What is a PO in Business? A Beginner's Guide to Purchase Orders
Learn purchase order basics, business uses, and how AI automation is reshaping the procure-to-pay process
Executive Summary
Purchase Orders (POs) represent one of the most critical control mechanisms in business procurement, yet many organizations struggle with manual, inefficient PO processes that drain resources and create operational bottlenecks. This guide provides a complete overview of what a PO is in business, covering fundamental concepts, the purchase order lifecycle, common challenges, and how modern AI automation is revolutionizing PO management.
Key takeaways include understanding PO meaning in business, mastering purchase order basics, recognizing the operational impact of inefficient PO processes, and discovering how AI Co-pilots can reduce operational costs by up to 80% while enhancing accuracy and compliance. Whether you're a CFO, Controller, or Procurement Head, this guide equips you with actionable insights to optimize your organization's purchase order workflow.
Understanding What PO Stands For in Business
A Purchase Order (PO) is a legally binding document issued by a buyer to a vendor that authorizes a purchase transaction. It specifies the types, quantities, and agreed prices for products or services the buyer intends to purchase. Once the vendor accepts the PO, it becomes a contract between both parties, protecting both the buyer and seller in the transaction.
Understanding what PO stand for in business is essential for finance professionals managing organizational spend. The PO meaning in business extends beyond a simple request; it represents a formal commitment of company funds, serves as a budgetary control mechanism, and creates an auditable trail for compliance purposes. According to research from Deloitte, organizations with robust PO processes experience 30% fewer purchasing discrepancies and significantly improved vendor relationships.
For U.S. enterprises, mastering purchase order basics has become increasingly critical as procurement volumes grow and regulatory scrutiny intensifies. The purchase order serves as the foundation of the procure-to-pay cycle, directly impacting cash flow management, vendor satisfaction, and financial reporting accuracy.
The Anatomy of a Purchase Order
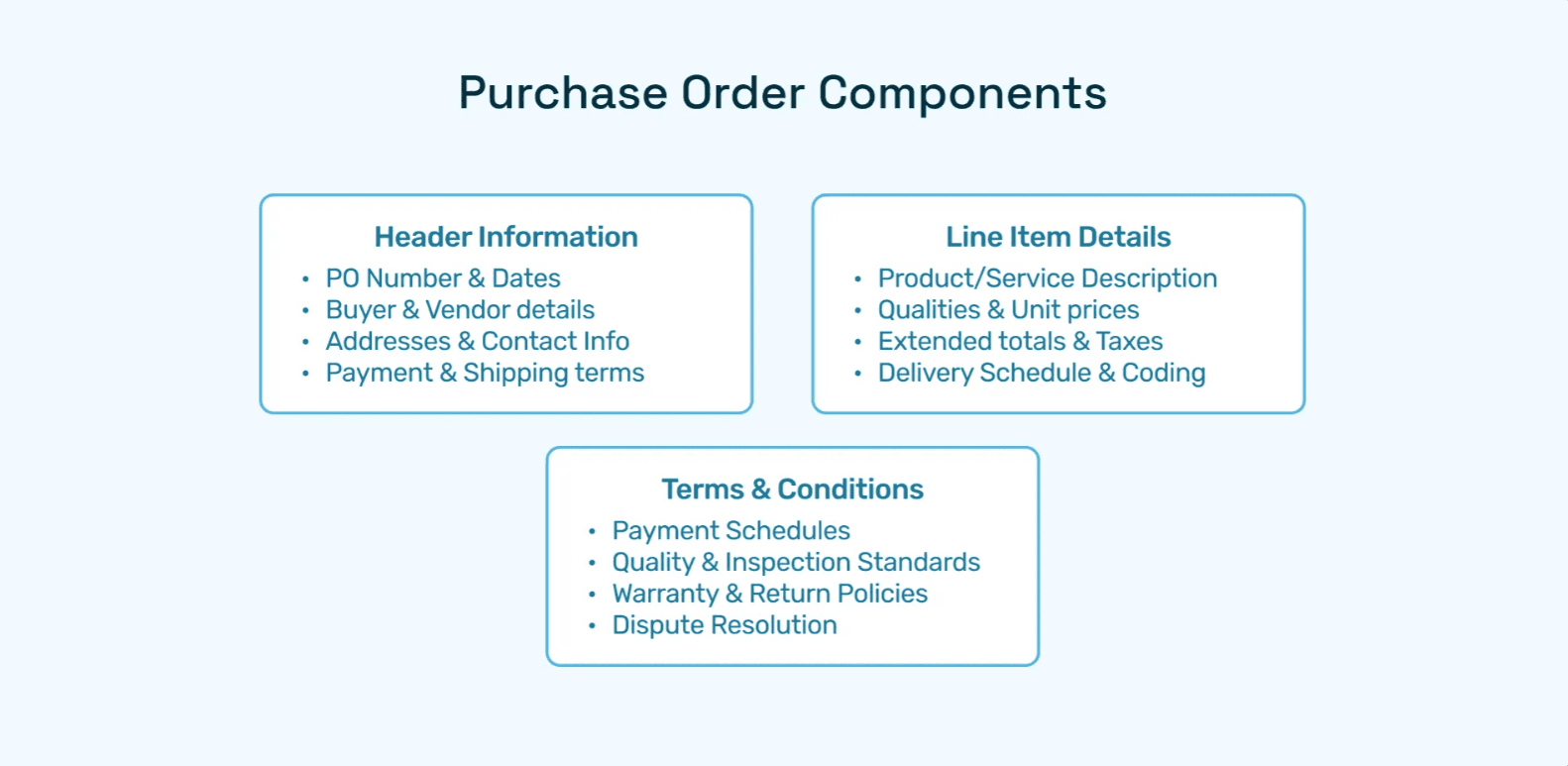
To fully grasp what PO is in business, it's important to understand its key components. Every purchase order contains essential information that protects both parties and ensures smooth transaction execution:
Standard PO Components:
PO Number: A unique identifier that tracks the order through its entire lifecycle, critical for reconciliation and audit trails
Vendor Information: Complete details, including vendor name, address, contact information, and payment terms
Ship-to and Bill-to Addresses: Specifies delivery location and billing entity, particularly important for multi-entity support
Line Items: Detailed description of goods or services, including item numbers, quantities, unit prices, and extended amounts
Total Amount: The complete purchase value, including taxes, shipping, and any applicable discounts
Delivery Date: Expected delivery timeframe or specific date for goods or services
Payment Terms: Net payment period (e.g., Net 30, Net 60), early payment discounts, and late payment penalties
Terms and Conditions: Legal terms governing the transaction, including warranty information, return policies, and liability clauses
Authorized Signatures: Approval from authorized personnel confirming the organization's commitment
General Ledger (GL) Codes: Accounting codes for proper expense categorization and financial reporting
Understanding these purchase order basics enables finance teams to establish appropriate controls and ensure compliance with organizational policies and external regulations.
Types of Purchase Orders in Business
The PO's meaning in business varies depending on the transaction type and organizational needs. Finance leaders should understand the different PO formats to implement appropriate processes for each:
1. Standard Purchase Order
The most common type, used for one-time purchases with clearly defined specifications, quantities, and delivery dates. Standard POs work well for equipment purchases, project-specific materials, or non-recurring services.
2. Blanket Purchase Order
Establishes an ongoing agreement with a vendor for repeated purchases over a specific period, typically with predetermined pricing but flexible quantities. Blanket POs reduce administrative burden for recurring purchases like office supplies, maintenance services, or regularly consumed materials. According to industry data, organizations using blanket POs for appropriate purchases reduce procurement processing time.
3. Contract Purchase Order
Similar to blanket POs but more formal, contract POs outline terms and conditions without specifying exact delivery schedules or quantities. These work well for service agreements, annual maintenance contracts, or framework agreements with preferred vendors.
4. Planned Purchase Order
Contains both a schedule of delivery dates and specific quantities, used when the buyer knows their requirements over a future period. This approach helps vendors with capacity planning while giving buyers predictability in supply chain management.
Understanding what PO stand for in a business context requires recognizing which PO type best suits specific procurement scenarios, optimizing both efficiency and control.
The Purchase Order Lifecycle: From Creation to Closure
The complete PO process encompasses multiple stages, each presenting opportunities for efficiency gains or potential bottlenecks:
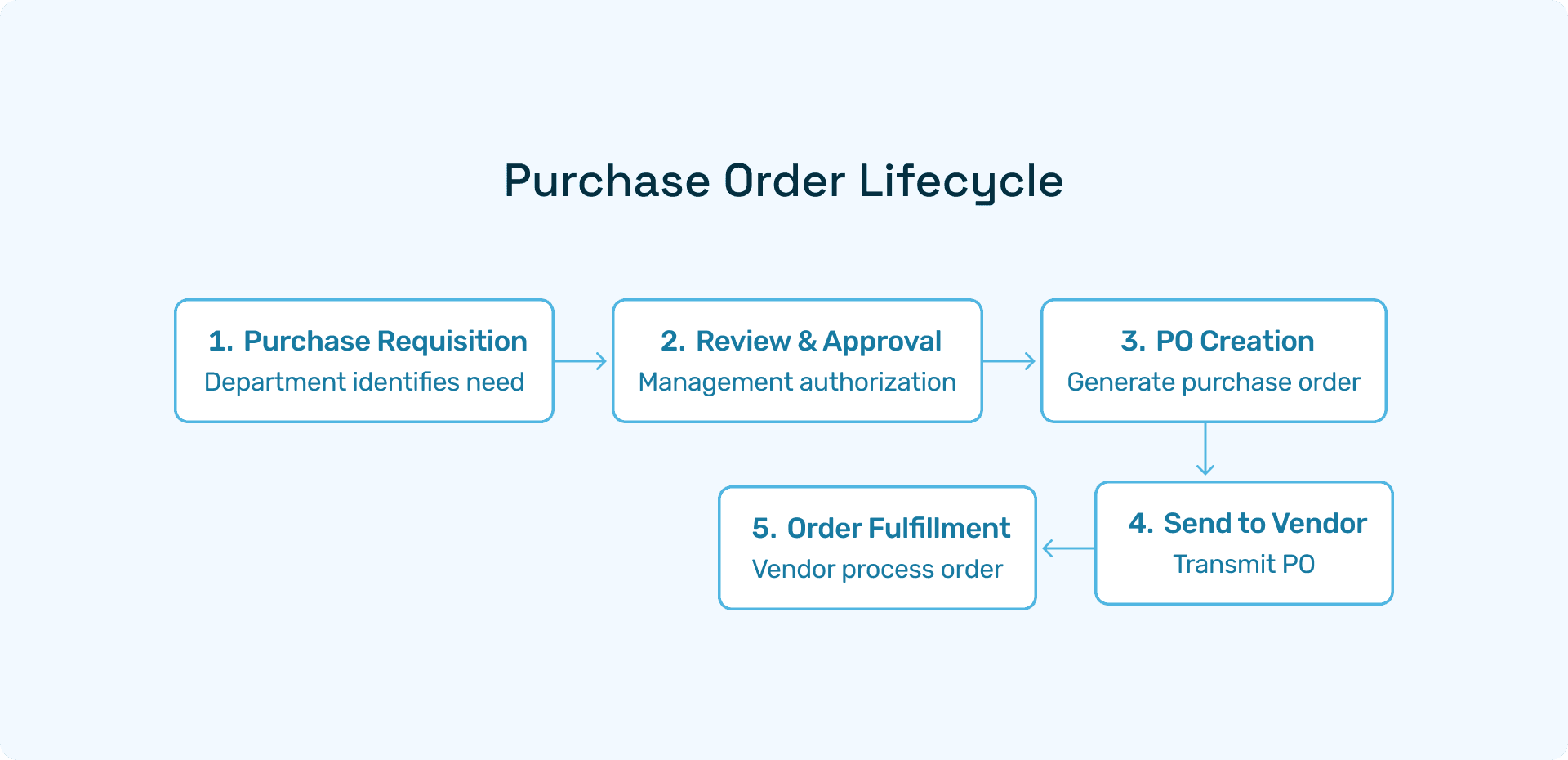
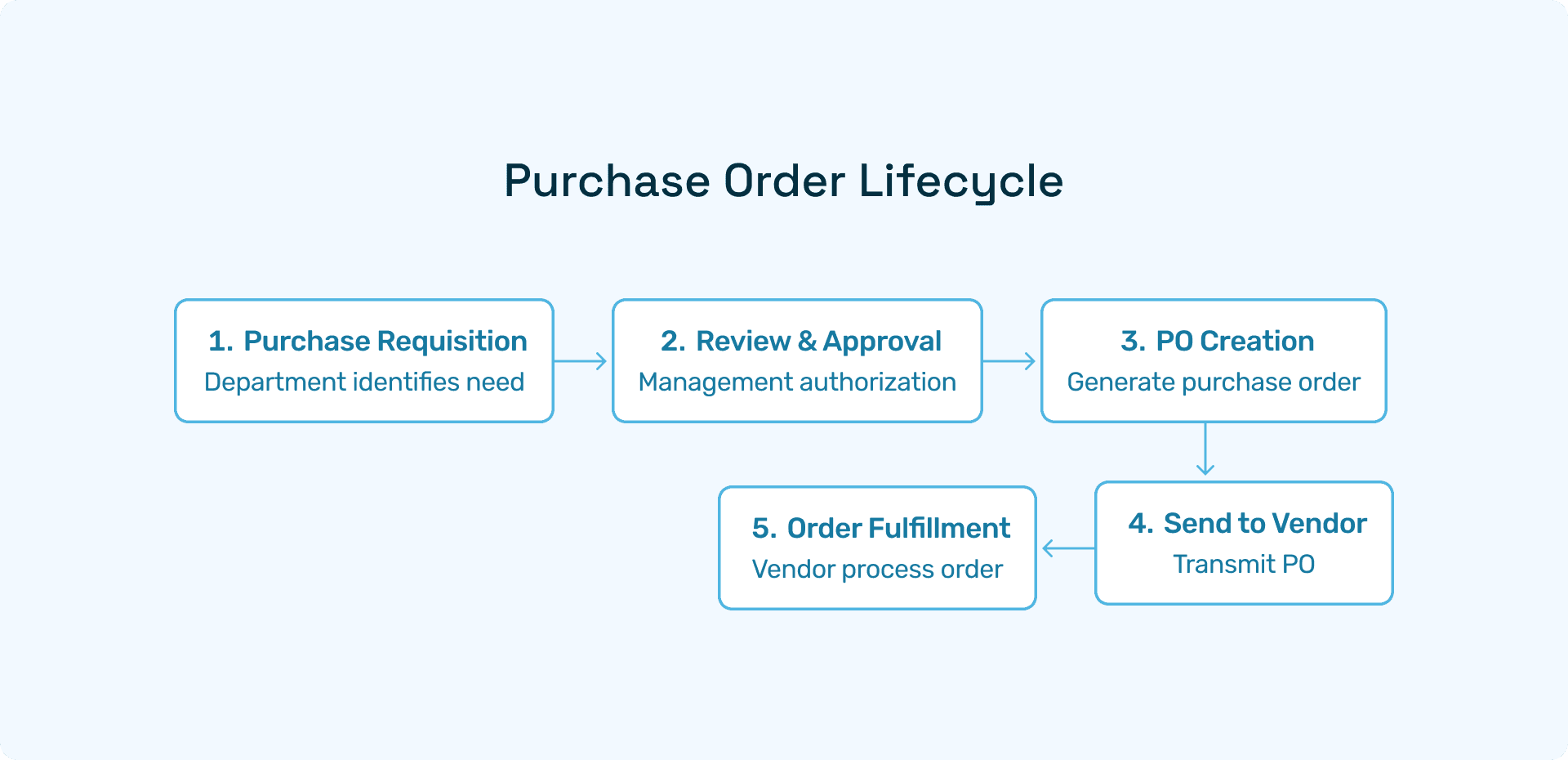
Stage 1: Purchase Requisition (PR)
The process begins when a department identifies a need and creates a purchase requisition. The PR details what is needed, why it's needed, estimated costs, and the requesting department's budget code. Manual PR creation typically consumes 15-20 minutes per request and is prone to incomplete information or coding errors.
Stage 2: PR Review and Approval
Once submitted, the PR enters an approval workflow based on organizational hierarchy and dollar thresholds. Multiple approvers may be required depending on purchase value, creating potential delays. Research indicates that approval delays represent one of the top three pain points in procurement, with the average PR taking 5-7 days to receive final approval in manual systems.
Stage 3: PO Creation
After PR approval, procurement converts the requisition into a purchase order. This involves vendor selection, price negotiation or confirmation, and formal PO document generation. Manual PO creation introduces risks of data entry errors, incorrect GL coding, and duplicate orders.
Stage 4: PO Transmission
The completed PO is sent to the vendor through email, EDI, or vendor portals. Poor PO sending processes can delay vendor acknowledgement and order fulfilment, impacting delivery timelines.
Stage 5: Order Fulfilment
The vendor receives the PO, acknowledges acceptance, and fulfils the order according to specified terms. Communication during this phase is crucial for managing expectations and addressing any issues.
Stage 6: Goods Receipt and Three-Way Matching
Upon delivery, the receiving department confirms goods or services match the PO specifications. Finance then performs three-way matching between the PO, goods receipt, and vendor invoice to verify accuracy before payment authorization.
Stage 7: Invoice Processing and Payment
Once the invoice matches the PO and receipt, payment is processed according to the agreed terms. Discrepancies during matching can delay payment and strain vendor relationships.
Stage 8: PO Closure
After complete fulfilment and payment, the PO is formally closed in the system. Many organizations struggle with PO closure, leaving hundreds of open POs that complicate reporting and reconciliation. Industry studies suggest that 20-30% of POs remain inappropriately open in manual systems.
Common Purchase Order Challenges in Modern Business
Despite understanding what PO is in business, many organizations face persistent challenges that undermine efficiency and increase operational costs:
Manual Data Entry and Errors
Traditional PO processes require manual field entry across multiple systems, consuming 15-20 minutes per PO and introducing error rates of 8-12%. These errors cascade through the procure-to-pay cycle, causing invoice mismatches, payment delays, and reconciliation headaches.
Labor-Intensive Workflows
Manual PR and PO creation, routing, approval tracking, and vendor communication demand significant staff time. For mid-sized organizations processing 500+ POs monthly, this can represent 2-3 full-time equivalent (FTE) resources dedicated solely to PO administration.
Approval Bottlenecks
Complex approval hierarchies and a lack of automated routing create delays that frustrate both internal stakeholders and vendors. The average manual approval cycle spans 5-7 days, though urgent purchases may require special expediting that bypasses controls.
Poor Purchasing Discipline
Without automated controls, maverick spending, unauthorized purchases, and PO policy violations occur frequently. Research from leading procurement analysts indicates that almost 20-30% of organizational spend occurs outside formal PO processes in companies with inadequate controls.
PO Closure Issues
Manual PO management makes it difficult to track partial deliveries, manage change orders, and ensure timely closure. Unclosed POs distort financial reporting, complicate period-end close, and create audit findings.
GL Coding Errors
Incorrect general ledger coding on purchase orders leads to misstated financial reports, budget overruns in some departments, and apparent surpluses in others. These errors require time-consuming corrections and reduce confidence in financial data.
Duplication and Fraud Risk
Manual processes struggle to detect duplicate POs, potentially fraudulent orders, or anomalies that indicate errors or intentional misconduct. The Association of Certified Fraud Examiners reports that procurement fraud represents approximately 20% of organizational fraud incidents.
Limited Visibility and Auditability
Paper-based or poorly integrated PO systems provide limited real-time visibility into spending, open commitments, and vendor performance. This opacity hampers strategic decision-making and complicates audit responses.
These challenges collectively drive organizations to seek modern solutions that address what PO means in business while dramatically improving operational efficiency.
How AI Is Transforming Purchase Order Management
Modern artificial intelligence offers transformational capabilities that address the fundamental question of what is PO in business within the context of operational excellence. AI-powered procurement automation represents a quantum leap beyond traditional workflow tools, delivering intelligent capabilities that continuously learn and improve.
Intelligent Field Extraction and Auto-Fill
Advanced AI analyzes purchase requisitions and historical data to automatically populate PO fields, reducing creation time. Natural language processing extracts vendor information, item details, and specifications from unstructured requests, while machine learning suggests appropriate GL codes based on purchase descriptions and historical patterns.
Validation and Anomaly Detection
AI systems perform sophisticated validation that goes far beyond rule-based checking. They identify duplicate POs by analyzing patterns beyond exact matches, detect anomalous pricing that deviates from historical norms or market benchmarks, flag potential fraud indicators through behavioural analysis, and ensure compliance with procurement policies and approval authorities.
Budget Control and Smart GL Coding
Real-time budget checking prevents overspend before PO creation, while AI recommends optimal GL codes based on purchase description, department, and historical classification patterns. This reduces coding errors by approximately 85% compared to manual processes.
Configurable Workflows
Modern AI platforms enable dynamic approval routing based on purchase characteristics, dollar thresholds, vendor risk profiles, and organizational hierarchies. Workflow configuration occurs through intuitive interfaces rather than complex programming, allowing finance teams to adjust processes as business needs evolve.
Automated PO Creation and Dispatch
Once approved, AI systems automatically generate properly formatted purchase orders and transmit them through the vendor's preferred channel - whether email, EDI, or portal submission. This eliminates manual sending delays and ensures vendors receive orders in standardized, complete formats.
End-to-End Auditability
AI-powered systems maintain comprehensive audit trails capturing every action, approval, modification, and communication throughout the PO lifecycle. This creates the transparency that auditors and compliance teams require while enabling performance analytics and continuous process improvement.
According to Gartner research, organizations implementing AI-driven procurement automation achieve a 80% reduction in processing time, fewer errors, and improved compliance rates.
Hyperbots: Leading AI Co-Pilots for Purchase Order Automation
Understanding what PO stand for in business is just the beginning—the real question is how to optimize PO management for maximum efficiency and control. Hyperbots delivers the market's most comprehensive AI Co-pilot suite specifically designed for finance and accounting automation, with purchase order management as a core strength.
The Hyperbots Procurement Co-Pilot
Hyperbots' Procurement Co-pilot represents the next generation of purchase order automation, combining advanced AI with deep financial process expertise:
Core Capabilities:
Automated Field Extraction and PR Autofill: Intelligent analysis of purchase requests with automatic population of requisition fields, reducing manual data entry and accelerating PR creation
Validation, duplication & Anomaly Detection: Multi-layered AI analysis identifies potential duplicates through pattern recognition, detects pricing anomalies by comparing against historical data and market benchmarks, and flags high-risk transactions requiring additional review
Budget controls & GL coding Recommendations: Real-time budget availability checking prevents unauthorized overspend, while machine learning algorithms recommend optimal GL codes accuracy based on purchase context and historical patterns
Configurable workflows: Flexible workflow engine adapts to organizational approval hierarchies without programming, supporting complex rules based on amount, department, vendor, and commodity. Custom form builders enable organizations to capture specific data fields required for their unique processes
Automated PO Creation & Dispatch: Seamless conversion of approved requisitions to purchase orders with automated vendor transmission through preferred channels, ensuring PO delivery and vendor acknowledgement tracking
PO closing & End-to-End Auditability: Intelligent PO closure management tracks partial deliveries, manages amendments, and automatically closes completed orders. Comprehensive audit trails capture every transaction detail, approval action, and system event for complete transparency
What Makes Hyperbots Different: Competitive Advantages
The procure-to-pay automation market includes numerous solutions, but Hyperbots delivers distinctive advantages that position it as the clear leader for finance-focused organizations:
1. Finance-First Design Philosophy
While many P2P platforms originated from supply chain or procurement perspectives, Hyperbots was designed by CFOs for CFOs. This financial operations DNA ensures that every feature prioritizes financial control, compliance, and reporting accuracy alongside operational efficiency.
2. True AI Intelligence, Not Just Automation
Many competitors offer workflow automation, but Hyperbots delivers genuine artificial intelligence that learns, adapts, and improves over time. The platform's machine learning models continuously refine GL code recommendations, enhance anomaly detection accuracy, and optimize approval routing based on organizational patterns.
3. Exhaustive ERP Integration
Hyperbots provides comprehensive integration with leading ERP systems, including both cloud and on-premise variants. Unlike competitors offering limited read-only integration, Hyperbots enables full read-write access for expenses, the Chart of Accounts, vendor master, item master, assets, and liabilities. Real-time synchronization ensures data consistency across systems without manual intervention.
4. Adaptability to ERP Customizations
Most organizations have customized their ERP systems to support unique business requirements. Hyperbots' configuration-driven integration framework adapts seamlessly to company-specific ERP customizations, enabling read-write access to custom fields without extensive development work.
5. Exception Handling and Data Integrity
Hyperbots ensures data integrity through read-back verification of ERP postings, intelligent retry logic for transient failures, and comprehensive exception reporting that enables user resolution of genuine issues. This robust approach prevents data inconsistencies that plague less sophisticated solutions.
6. Holistic Procure-to-Pay Coverage
Rather than addressing purchase orders in isolation, Hyperbots covers the complete P2P cycle from requisition through payment. This end-to-end approach eliminates integration gaps between point solutions and delivers superior outcomes.
7. Rapid Deployment and Time-to-Value
Hyperbots' modern architecture and pre-built ERP connectors enable deployment in weeks rather than months. Organizations typically achieve positive ROI significantly faster than legacy P2P platforms requiring extensive customization.
8. Scalability Without Complexity
The platform scales effortlessly from mid-sized businesses processing hundreds of monthly POs to enterprises managing tens of thousands of transactions, maintaining consistent performance and user experience across deployment sizes.
These differentiators explain why leading CFOs and finance executives choose Hyperbots when they seek more than basic automation; they want transformational capabilities that redefine what PO means in business operations.
Best Practices for Purchase Order Management
Whether implementing AI automation or optimizing existing processes, these best practices enhance PO effectiveness:
Establish Clear Policies: Document comprehensive procurement policies covering PO requirements by dollar threshold, approval authorities, preferred vendors, and prohibited purchases. Ensure policies align with organizational objectives and compliance requirements.
Implement Tiered Approval Workflows: Design approval hierarchies based on purchase amount, department, and risk profile. Avoid unnecessarily complex workflows that create bottlenecks while ensuring appropriate oversight for high-value or sensitive purchases.
Maintain Clean Vendor Master Data: Accurate vendor information prevents payment delays, duplicate vendor records, and communication failures. Implement validation processes for new vendor setup and periodic master data cleansing.
Standardize GL Coding: Develop clear guidelines for expense categorization with documented coding rules. Train requisitioners on proper GL code selection and implement validation to catch obvious errors.
Enforce Three-Way Matching: Require matching between purchase order, goods receipt, and invoice before payment authorization. This fundamental control prevents unauthorized payments and identifies discrepancies requiring resolution.
Monitor PO Metrics: Track key performance indicators, including average PO processing time, approval cycle duration, error rates, PO closure timeliness, and vendor satisfaction. Use metrics to identify improvement opportunities and measure progress.
Manage PO Lifecycle Actively: Implement processes for managing partial deliveries, handling amendments, resolving discrepancies, and ensuring timely closure. Don't let POs languish in open status indefinitely.
Leverage Technology Appropriately: Modern AI platforms like Hyperbots eliminate manual work while enhancing control and visibility. Evaluate automation solutions based on capability, integration quality, and long-term scalability rather than initial cost alone.
Invest in User Training: Even the best systems fail without proper user adoption. Provide comprehensive training for requisitioners, approvers, and procurement staff, emphasizing both system mechanics and underlying policy rationale.
Conduct Regular Process Reviews: Business needs evolve, requiring periodic procurement process assessment. Review workflows, approval thresholds, and policies annually to ensure they remain appropriate and effective.
These practices, combined with modern AI automation, transform purchase order management from an administrative burden to a strategic capability.
The Future of Purchase Order Management
Understanding what PO is in business today provides a foundation for anticipating tomorrow's procurement landscape. Several trends are reshaping how organizations manage purchase orders:
Predictive Procurement: Advanced AI will increasingly predict purchasing needs based on consumption patterns, inventory levels, and business activity forecasts. This enables proactive PO creation before stockouts occur, optimizing inventory investment while ensuring availability.
Autonomous Procurement Agents: Next-generation AI agents will independently execute routine procurement decisions within defined parameters, requiring human approval only for unusual circumstances or high-value purchases. This represents evolution from automation (executing predefined tasks) to autonomy (making contextual decisions).
Dynamic Supplier Networks: Integration between buyer and supplier systems will enable real-time communication about inventory availability, delivery timing, and pricing. POs will transform from static documents to dynamic agreements that adapt to changing conditions.
Blockchain-Based PO Management: Distributed ledger technology promises immutable audit trails, automated smart contract execution, and seamless multi-party collaboration. While early-stage today, blockchain may fundamentally alter how POs create and enforce commercial agreements.
Sustainability Integration: Growing emphasis on environmental, social, and governance (ESG) factors will drive the incorporation of sustainability criteria into PO decisions. AI will evaluate vendor ESG performance alongside traditional factors like price and quality.
Hyper-Personalization: AI systems will learn individual user preferences and work patterns, customizing the PO experience for each requisitioner, approver, and procurement professional. This personalization enhances user adoption while maintaining standardized processes.
Organizations positioning themselves for this future are implementing modern AI platforms like Hyperbots today, building the foundation for continuous evolution as technology advances.
Getting Started with AI-Powered PO Automation
Finance leaders ready to transform their purchase order processes should approach AI implementation systematically:
Step 1: Assess Current State
Document existing PO volumes, processing times, error rates, and pain points. Quantify costs of current processes to establish a baseline for ROI measurement.
Step 2: Define Success Criteria
Establish specific, measurable objectives for PO automation, including processing time reduction, error rate targets, cost savings goals, and user satisfaction improvements.
Step 3: Evaluate Solution Options
Assess AI automation platforms based on capability depth, ERP integration quality, implementation approach, vendor stability, and long-term scalability. Request demonstrations focused on your specific requirements and use cases.
Step 4: Plan Phased Implementation
Design implementation approach starting with pilot departments or PO categories before enterprise-wide rollout. This manages risk while enabling learning and optimization.
Step 5: Prepare Organization
Communicate changes to all stakeholders emphasizing benefits for each group. Provide comprehensive training and ongoing support to ensure adoption.
Step 6: Monitor and Optimize
Track performance against defined success criteria, gathering user feedback and identifying opportunities for additional optimization. Modern AI platforms continuously improve through usage, but active monitoring maximizes benefits.
Step 7: Expand Scope
Once PO automation delivers proven value, extend AI capabilities to adjacent processes like invoice processing, accruals, and payments, ultimately achieving end-to-end procure-to-pay automation.
This systematic approach maximizes success probability while managing organizational change effectively.
Ready to Transform Your Purchase Order Process?
Understanding what PO is in business is just the first step. The real opportunity lies in transforming purchase order management from a manual, error-prone process into a streamlined, intelligent capability that drives organizational performance.
Hyperbots' AI Co-pilot suite represents the most comprehensive, finance-focused solution for purchase order automation available today. Designed by CFOs for CFOs, Hyperbots delivers 80% operational cost reduction while enhancing accuracy, compliance, and strategic visibility.
Whether you're processing hundreds or thousands of monthly POs, struggling with approval bottlenecks, battling GL coding errors, or simply seeking to free your finance team for higher-value work, Hyperbots provides the transformational capabilities your organization needs.
Discover how Hyperbots can transform your purchase order process. Explore detailed platform capabilities, review customer success stories, and see the solution in action. Visit our Procurement Co-pilot product page to learn more, or schedule a personalized demonstration with our finance automation experts.
The future of purchase order management is intelligent, automated, and strategic. Start your transformation journey today with Hyperbots.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What does PO stand for in business?
A: PO stands for Purchase Order, a binding document authorizing vendor purchase with specified quantities, prices, and terms.
2. What is the difference between a purchase requisition and a purchase order?
A: Purchase requisitions are internal approval requests; purchase orders are external vendor authorizations created after requisition approval.
3. Do all businesses need to use purchase orders?
A: Not legally required, but POs provide spend control, audit trails, and vendor clarity for organizations.
4. What is three-way matching in purchase order management?
A: Three-way matching compares purchase orders, receipts, and invoices to verify accuracy before authorizing vendor payment.
5. How long should purchase order records be retained?
A: Organizations should retain PO records for seven to ten years to satisfy audit and regulatory requirements.
6. Can purchase orders be modified after issuance?
A: Yes, POs can be amended through formal change orders acknowledged by both buyer and vendor parties.
7. How does AI improve purchase order processing compared to traditional automation?
A: AI learns patterns, makes contextual decisions, detects complex anomalies, and continuously improves without rigid rule programming.