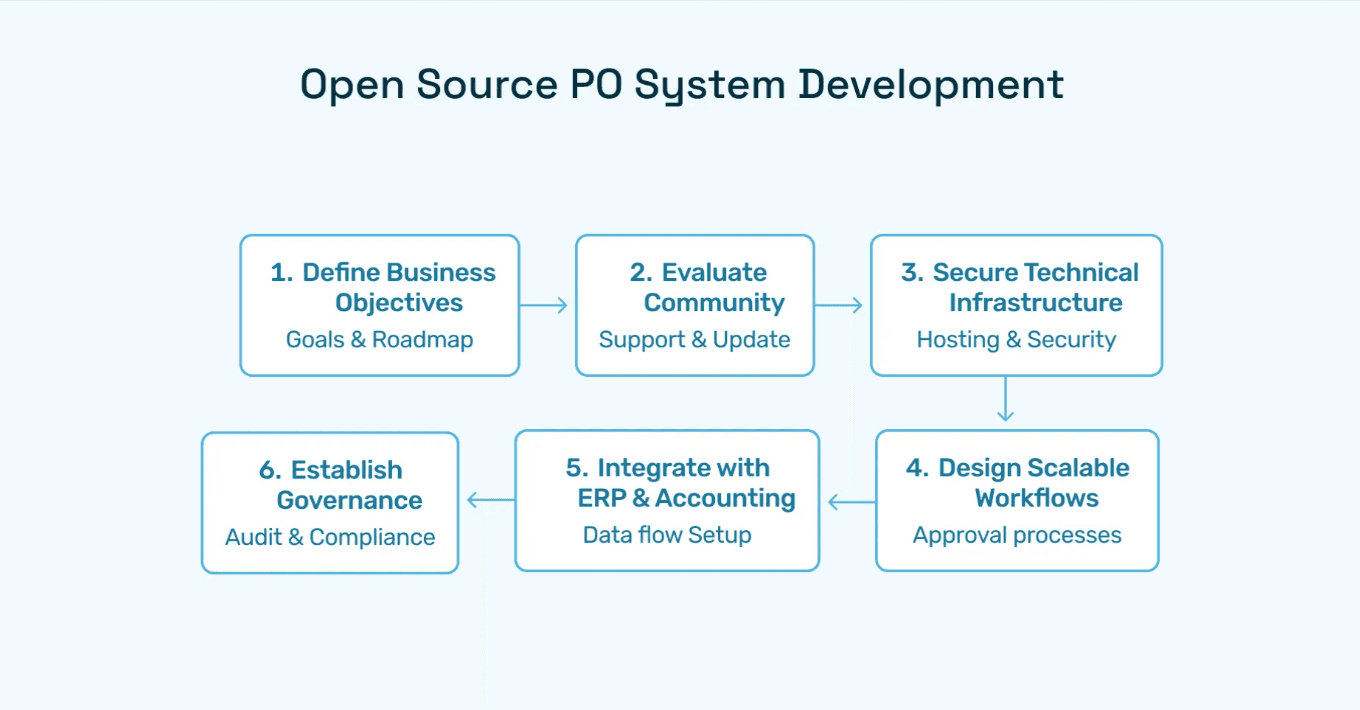
Step 1: Define Business Objectives First
Too often, organizations adopt an open source procurement system simply because it’s “free.” But without aligning the technology to business objectives, the deployment quickly turns into a sunk cost.
Key objectives may include:
Reducing PO cycle time from days to hours
Creating auditable workflows for compliance
Standardizing vendor selection and approvals
Integrating procurement with accounting or ERP
👉 Tip: Draft a procurement automation roadmap before installation, ensuring the system supports both current and future objectives.
Step 2: Evaluate the Community and Support Model
Not all open source systems have active developer ecosystems. For long-term sustainability, organizations should evaluate:
Size of the user community
Frequency of code updates and patches
Availability of documentation
Paid support options (often required for enterprise-grade deployments)
Step 3: Secure Technical Infrastructure
Open source systems require hosting, either on-premises or in the cloud. Enterprises must account for:
Server infrastructure (hardware or cloud costs)
Database management (e.g., MySQL, PostgreSQL)
Backup and disaster recovery plans
Security patching schedules
In regulated industries, compliance teams may also demand penetration testing, vulnerability scanning, and role-based access controls before go-live.
Step 4: Design Scalable Workflows
Open source platforms often allow configuration of approval flows, vendor categories, and budget tagging. CFOs and procurement leaders should standardize these workflows early.
Example of a scalable workflow design:
Requester submits purchase requisition.
System checks budget allocation.
Supervisor or budget owner approves.
Finance validates compliance with GL coding.
System generates a PO and dispatches it to the vendor.
Such workflows ensure consistency while minimizing exceptions.
Step 5: Integrate with ERP and Accounting Systems
For procurement to be effective, POs must flow seamlessly into financial systems. Integrations often require custom coding in open source systems. Common integration points include:
General Ledger (GL) updates
Accounts Payable for invoice matching
Inventory and warehouse systems
Vendor master databases
Failure to integrate leads to siloed data, manual reconciliations, and audit issues.
Step 6: Establish Governance and Auditability
Compliance is one of the biggest gaps in open source procurement deployments. Organizations should proactively implement:
Documented approval policies
Automated audit logs
SLA monitoring for vendor performance
Exception reporting
This prevents fraud, ensures accountability, and makes the system enterprise-ready.
Risks and Limitations of Open Source Deployment
While appealing at first, a purchase order management system open source comes with hidden risks that finance leaders must evaluate carefully.
Hidden Costs of “Free” Software
Although an electronic purchase order system free from licensing fees seems attractive, enterprises often incur significant indirect costs:
IT staff for maintenance and customization
Servers, storage, and cloud hosting fees
Third-party consultants for integration
Time spent managing security and upgrades
A 2023 Deloitte study found that hidden IT costs in open source deployments can exceed 50% of total TCO over five years. This often offsets the licensing savings.
Compliance and Audit Gaps
Open source systems often lack:
SOX-compliant audit trails
Configurable access controls
Automated exception handling
Regulatory reporting features
For CFOs, these gaps pose unacceptable risks. Audit failures can lead to fines, reputational damage, and vendor disputes.
Security Vulnerabilities
Unlike enterprise SaaS platforms where vendors guarantee security patches, open source systems depend on community updates. This creates exposure to:
Outdated libraries with vulnerabilities
Delays in patch adoption
Lack of penetration testing
Weak encryption for vendor data
In industries like healthcare or finance, these risks are prohibitive.
Scalability and Performance
As procurement scales beyond thousands of POs per month, open source systems often struggle with:
Database performance bottlenecks
Slow approval routing
Lack of AI-powered automation
Limited reporting capabilities
At this stage, many organizations transition to platforms like Hyperbots’ Procurement Co-pilot, which are engineered for high-volume, enterprise-grade automation.
Why Enterprises Move Beyond Open Source
Open source systems may serve as an entry point, but as organizations mature, their requirements evolve.
Key Drivers for Transition
Regulatory Compliance Needs
Audit trails, GL coding recommendations, and SOX compliance require enterprise-grade systems.
Scalability
Enterprises cannot rely on community support to handle millions of dollars in spending.
AI-Powered Insights
CFOs demand predictive analytics, anomaly detection, and real-time budget control.
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO)
IT burden and hidden costs often outweigh licensing savings.
End-to-End Automation
Beyond POs, enterprises need integration with invoices, accruals, payments, and vendor management.
This is why Hyperbots is winning market share: its AI Co-pilots deliver holistic procure-to-pay automation, far beyond what open source systems can provide.
Hyperbots’ Differentiated Approach to Purchase Order Automation
Hyperbots is not just another procurement software vendor. It has redefined the category with AI Co-pilots purpose-built for finance and accounting teams.
Core Procurement Co-pilot Capabilities
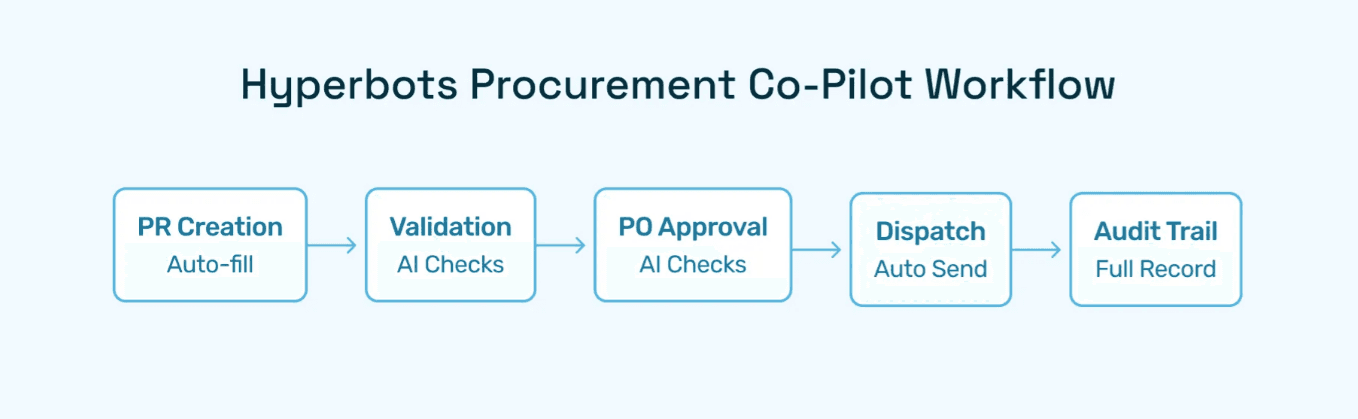
The Procurement Co-pilot is Hyperbots’ flagship AI agent, delivering:
Automated field extraction & PR autofill from PDFs, contracts, and emails
Validation, duplication & anomaly detection to eliminate errors
Budget controls & GL coding recommendations powered by AI
Configurable workflows & forms across departments
Automated PO creation & dispatch with vendor master validation
PO closing & reconciliation with invoices for auditability
Unlike open source systems, where each feature requires customization, Hyperbots provides these out of the box with AI-driven intelligence.
Supporting AI Co-pilots for Procure-to-Pay
Hyperbots extend far beyond POs. It's supporting Co-pilots to automate adjacent finance functions:
Invoice Processing Co-pilot – Automates invoice capture and 3-way match.
Accruals Co-pilot – Ensures accurate period-end accruals.
Payments Co-pilot – Streamlines vendor payments with compliance checks.
Sales Tax Verification Co-pilot – Validates tax rules and compliance.
Vendor Management Co-pilot – Centralizes vendor onboarding, risk, and lifecycle management.
Together, these agents deliver an 80% cost reduction across procure-to-pay operations.
Why Hyperbots Is Different from Other Players
Most procure-to-pay platforms offer workflow automation but stop short of true intelligence. Hyperbots’ differentiation lies in:
Generative AI intelligence is embedded across requisition intake and approvals.
LLM-based approval assistant that understands natural language and context.
End-to-end auditability is built into every workflow.
Seamless integration with ERP, accounting, and vendor systems.
In other words, Hyperbots doesn’t just digitize procurement; it transforms it into a profit-driving engine.
ROI Improvements with Hyperbots’ Procurement Co-pilot
When finance leaders evaluate procurement technology, ROI is the ultimate metric. While open source systems may seem cost-effective upfront, they rarely deliver sustained business impact. Hyperbots, on the other hand, demonstrate measurable ROI in both tangible and intangible ways.
Tangible ROI Metrics
Enterprises that implement Hyperbots’ Procurement Co-pilot report:
80% reduction in operational costs across procurement cycles.
Faster purchase order approvals, cutting cycle times from days to hours.
Decrease in vendor disputes, thanks to automated validation and anomaly detection.
Reduction in maverick spend, through enforced budget and GL compliance.
Lower audit costs, due to automated logs and transparent workflows.
These numbers position Hyperbots far ahead of traditional P2P providers and completely out of reach for open source platforms.
Intangible ROI Benefits
ROI isn’t just about cost savings. Hyperbots also delivers:
Enhanced compliance confidence – Audit readiness at all times.
Employee productivity gains – Finance teams focus on strategy, not data entry.
Supplier trust and loyalty – Faster approvals improve vendor performance.
CFO visibility – Real-time dashboards empower data-driven decision-making.
Together, these benefits transform procurement from a back-office function into a strategic driver of enterprise value.
External Validation – Why Analysts Recommend Enterprise Automation
Gartner’s 2023 report on Procure-to-Pay Platforms highlighted that AI-driven automation delivers 3–5x ROI compared to workflow-only solutions. Deloitte’s 2022 finance automation survey similarly found that CFOs prioritizing AI in procurement realized 30% higher cost savings versus peers.
Open source platforms were barely mentioned in these reports—reinforcing the fact that while useful for small organizations, they cannot meet the compliance and scalability demands of enterprise finance.
By aligning with Hyperbots, enterprises future-proof their procurement processes while meeting analyst-backed benchmarks.
Choosing the Right Path Forward
For finance and procurement leaders, the decision isn’t whether to digitize POs—it’s how to do it. An open source purchase order system can be a valuable entry point, especially for startups and budget-conscious organizations. It provides basic automation, flexibility, and zero licensing costs.
However, as organizations grow, compliance demands intensify, and transaction volumes scale, the limitations of open source become apparent. Hidden costs, IT overhead, and compliance risks often outweigh the initial savings.
This is where Hyperbots’ Procurement Co-pilot shines. With AI-driven automation, seamless ERP integration, and end-to-end auditability, Hyperbots transforms procurement from a cost center into a value generator.
👉 Finance leaders ready to unlock this transformation can explore Hyperbots’ full AI Co-pilot Suite or schedule a personalized demo today.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. What is the main difference between an open source purchase order system and Hyperbots?
A: Open source systems digitize workflows at low cost but lack compliance, scalability, and intelligence. Hyperbots provides AI-powered, enterprise-ready automation that reduces costs by 80% while ensuring audit readiness.
Q2. Can open source systems be integrated with ERP?
A: Yes, but often through custom development. Hyperbots, by contrast, offers out-of-the-box integrations with leading ERPs and accounting systems.
Q3. Are free electronic purchase order systems suitable for large enterprises?
A: Not typically. They work for startups, NGOs, or small businesses. Enterprises require features like anomaly detection, SLA monitoring, and regulatory compliance—available natively in Hyperbots.
Q4. How does Hyperbots ensure compliance?
A: Through automated audit logs, budget control, GL-coding recommendations, and anomaly detection. Every PO is fully traceable and compliant with enterprise standards.
Q5. What ROI can CFOs expect from Hyperbots?
A: Most clients report upto 80% cost reduction, faster cycle times, and improved compliance confidence within the first year.