Purchase Order Control Process: Complete Guide to Controls, Matching & Exception Handling
Learn how to manage purchase orders with effective controls, matching, and exception handling.

Executive Summary
The purchase order control process has evolved from a manual, error-prone workflow into a strategic advantage for modern organizations. With the Purchase Order Software Market projected to reach USD 8.2 Billion by 2033 and organizations finding they can automate more than 80% of the procure-to-pay process, finance leaders are recognizing that robust purchase order controls are essential for operational efficiency and cost management.
This comprehensive guide explores the critical components of effective purchase order control processes, including three-way matching protocols, exception handling procedures, and the transformational impact of AI-powered automation.
For CFOs, Controllers, and Procurement leaders managing enterprise-scale operations, understanding and implementing sophisticated purchase order control processes isn't just about compliance—it's about unlocking operational excellence and driving measurable business value.
Understanding the Purchase Order Control Process Framework
The purchase order control process serves as the financial backbone of organizational procurement, establishing systematic procedures that govern how purchase orders are created, approved, matched, and processed. This framework encompasses multiple control layers designed to prevent fraud, ensure compliance, and maintain spending accuracy.
At its core, the purchase order control process operates on the principle of segregation of duties, where different individuals handle requisition, approval, receiving, and payment functions. This approach creates natural checkpoints that catch errors before they become costly mistakes.
Modern organizations are moving beyond traditional manual controls toward intelligent automation. Nearly 55% of procurement professionals utilize automation for processes they previously did manually, recognizing that automated controls provide both enhanced accuracy and operational scalability.
The purchase order matching process forms the cornerstone of these controls, typically involving three-way matching between the purchase order, goods receipt, and invoice. Top-performing organizations approve 98 percent of purchase orders electronically, as compared to only a little more than half of POs approved electronically among bottom-performing organizations.
Key Components of Effective Purchase Order Controls
Authorization Controls: These establish spending limits and approval hierarchies based on dollar amounts and commodity types. Organizations typically implement multiple approval levels, with higher-value purchases requiring senior management authorization.
Vendor Validation: Systematic verification of supplier credentials, including tax identification numbers, banking information, and business licenses. This control prevents payments to fraudulent or non-existent vendors.
Budget Verification: Real-time checks against departmental budgets and spending allocations to prevent over-expenditure and maintain fiscal discipline.
Compliance Monitoring: Automated checks ensuring all purchase orders comply with internal policies, regulatory requirements, and contract terms.
The Purchase Order Matching Process: Beyond Three-Way Matching
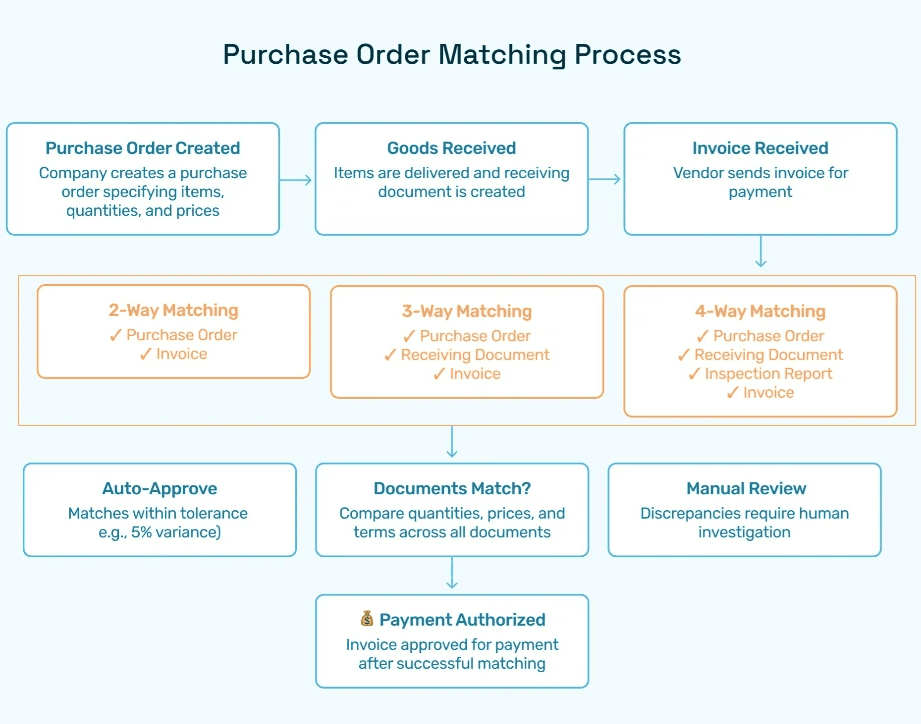
The purchase order matching process represents the most critical control mechanism in procurement operations, serving as the final verification step before payment authorization. While traditional three-way matching remains the gold standard, innovative organizations are implementing more sophisticated matching protocols to address complex procurement scenarios.
Traditional three-way matching compares purchase orders, receiving documents, and vendor invoices to ensure alignment across quantity, pricing, and terms. However, this approach often creates bottlenecks when dealing with partial shipments, service-based purchases, or complex multi-line orders.
Advanced matching processes now incorporate intelligent tolerance settings that automatically approve transactions within predefined variance thresholds. For instance, a 5% price variance might trigger automatic approval, while larger discrepancies route to human reviewers for investigation.
The evolution toward four-way matching adds inspection reports as a fourth verification point, particularly valuable for quality-sensitive industries like pharmaceuticals or aerospace. This additional layer ensures that received goods meet specified quality standards before payment processing.
Automated Matching Technologies
Modern purchase order matching leverages artificial intelligence to handle complex scenarios that previously required manual intervention. These systems can:
Extract Data from Multiple Formats: AI-powered optical character recognition (OCR) technology processes invoices in various formats, from PDF documents to scanned images, automatically extracting relevant matching data.
Handle Complex Line-Item Matching: Advanced algorithms can match purchase orders with invoices containing hundreds of line items, identifying discrepancies and routing exceptions appropriately.
Manage Partial Deliveries: Intelligent systems track partial shipments and automatically adjust matching requirements, preventing payment delays for legitimate partial deliveries.
Currency and Tax Calculations: Automated systems handle complex currency conversions and tax calculations, ensuring accurate matching across international transactions.
Exception Handling in Purchase Order Processing
Exception handling represents one of the most challenging aspects of the purchase order control process, yet it's where organizations often achieve the greatest efficiency gains through automation. Exceptions typically account for 15-30% of all purchase order transactions, making effective exception management crucial for operational efficiency.
Common exceptions include price variances, quantity discrepancies, missing purchase orders, duplicate invoices, and vendor master data issues. Traditional exception handling relies on email notifications and manual research, often creating delays that strain vendor relationships and internal productivity.
Intelligent Exception Management
Advanced exception handling systems categorize exceptions by type and severity, automatically routing them to appropriate personnel based on predefined business rules. This approach ensures that critical exceptions receive immediate attention while routine variances are handled through automated workflows.
Priority-Based Routing: High-value discrepancies or potential fraud indicators receive immediate escalation to senior finance staff, while minor variances may be auto-approved within tolerance limits.
Automated Resolution: Many exceptions can be resolved automatically through integration with ERP systems and vendor portals. For example, a missing purchase order number might be automatically matched using vendor information and line-item details.
Exception Analytics: Sophisticated systems track exception patterns to identify systemic issues, such as frequent price variances from specific vendors or recurring quantity discrepancies in certain product categories.
Vendor Self-Service: Modern platforms provide vendor portals where suppliers can view their purchase orders, submit invoices electronically, and resolve minor discrepancies independently, reducing the burden on internal teams.
After Purchase Order Process: Ensuring Continuous Control
The after purchase order process encompasses all activities following initial purchase order approval, including receiving, invoicing, payment, and closing procedures. This phase often presents the greatest risk for control failures, as attention typically shifts from approval workflows to operational execution.
Effective post-purchase order controls ensure that goods and services are received as specified, invoices are accurate and timely, and purchase orders are properly closed to prevent unauthorized future charges. Organizations frequently discover that weak after purchase order controls lead to duplicate payments, unauthorized charges, and incomplete delivery management.
Receipt Verification Controls
Digital Receiving: Electronic receiving systems capture delivery details in real-time, including quantities, condition, and delivery dates. This digital approach eliminates paper-based receiving reports that can be lost or manipulated.
Mobile Receiving Applications: Warehouse staff use mobile devices to scan barcodes and capture delivery photos, creating immediate verification records that integrate with the purchase order matching process.
Quality Inspection Integration: For items requiring quality verification, integrated inspection workflows ensure that quality approvals are captured before matching approval, preventing payment for defective goods.
Invoice Processing Controls
Automated Invoice Capture: Advanced systems automatically capture invoice data from email attachments, vendor portals, and EDI transmissions, reducing data entry errors and processing time.
Duplicate Invoice Detection: Sophisticated algorithms identify potential duplicate invoices using multiple data points, including vendor information, invoice amounts, and line-item details.
Tax and Regulatory Compliance: Automated tax calculations ensure compliance with local, state, and federal requirements while maintaining detailed audit trails for regulatory reporting.
Non Purchase Order Process: Managing Unplanned Procurement
The non purchase order process addresses procurement scenarios where goods or services are acquired without prior purchase order authorization. While organizations strive to minimize non-PO transactions, emergency purchases, recurring services, and certain vendor categories often require alternative processing approaches.
Non-PO transactions present elevated risk because they bypass traditional approval controls, making robust post-transaction verification essential. 98% of procurement leaders are investing in analytics and insights tools, automation, and AI specifically to address these control gaps.
Controlled Non-PO Processing
Retroactive Approval Workflows: Systems that route non-PO invoices through appropriate approval channels based on spend amount, vendor, and department coding, ensuring management oversight despite the lack of pre-approval.
Vendor Category Management: Certain vendor categories, such as utilities or professional services, may be pre-approved for non-PO processing within specified parameters, streamlining routine transactions while maintaining control.
Emergency Purchase Protocols: Formal procedures for handling urgent purchases, including temporary approval authorities and mandatory post-transaction reporting to ensure accountability.
Analytics and Monitoring: Advanced reporting systems track non-PO spending patterns, identifying opportunities to convert frequent non-PO vendors to standard purchase order processes.
Hyperbots Platform: Transforming Purchase Order Automation
Hyperbots has revolutionized the purchase order control process through its comprehensive suite of AI-powered co-pilots, delivering measurable operational improvements for finance teams across industries. The platform's unique approach combines intelligent automation with human-centered design, creating solutions that enhance rather than replace human judgment.
Procurement Co-Pilot: The Core of Purchase Order Excellence
The Hyperbots Procurement Co-Pilot transforms traditional purchase order workflows by shrinking cycle times from request to purchase order approval. This intelligent system integrates seamlessly with existing ERP environments, providing real-time spend visibility while maintaining strict compliance controls.
Instant ERP-Synced Approvals: The platform eliminates manual approval routing through intelligent workflow automation that respects organizational hierarchies while accelerating decision-making processes.
Real-Time Spend Visibility: Finance teams gain immediate insights into spending patterns, budget utilization, and vendor performance through integrated dashboards that update dynamically with each transaction.
Compliance-First Design: Built-in controls ensure that every purchase order meets organizational policies, regulatory requirements, and contract terms before approval, reducing compliance risk by up to 95%.
Supporting Co-Pilots: End-to-End Automation
Invoice Processing Co-Pilot: Handles complex invoice matching scenarios with 99% accuracy, automatically resolving routine discrepancies while escalating significant variances to human reviewers.
Vendor Management Co-Pilot: Maintains comprehensive vendor records, monitors performance metrics, and identifies optimization opportunities across the supplier ecosystem.
The integrated approach ensures seamless data flow between procurement, invoicing, and vendor management functions, eliminating traditional process silos that create inefficiencies and control gaps.
Hyperbots Market Differentiation: Beyond Traditional Automation
Hyperbots distinguishes itself in the competitive procure-to-pay market through several key innovations that address fundamental limitations of traditional automation platforms.
Intelligent Context Understanding
Unlike rule-based systems that require extensive configuration, Hyperbots co-pilots understand business context through advanced natural language processing and machine learning algorithms. This capability enables the platform to handle complex scenarios that would typically require human intervention.
Contextual Decision Making: The system analyzes purchase requests within broader business contexts, considering factors such as budget cycles, vendor relationships, and historical patterns to make intelligent routing decisions.
Adaptive Learning: Machine learning algorithms continuously improve system performance by learning from human decisions and outcomes, reducing false positives and enhancing automation accuracy over time.
Human-AI Collaboration Model
Rather than replacing human judgment, Hyperbots enhances human capabilities by handling routine decisions while escalating complex scenarios with comprehensive analysis and recommendations.
Augmented Intelligence: The platform provides human reviewers with detailed analysis, risk assessments, and recommendations for complex purchase orders, improving decision quality while reducing research time.
Continuous Feedback Loops: Human decisions feed back into the AI models, creating systems that become increasingly aligned with organizational preferences and risk tolerance.
Enterprise Integration Excellence
Hyperbots co-pilots integrate with over 150 ERP and financial systems through pre-built connectors and flexible APIs, ensuring rapid deployment without extensive customization.
Zero-Disruption Implementation: The platform overlays existing systems without requiring changes to core ERP configurations, minimizing implementation risk and deployment time.
Bidirectional Data Synchronization: Real-time data synchronization ensures that purchase order information remains consistent across all integrated systems, preventing data discrepancies that compromise control effectiveness.
ROI and Performance Metrics: Quantifying Purchase Order Excellence
Organizations implementing Hyperbots co-pilots achieve significant performance improvements across multiple dimensions, with many clients reporting transformational impact within the first quarter of deployment.
Operational Cost Reduction
Reduction in Operational Costs: The most significant benefit reported by Hyperbots clients is the dramatic reduction in manual processing costs through intelligent automation of routine tasks.
Faster Cycle Times: Purchase order processing cycles shrink from days to hours through automated routing, approval, and matching processes that eliminate traditional bottlenecks.
Exception Resolution Rate: Advanced exception handling capabilities resolve routine exceptions automatically, freeing human resources for strategic activities.
Financial Performance Improvements
Enhanced Cash Flow Management: Improved processing accuracy and speed enables better cash flow forecasting and supplier payment optimization, with many organizations improving in working capital management.
Reduced Maverick Spending: Comprehensive spend visibility and control mechanisms reduce off-contract spending, contributing directly to bottom-line savings.
Improved Vendor Relationships: Faster processing and reduced disputes strengthen vendor relationships, leading to improved terms and preferential treatment from key suppliers.
Compliance and Risk Mitigation
Control Compliance: Automated control enforcement ensures consistent application of organizational policies across all purchase orders, virtually eliminating compliance failures.
Fraud Prevention: Advanced analytics identify unusual patterns and potential fraudulent activities, with the system detecting and preventing fraudulent attempts per quarter for mid-sized organizations.
Audit Trail Excellence: Comprehensive audit trails and documentation exceed regulatory requirements, reducing audit preparation time.
Implementation Strategy: Maximizing Purchase Order Control Success
Successful purchase order control process implementation requires careful planning, stakeholder engagement, and systematic approach to change management. Organizations that achieve the greatest success follow structured methodologies that address both technical and human factors.
Assessment and Planning Phase
Current State Analysis: Comprehensive evaluation of existing purchase order processes, identifying control gaps, inefficiencies, and automation opportunities.
Stakeholder Mapping: Identification of key users, decision-makers, and affected parties across procurement, finance, and operations functions.
Success Metrics Definition: Establishment of clear, measurable objectives for cycle time reduction, cost savings, and control effectiveness improvements.
Technology Configuration and Integration
System Integration Planning: Detailed mapping of data flows between existing ERP systems and new automation platforms, ensuring seamless information exchange.
Control Framework Design: Development of comprehensive control matrices that define approval hierarchies, tolerance limits, and exception handling procedures.
Testing and Validation: Systematic testing of all automation workflows using representative transaction volumes and scenarios to ensure reliable performance.
Change Management and Training
User Adoption Programs: Comprehensive training programs that help users understand new processes while highlighting personal productivity benefits.
Communication Strategy: Regular updates and success stories that maintain momentum and address concerns throughout the implementation process.
Continuous Improvement: Ongoing optimization based on user feedback, performance metrics, and evolving business requirements.
Future Trends in Purchase Order Control Technology
The purchase order control process continues evolving rapidly, driven by advances in artificial intelligence, blockchain technology, and integrated business platforms. Understanding these trends helps organizations make strategic decisions about technology investments and process improvements.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
Predictive Analytics: AI systems increasingly predict potential issues before they occur, such as vendor delivery delays or budget overruns, enabling proactive management responses.
Natural Language Processing: Advanced NLP capabilities enable systems to process unstructured data from emails, contracts, and vendor communications, extracting relevant information for purchase order processing.
Intelligent Automation: Machine learning algorithms handle increasingly complex scenarios that previously required human judgment, expanding the scope of automated processing.
Blockchain and Distributed Ledger Technology
Immutable Audit Trails: Blockchain technology provides tamper-proof records of all purchase order transactions, enhancing security and simplifying audit processes.
Smart Contracts: Automated contract execution based on predefined conditions streamlines purchase order fulfillment while ensuring compliance with agreed terms.
Supplier Network Integration: Distributed ledger technology enables secure, real-time information sharing across complex supplier networks, improving visibility and coordination.
Integrated Business Ecosystems
Platform Convergence: Purchase order systems increasingly integrate with broader business platforms, including CRM, inventory management, and business intelligence tools.
API-First Architecture: Modern systems prioritize flexible integration capabilities, enabling organizations to create customized automation workflows that align with specific business requirements.
Mobile-First Design: Advanced mobile capabilities enable purchase order processing from any location, supporting hybrid work environments and field-based operations.
Transforming Your Purchase Order Control Process
Modern organizations require sophisticated purchase order control processes that balance automation with human oversight, delivering both operational efficiency and strategic value. The evolution from manual, paper-based systems to AI-powered automation platforms represents more than technology upgrade—it's a fundamental transformation in how finance organizations operate.
Hyperbots co-pilots provide the comprehensive capabilities needed to achieve this transformation, combining intelligent automation with human-centered design to deliver measurable business results. Organizations implementing these advanced systems report not only cost savings and efficiency gains but also enhanced decision-making capabilities and strategic insights that drive competitive advantage.
The purchase order control process serves as a foundation for broader financial operations excellence. By implementing robust controls, intelligent matching processes, and comprehensive exception handling, organizations create the operational discipline necessary for sustainable growth and profitability.
For finance leaders evaluating purchase order automation opportunities, the key lies in selecting platforms that enhance rather than replace human judgment while delivering the scalability and control necessary for modern business operations. The investment in advanced purchase order control processes pays dividends across multiple dimensions, from operational cost reduction to strategic insight generation.
Ready to transform your purchase order control process? Discover how Hyperbots co-pilots can reduce your operational costs while enhancing control effectiveness and strategic visibility. Our Procurement Co-Pilot delivers instant ERP-synced approvals and real-time spend visibility, enabling your finance team to focus on strategic value creation rather than manual processing tasks.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: What is a purchase order control process?
A: A purchase order control process is a systematic framework that governs how organizations create, approve, match, and process purchase orders. It includes authorization controls, vendor validation, budget verification, and compliance monitoring to prevent fraud, ensure accuracy, and maintain spending discipline.
Q2: How does three-way matching work in purchase order processing?
A: Three-way matching compares purchase orders, receiving documents, and vendor invoices to verify alignment across quantity, pricing, and terms before payment approval. Advanced systems use intelligent tolerance settings to automatically approve transactions within predefined variance thresholds while routing larger discrepancies for human review.
Q3: What are the benefits of automating the purchase order matching process?
A: Automated purchase order matching reduces processing time eliminating data entry errors, handles complex scenarios like partial deliveries, and provides real-time exception alerts. Organizations report 80% reduction in operational costs through intelligent automation of routine matching tasks.
Q4: How do you handle exceptions in purchase order processing?
A: Exception handling involves categorizing discrepancies by type and severity, automatically routing them to appropriate personnel based on business rules, and providing vendor self-service portals for minor issues. Advanced systems resolve routine exceptions automatically while escalating significant variances for human intervention.
Q5: What is the difference between PO and non-PO processing?
A: Purchase order processing follows formal approval workflows before goods or services are acquired, while non-PO processing handles emergency or unplanned purchases through retroactive approval procedures. Non-PO transactions require additional controls due to elevated risk from bypassing traditional approval mechanisms.
Q6: What ROI can I expect from purchase order automation?
A: Organizations implementing advanced purchase order automation report doubling of ROI compared to traditional methods, with some seeing 5x returns. Specific benefits include reduction in operational costs, faster processing cycles, and reduction in maverick spending.
Q7: How does AI improve purchase order control processes?
A: AI enhances purchase order controls through intelligent matching algorithms, predictive analytics for identifying potential issues, natural language processing for handling unstructured data, and machine learning that improves accuracy over time by learning from human decisions and outcomes.

