PO in Sales: How Purchase Orders Fit into the Sales Cycle
Discover the critical moment where the Purchase Order (PO) seals the deal. Learn how to align your sales efforts with the PO process to ensure faster closures and smoother revenue recognition.
Executive Summary
Purchase orders (POs) serve as critical financial instruments that bridge the gap between buyer procurement and seller sales operations. While commonly associated with purchasing functions, understanding the PO in sales context is essential for finance leaders seeking to optimize revenue recognition, cash flow management, and operational efficiency.
This comprehensive guide examines how purchase orders integrate into the sales cycle from the seller's perspective, clarifies the purchase order vs sales order distinction, explains sales PO meaning in practical terms, and explores how the PO in the sales process impacts everything from order fulfillment to revenue accounting. Finance leaders will discover how AI-powered automation—particularly Hyperbots' Procurement Co-Pilot—can reduce operational costs by 80% while accelerating cycle times and enhancing accuracy across the entire procure-to-pay ecosystem.
For CFOs, Controllers, and Procurement Heads managing mid-sized to enterprise operations, mastering the PO-sales relationship unlocks competitive advantages in working capital management, customer satisfaction, and financial reporting accuracy.
Understanding PO in Sales: Seller-Side Perspective
What Does PO Mean in Sales?
The sales PO meaning refers to the purchase order document received from a customer that authorizes the seller to fulfill a specific order. From the seller's viewpoint, an incoming PO represents a legally binding commitment to deliver goods or services at agreed-upon terms. This document triggers the sales order creation, inventory allocation, fulfillment operations, and ultimately revenue recognition.
When a buyer issues a PO, the seller's finance and operations teams use it to:
Validate order details against quotations and contracts
Create corresponding sales orders in their ERP system
Allocate inventory or schedule service delivery
Establish baseline documentation for invoicing and payment collection
Track order fulfillment status and manage customer expectations
For finance leaders, understanding PO in sales means recognizing that every customer PO directly impacts revenue forecasting, accounts receivable management, and cash flow projections.
The Strategic Value of POs in Revenue Operations
Purchase orders provide sellers with several strategic advantages. They formalize customer commitments, reducing order cancellation risks and enabling more accurate revenue forecasting. POs establish clear terms for pricing, quantities, delivery schedules, and payment conditions—minimizing disputes that could delay payment collection.
From a financial control perspective, POs create an audit trail that supports revenue recognition policies under accounting standards like ASC 606. They provide evidence of enforceable rights and obligations necessary for recognizing revenue at the appropriate time. For companies with subscription models or complex delivery schedules, POs help finance teams determine when performance obligations are satisfied.
Customer POs also enable better working capital management. When sellers receive POs with clearly defined payment terms, treasury teams can more accurately forecast cash inflows and optimize their own payment strategies. This becomes especially valuable when managing early payment discounts or negotiating supplier terms based on predictable revenue streams.
Purchase Order vs Sales Order: Key Distinctions
Fundamental Differences Between PO and SO
Understanding purchase order vs sales order differences is crucial for finance professionals managing both sides of commercial transactions. While these documents are complementary, they serve distinct purposes and originate from different parties.
Purchase Order (PO):
Issued by the buyer to the seller
Represents buyer's commitment to purchase
Authorizes seller to deliver and invoice
Controls buyer's procurement process
Creates accounts payable entry for the buyer
Sales Order (SO):
Created by the seller upon receiving PO
Confirms seller's acceptance of terms
Initiates fulfillment and delivery process
Triggers revenue recognition activities
Creates accounts receivable entry for the seller
The critical distinction lies in perspective and workflow. The PO is the buyer's outbound document that becomes the seller's inbound trigger. The seller then generates an internal sales order to operationalize that customer commitment.
How POs and SOs Interact in Transaction Flow
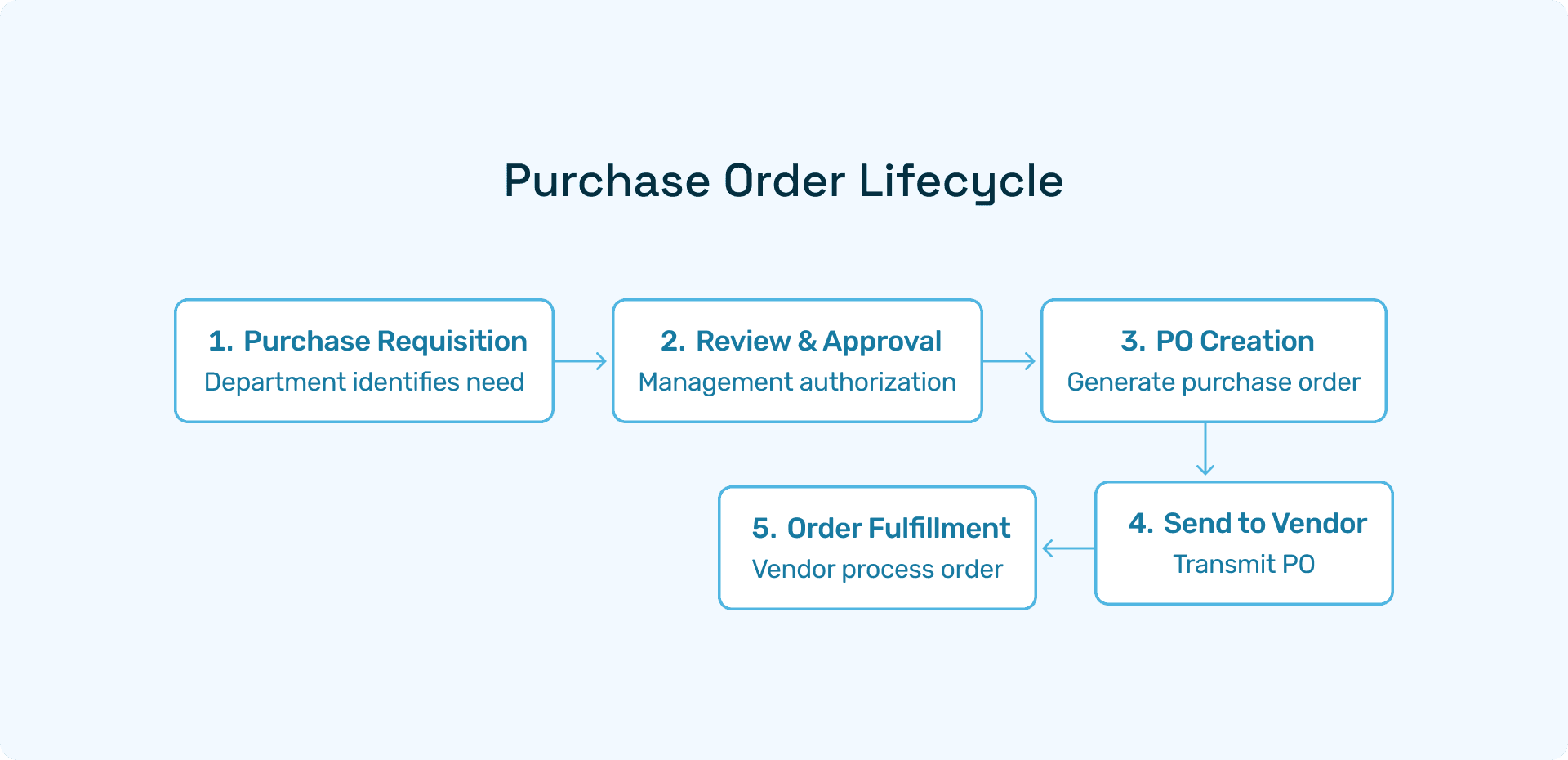
In practice, the PO in sales process follows this sequence:
Buyer creates purchase requisition internally to request goods/services
Buyer issues PO to seller after approval and vendor selection
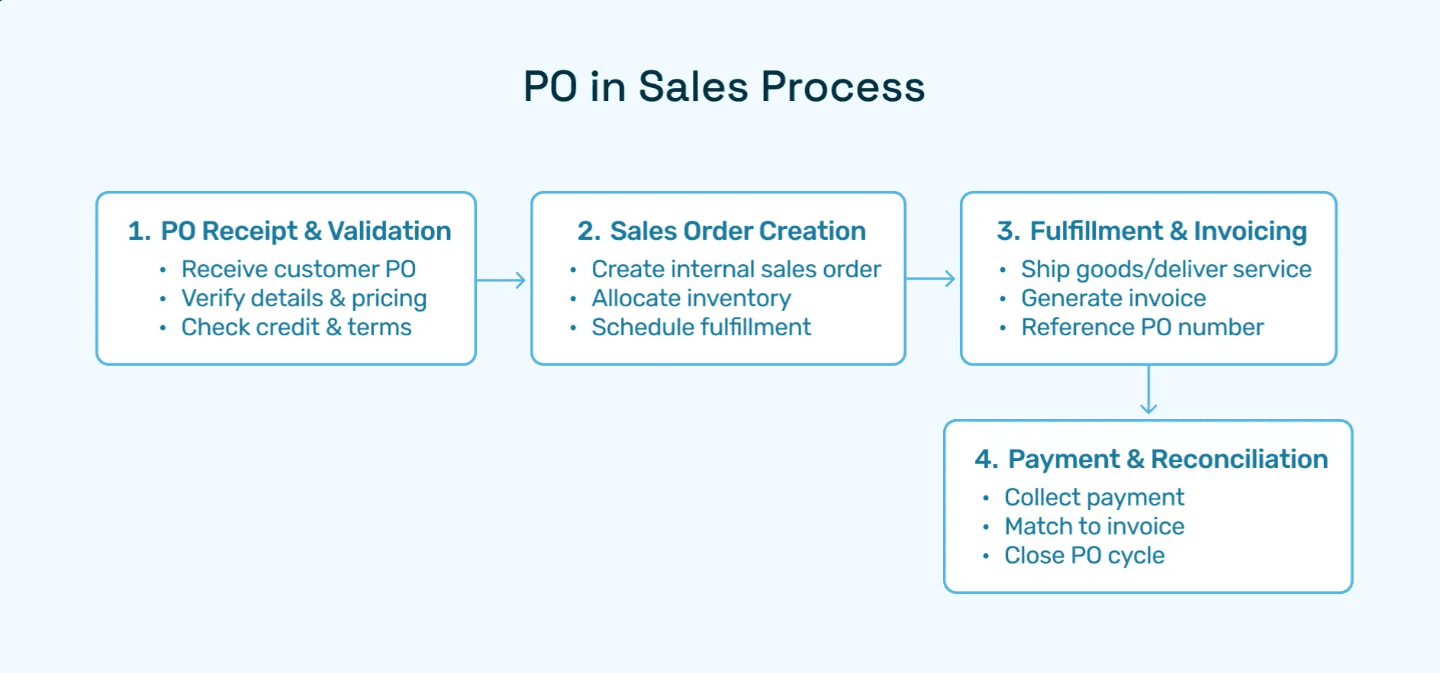
Seller receives PO and validates against quotes, contracts, or catalogs
Seller creates sales order in their ERP system, mirroring PO details
Seller fulfills order based on sales order specifications
Seller generates invoice referencing both PO and sales order numbers
Buyer receives goods and matches invoice to PO for payment approval
This interconnected workflow highlights why purchase order vs sales order clarity matters. Misalignment between these documents causes payment delays, fulfillment errors, and customer satisfaction issues. Finance teams must ensure robust processes for validating incoming POs against sales orders and maintaining data accuracy throughout the cycle.
Document Hierarchy and Financial Impact
In the document hierarchy, POs typically precede sales orders but both must align with upstream documents (quotations, contracts) and downstream documents (packing slips, invoices, receipts). For sellers, the PO represents external authorization while the sales order represents internal execution.
From a financial reporting standpoint, sellers use sales orders to recognize revenue while buyers use POs to record purchase commitments and eventual expenses. This asymmetry requires careful coordination between buyer and seller systems to ensure three-way matching (PO, receipt, invoice) functions properly during payment processing.
The PO in Sales Process: Step-by-Step Workflow

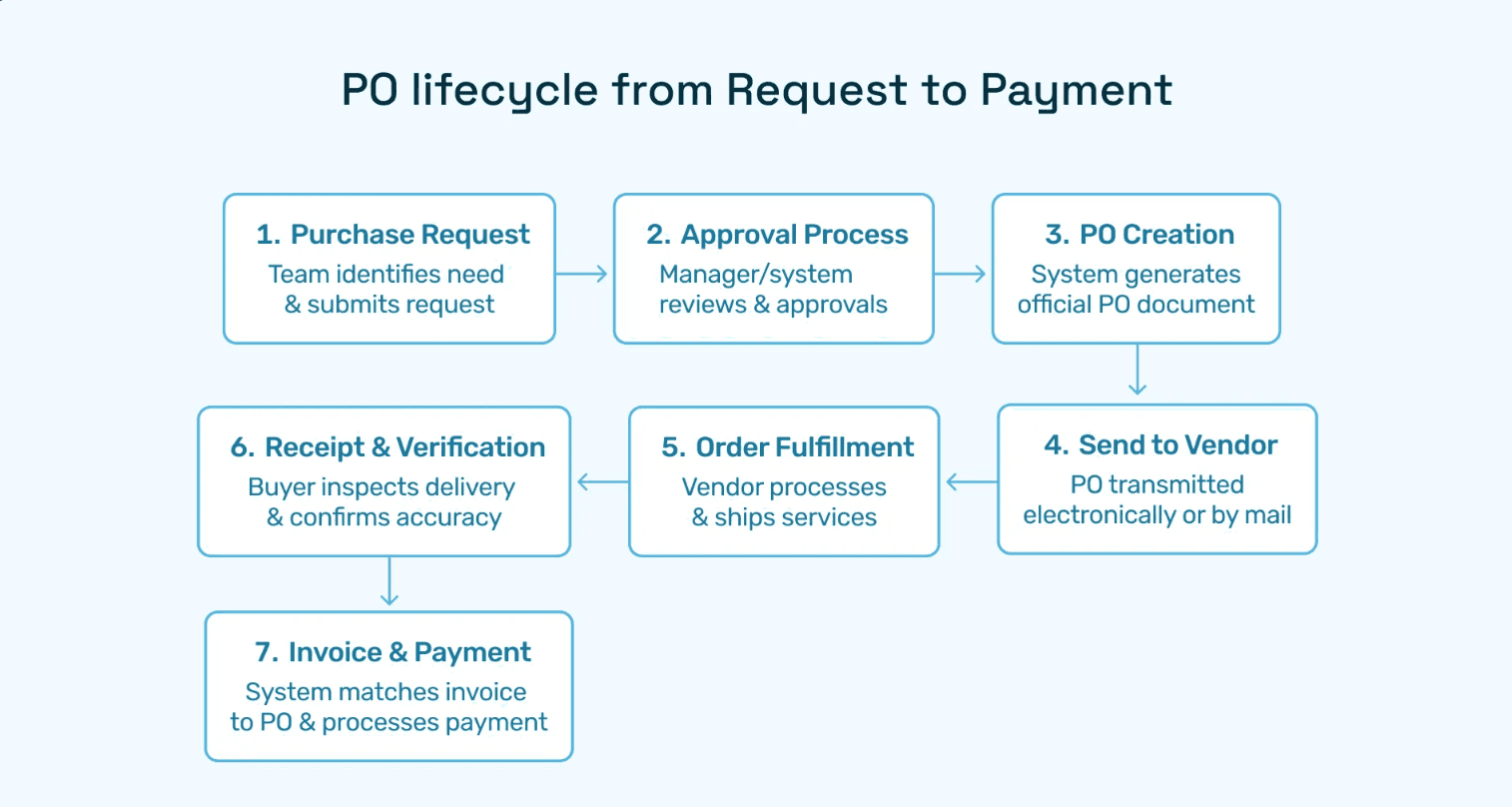
Stage 1: PO Receipt and Validation
The PO in the sales process begins when the seller's order management or procurement team receives a customer PO. This document may arrive via email, EDI, supplier portal, or integrated system connection. Upon receipt, several validation steps occur:
Initial Review:
Verify PO number uniqueness to prevent duplicate processing
Confirm customer identity and credit standing
Validate requested delivery dates against capacity
Check pricing against active quotations or contracts
Ensure terms align with company policies
System Entry:
Import PO data into ERP system (manually or via automation)
Match PO line items to product/service catalogs
Flag discrepancies for commercial team review
Assign internal order number (sales order)
Modern finance operations leverage AI-powered solutions like Hyperbots' Procurement Co-Pilot to automate PO intake and validation. These systems extract data from PO documents regardless of format, cross-reference against master data, and route exceptions to appropriate reviewers—reducing processing time from hours to minutes.
Stage 2: Sales Order Creation and Fulfillment
Once validated, the PO triggers sales order creation in the seller's system. This internal document mirrors the customer's PO but includes additional operational details:
Warehouse location for inventory allocation
Production or service delivery schedules
Shipping methods and carrier information
Internal cost accounting codes
Assigned sales representatives or account managers
The sales order serves as the master document for fulfillment teams, guiding picking, packing, shipping, and delivery activities. For service-based businesses, the sales order defines service delivery milestones and resource assignments.
Finance teams monitor sales order status to track revenue recognition milestones. Under ASC 606 guidelines, revenue is recognized when (or as) performance obligations are satisfied. The sales order provides the framework for determining when goods transfer control or services are substantially complete.
Stage 3: Invoicing Against Purchase Orders
After fulfillment, the seller generates invoices referencing the original customer PO number. This linkage is crucial for the buyer's three-way matching process. The invoice must align with:
PO terms for pricing, quantities, and delivery schedules
Actual goods received or services rendered
Sales order specifications and any authorized changes
Invoice accuracy directly impacts payment speed and customer satisfaction. Discrepancies between PO, sales order, and invoice create payment holds that extend days sales outstanding (DSO) and strain working capital.
Hyperbots' Invoice Processing Co-Pilot automates invoice generation with PO validation, ensuring perfect alignment and minimizing payment disputes. This automation reduces invoice processing costs by up to 80% while accelerating payment cycles.
Stage 4: Payment Collection and Reconciliation
The final stage involves collecting payment from the customer and reconciling cash receipts against invoices and POs. Sellers must track:
Payment terms (Net 30, 2/10 Net 30, etc.)
Payment methods (ACH, wire, check, card)
Early payment discounts taken or forfeited
Payment application to specific invoices
For sellers managing hundreds or thousands of customer POs monthly, manual reconciliation becomes untenable. AI-driven payment matching—like that offered by Hyperbots' Payment Co-Pilot—automatically matches customer remittances to open invoices, flags discrepancies, and provides real-time visibility into cash positions.
Common Challenges in Managing POs Within Sales Operations
Data Inconsistency and Format Variations
One of the most persistent challenges in the PO in sales process is managing data inconsistency across customer POs. Each buyer may use different:
PO numbering conventions
Product description formats
Unit of measure specifications
Delivery instruction formats
Special terms or custom fields
These variations complicate automated processing and require extensive manual intervention. Finance teams waste hours reconciling mismatched part numbers, decoding ambiguous descriptions, and clarifying terms with customers.
AI-powered document processing solves this challenge by learning from historical patterns, normalizing data variations, and mapping customer-specific formats to internal standards. Hyperbots' technology achieves 99.8% accuracy in extracting and normalizing PO data across diverse formats.
PO Amendments and Change Management
Purchase orders frequently undergo changes after initial issuance. Customers may modify quantities, adjust delivery dates, cancel line items, or change shipping addresses. Each amendment requires:
Version control to track PO history
Impact analysis on production or service delivery
Repricing calculations if quantities change
Communication with fulfillment teams
Updated sales orders and financial forecasts
Without robust change management processes, PO amendments create fulfillment errors, invoicing disputes, and revenue recognition complications. Sellers must implement structured approval workflows that evaluate change requests, obtain necessary approvals, and update all dependent documents.
Integration Gaps Between Systems
Many sellers operate with disconnected systems for order management, inventory, shipping, and accounting. When customer POs arrive, data must be manually rekeyed across multiple platforms—introducing errors and delays.
Integration gaps create particular problems for:
Real-time inventory visibility during PO validation
Synchronizing sales orders with warehouse management systems
Coordinating shipping notifications with invoicing
Reconciling financial data across platforms
Hyperbots addresses these integration challenges through comprehensive ERP connectivity that synchronizes PO data across NetSuite, SAP, Microsoft Dynamics, Sage, and other major platforms. This eliminates rekeying while maintaining data integrity across the order-to-cash cycle.
Compliance and Audit Requirements
Finance leaders must ensure PO processing complies with internal controls and external audit requirements. This includes:
Segregation of duties between order entry, fulfillment, and invoicing
Authorization protocols for order acceptance
Documentation retention for tax and legal purposes
Revenue recognition audit trails
Manual PO processing makes compliance difficult to enforce consistently. Automated workflows with built-in controls ensure every PO follows proper approval paths, maintains complete audit trails, and enforces segregation of duties without adding bureaucratic overhead.
How AI Transforms PO Management in Sales Operations
Intelligent Document Processing
Traditional PO processing relies on manual data entry or basic OCR technology that struggles with format variations. Modern AI—specifically the type employed in Hyperbots' solutions—uses advanced natural language processing and machine learning to:
Extract data from any PO format (PDF, email, EDI, scanned images)
Understand context to accurately identify fields regardless of layout
Normalize extracted data to match internal standards
Learn from corrections to continuously improve accuracy
Handle complex scenarios like multi-line items and special terms
Automated Validation and Exception Management
AI systems validate incoming POs against multiple data sources simultaneously:
Active quotations and contracts for pricing accuracy
Customer master data for credit limits and terms
Product catalogs for item number verification
Inventory systems for availability confirmation
Historical patterns for anomaly detection
When discrepancies arise, AI routes exceptions to appropriate reviewers with contextual information and suggested resolutions. This intelligent exception management ensures issues are resolved quickly without derailing the entire process.
Predictive Analytics for Revenue Optimization
By analyzing historical PO patterns, AI provides finance leaders with predictive insights:
Revenue forecasting based on PO pipeline
Customer behavior patterns and reorder predictions
Optimal pricing strategies based on acceptance rates
Risk indicators for payment delays or disputes
Working capital optimization recommendations
Hyperbots' platform continuously analyzes PO data to identify opportunities for improving terms, accelerating cycles, and reducing costs across the order-to-cash process.
Hyperbots: Transforming Purchase Order Automation
The Hyperbots Procurement Co-Pilot Advantage
Hyperbots' Procurement Co-Pilot represents the next generation of procure-to-pay automation. Unlike traditional solutions that simply digitize existing processes, Hyperbots reimagines the entire workflow with AI-native design.
Key Differentiators:
Agentic AI Architecture: Hyperbots employs multiple specialized AI agents that collaborate to handle complex procurement scenarios. Rather than following rigid rules, these agents adapt to context, learn from outcomes, and optimize decisions over time. This multi-agent collaboration enables handling of edge cases that break traditional automation.
True Touchless Processing: While competitors claim automation but still require human intervention for exceptions, Hyperbots achieves genuine straight-through processing. The system independently resolves common exceptions, escalating only genuinely ambiguous scenarios.
ERP-Agnostic Integration: Hyperbots connects seamlessly with NetSuite, SAP, Microsoft Dynamics, Sage, QuickBooks, and other major ERP systems through pre-built connectors. Implementation takes weeks, not months, and requires minimal IT involvement.
Contextual Intelligence: The platform understands business context beyond data extraction. It recognizes when PO terms deviate from contracts, identifies suspicious patterns indicating fraud, and proactively flags compliance risks—acting as an intelligent assistant rather than a blind processor.
End-to-End Automation Across the P2P Lifecycle
Hyperbots doesn't just automate purchase order processing in isolation. The platform provides comprehensive P2P coverage through specialized co-pilots:
Procurement Co-Pilot: Manages the complete journey from requisition creation through PO issuance, including:
Automated requisition intake and validation
Policy-based approval routing with SLA enforcement
Intelligent vendor selection based on performance and pricing
Real-time spend visibility and budget tracking
Contract compliance monitoring
Invoice Processing Co-Pilot: Handles the seller side of PO-based transactions:
Automated invoice capture from any channel (email, portal, EDI)
Three-way matching with POs, receipts, and contracts
Intelligent exception resolution and dispute management
Payment term optimization and discount capture
Vendor Management Co-Pilot: Optimizes supplier relationships that make PO transactions smoother:
Streamlined vendor onboarding with automated data validation
Performance tracking and scorecard management
Communication automation for PO clarifications and updates
Risk monitoring and compliance verification
This integrated approach eliminates the hand-offs and data gaps that plague point solutions, creating a seamless experience from purchase request to payment completion.
Measurable ROI and Transformational Impact
Organizations implementing Hyperbots' AI co-pilots consistently achieve dramatic improvements:
Operational Efficiency Gains:
Reduction in manual processing effort
Faster cycle times from requisition to PO
Decrease in invoice processing costs
80% straight-through processing rates
Financial Impact:
Improvement in early payment discount capture
Reduction in late payment penalties
Better working capital efficiency through optimized payment timing
Elimination of duplicate payment risks
Strategic Advantages:
Real-time spend visibility enabling proactive decision-making
Enhanced compliance and audit readiness with complete documentation
Scalability to handle 10x transaction volumes without proportional cost increases
Employee satisfaction improvements as teams focus on strategic work
Differentiation from Traditional P2P Players
The procure-to-pay software market includes established players like Coupa, SAP Ariba, and Jaggaval. While these platforms offer breadth, they typically suffer from:
High implementation costs and long deployment timelines
Complexity requiring dedicated administrators and extensive training
Rigid workflows that don't adapt to organizational nuances
Limited AI capabilities focused primarily on data extraction
Expensive pricing models with per-transaction or per-user fees
How Hyperbots Stands Apart:
AI-First Design: Built from the ground up for intelligent automation rather than retrofitting AI onto legacy architectures. Every feature leverages advanced machine learning, natural language processing, and predictive analytics.
Unlimited User Access: Unlike competitors charging per seat, Hyperbots offers unlimited user access under a single enterprise license. This democratizes access across finance, procurement, and operational teams without creating budget constraints.
Rapid Implementation: Hyperbots' AI learns organizational patterns quickly, minimizing configuration requirements and accelerating time-to-value.
Outcome-Based Pricing: Rather than charging per transaction or user, Hyperbots aligns pricing with customer success through outcome-based models. This creates a true partnership focused on delivering measurable business impact.
Continuous Learning: The platform becomes smarter over time, automatically adapting to changing business needs, vendor behaviors, and procurement patterns. This "set it and forget it" approach contrasts with competitors requiring constant manual tuning.
Best Practices for Optimizing PO Management in Sales
Establish Clear PO Acceptance Criteria
Finance leaders should define explicit criteria for accepting or rejecting customer POs. This includes:
Minimum acceptable payment terms
Credit limit verification requirements
Pricing tolerance bands versus quotes
Required fields and documentation
Delivery timeline feasibility assessment
Document these criteria in a formal policy and encode them into automated validation rules. This ensures consistent decision-making and prevents problematic orders from entering the fulfillment pipeline.
Implement Robust Change Management Protocols
Since PO amendments are inevitable, establish structured processes for handling them:
Require formal change requests from customers
Assess impact on delivery, pricing, and revenue recognition
Obtain internal approvals before confirming changes
Update all related documents (sales orders, shipments, invoices)
Communicate changes to all stakeholders
Automated workflows ensure change requests follow proper paths and maintain complete audit trails.
Standardize Customer Communication
Create templates and automated workflows for common customer interactions:
PO acknowledgment confirmations
Shipping notifications with tracking information
Invoice delivery with PO references
Payment reminders with PO and invoice details
Exception notifications requiring customer clarification
Standardized communication reduces back-and-forth delays and improves customer satisfaction.
Monitor Key Performance Indicators
Track metrics that reveal PO process performance:
Average PO processing time from receipt to sales order creation
PO rejection rate and reasons
PO amendment frequency and causes
Invoice dispute rates related to PO mismatches
Days sales outstanding (DSO) segmented by PO accuracy
Use these metrics to identify improvement opportunities and measure automation impact.
Integrate Customer Portals
Self-service customer portals allow buyers to:
Submit POs electronically with built-in validation
Track order status in real-time
View invoices and payment status
Request changes through structured workflows
Access historical transaction data
Portals reduce manual processing while improving customer experience and reducing inquiry volumes.
The Future of PO Management in Sales Operations
Blockchain for PO Authenticity
Emerging blockchain applications promise to enhance PO management by:
Creating immutable records of PO issuance and acceptance
Enabling smart contracts that automatically trigger fulfillment
Reducing fraud through cryptographic verification
Streamlining multi-party transactions in complex supply chains
While still early-stage, blockchain integration with AI automation platforms like Hyperbots will further enhance trust and efficiency.
Predictive Order Management
Advanced AI will move beyond reactive processing to predictive capabilities:
Forecasting customer reorder timing and quantities
Proactively suggesting optimal terms for upcoming POs
Identifying customers likely to experience payment difficulties
Recommending inventory positioning based on PO patterns
These predictive capabilities enable sellers to transition from order-takers to strategic partners.
Hyper-Personalization
AI will enable mass customization of PO handling based on customer segments:
Tailored approval workflows for strategic accounts
Customized payment terms optimized for each relationship
Personalized communication cadences matching customer preferences
Segment-specific exception handling protocols
This balances standardization's efficiency with relationship-based flexibility.
Transform Your PO Management with Hyperbots
The intersection of purchase orders and sales operations represents a critical leverage point for finance transformation. Organizations that master the PO in the sales process through intelligent automation gain competitive advantages in working capital efficiency, customer satisfaction, and operational scalability.
Traditional approaches—manual processing, basic OCR, or rigid workflow tools—no longer suffice in today's fast-paced business environment. Finance leaders need AI-native solutions that adapt to complexity, learn from experience, and deliver measurable business outcomes.
Hyperbots' comprehensive suite of AI co-pilots provides exactly this capability. From requisition intake through payment optimization, Hyperbots automates the entire procure-to-pay lifecycle with intelligence, flexibility, and unprecedented ROI.
Whether you're processing hundreds or hundreds of thousands of POs annually, Hyperbots scales to meet your needs while reducing costs, accelerating cycles, and enhancing control. The platform's AI-first architecture, unlimited user access, and rapid implementation timeline make it the ideal solution for forward-thinking finance organizations.
Ready to transform your PO and sales operations? Explore Hyperbots' Procurement Co-Pilot or schedule a personalized demo to see how AI can deliver 80% cost reductions and transformational impact across your finance function.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: What is the difference between a purchase order and a sales order?
A: A purchase order (PO) is issued by the buyer to authorize a purchase, while a sales order (SO) is created by the seller upon receiving the PO to initiate fulfillment. The PO represents the buyer's commitment; the SO represents the seller's acceptance and execution plan.
Q2: How do purchase orders impact revenue recognition for sellers?
A: Purchase orders provide documentation of enforceable customer commitments necessary for revenue recognition under ASC 606. They establish contract terms, performance obligations, and transaction prices that guide when and how sellers recognize revenue.
Q3: Can small businesses benefit from PO automation?
A: Absolutely. While enterprise organizations process higher volumes, small and mid-sized businesses often face greater resource constraints. AI-powered automation like Hyperbots delivers proportionally larger benefits by eliminating manual effort that smaller teams can't afford to sustain.
Q4: What ROI can organizations expect from PO automation?
A: Typical ROI includes reduction in processing costs, faster cycle times, and improvement in early payment discount capture. Most organizations achieve full payback within 6-12 months with benefits continuing to compound over time.
Q5: Does Hyperbots replace our existing ERP system?
A: No. Hyperbots integrates with your existing ERP (NetSuite, SAP, Microsoft Dynamics, Sage, etc.) to enhance its capabilities with AI-powered automation. The platform complements rather than replaces your core financial systems.
Q6: How does AI handle exceptions in PO processing?
A: Hyperbots' AI analyzes exceptions in context, comparing against historical patterns, contract terms, and business rules. It automatically resolves common exceptions and routes genuinely ambiguous cases to appropriate reviewers with suggested resolutions and supporting context.
Q7: Is PO data secure with Hyperbots?
A: Yes. Hyperbots employs enterprise-grade security including data encryption, role-based access controls, SOC 2 compliance, and secure cloud infrastructure. The platform meets the stringent security requirements of regulated industries including financial services and healthcare.