What is the Purchase Order Process? Steps, Roles, and Flow Explained
A complete guide to understanding the purchase order process - steps, roles, flow, and how Hyperbots AI Co-pilots are redefining automation.

Executive Summary
The purchase order process is the backbone of procurement for enterprises. It ensures financial control, regulatory compliance, and transparency in vendor relationships. Yet, despite its importance, most organizations still manage purchase orders through manual, fragmented workflows that cause delays, errors, and compliance risks.
This guide explains what the purchase order process is, how the purchase order process works, the purchase order process steps, and roles involved. We also explore the transformational role of Hyperbots’ Procurement Co-pilot, which is redefining purchase order automation by cutting costs up to 80%, enabling real-time audit readiness, and accelerating approval cycles. By the end, CFOs, Procurement Leaders, and Vendor Management Heads will not only understand the purchase ordering process but also see how an AI-first approach ensures speed, accuracy, and compliance at enterprise scale.
Understanding the Purchase Order Process
What is a Purchase Order Process?
The purchase order process is a structured workflow that organizations use to request, approve, issue, and track purchase orders (POs) for goods and services. It creates a formal contract between buyer and vendor, ensuring purchases are authorized, budget-aligned, and auditable.
Without it, companies face uncontrolled spending, duplicate orders, and compliance risks.
Purchase Requisition vs Purchase Order
Purchase Requisition (PR): Internal request from an employee or department to buy something.
Purchase Order (PO): A Formal, approved document sent to a vendor, legally binding once accepted.
Why the Purchase Order Process Matters in Finance
A well-defined purchase order process ensures:
Budget Control – Aligns purchases with cost centers and financial planning.
Compliance – Ensures approvals follow internal policies and external regulations.
Vendor Accountability – Provides a legal record of what was agreed.
Audit Readiness – Creates traceability for every transaction.
According to Deloitte research, companies automating procurement processes see up to 35% faster cycle times and significantly reduced fraud exposure.
Still, many organizations struggle because manual processes are slow, prone to errors, and lack real-time visibility.
The Purchase Order Process Steps
Step 1 – Purchase Requisition Creation
Employee/department raises a PR for goods/services.
Includes description, quantity, budget code, and justification.
Challenges: Missing fields, duplicate requests.
Hyperbots Advantage: Automated field extraction from contracts & templates, duplicate detection.
Step 2 – Approval Workflows
PR routed to managers/finance for approval.
Multi-level approval ensures budget compliance.
Challenges: Bottlenecks, policy deviations.
Hyperbots Advantage: AI-driven validation, GL-coding recommendations, anomaly detection.
Step 3 – Purchase Order Creation
Approved PR converted into a PO.
PO includes line items, vendor details, and payment terms.
Challenges: Manual data entry delays, template errors.
Hyperbots Advantage: Automated PO creation with configurable templates.
Step 4 – Dispatch to Vendor
PO is sent to the vendor via email, portal, or EDI.
Challenges: Version control, lost communication.
Hyperbots Advantage: Automated dispatch and vendor management acknowledgment tracking.
Step 5 – Goods/Services Delivery & GRN
Vendor delivers goods/services.
Buyer confirms receipt with a Goods Receipt Note (GRN).
Challenges: Inconsistent updates, mismatched delivery reports.
Hyperbots Advantage: Automated receipt reconciliation against PO.
Step 6 – Invoice Matching & Payment
Vendor invoice matched with PO and GRN (3-way match).
Payment is processed.
Challenges: Mismatched invoices, payment delays.
Hyperbots Advantage: Integrated with Invoice Processing Co-pilot for seamless 3-way match.
Step 7 – PO Closure & Audit Trail
PO closed after fulfillment.
Records archived for audits and compliance.
Challenges: Poor audit readiness, incomplete documentation.
Hyperbots Advantage: End-to-end PO audit trail with configurable retention policies.
Roles in the Purchase Ordering Process
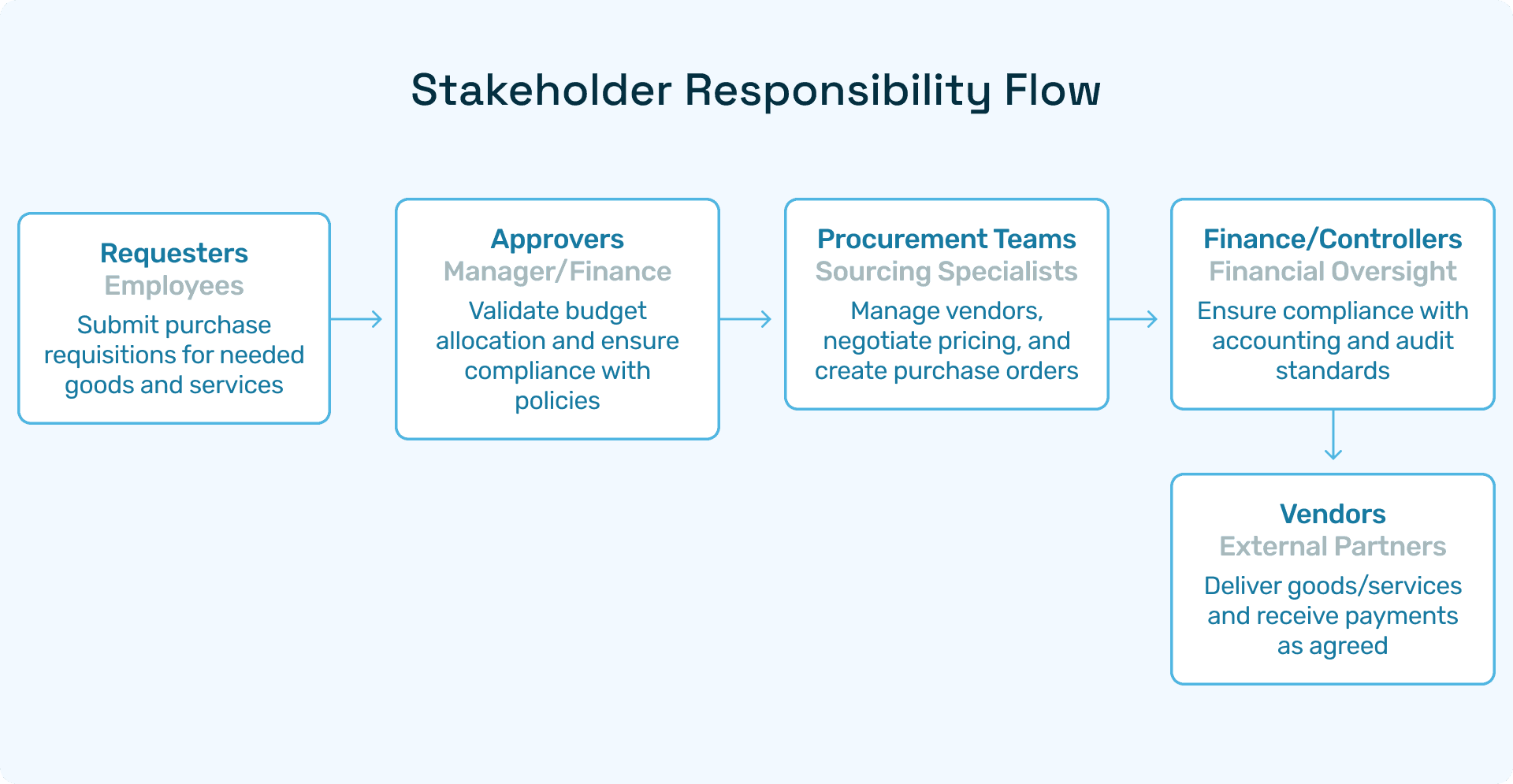
Key participants:
Requester: Raises a purchase requisition.
Approver: Department head/finance approver.
Procurement Officer: Converts PR to PO and manages vendors.
Finance Team: Oversees payment and compliance.
Vendor: Fulfills order and invoices the buyer.
With Hyperbots Procurement Co-pilot:
Automated workflows reduce manual approvals.
AI agents monitor compliance in real-time.
Vendors are integrated into the digital flow, reducing disputes.
Purchase Order Process Flow (Traditional vs Automated)
Factor | Traditional PO Process | AI-Driven PO Process (Hyperbots) |
Cycle Time | 5–10 days | <2 days |
Errors | High (manual entry) | <1% (AI validation) |
Compliance Risk | Moderate to high | Real-time monitoring |
Cost per PO | $35–$50 (avg) | $5–$10 |
Audit Readiness | Manual, fragmented | End-to-end digital audit trail |
Hyperbots: Transforming the Purchase Order Process with AI Co-pilots
Unlike other P2P players who rely on rigid RPA or workflow engines, Hyperbots offers true Gen AI-powered procurement automation.
Core Procurement Co-pilot functions:
Automated field extraction & PR autofill from PDFs, contracts, and emails
Validation, duplication & anomaly detection to eliminate errors
Budget controls & GL coding recommendations powered by AI
Configurable workflows & forms across departments
Automated PO creation & dispatch with vendor master validation
PO closing & reconciliation with invoices for auditability
Supporting Co-pilots:
Invoice Processing Co-pilot for 3-way match.
Accruals Co-pilot for real-time expense tracking.
Payments Co-pilot for seamless settlement.
Sales Tax Verification Co-pilot for compliance.
Vendor Management Co-pilot for improved collaboration.
ROI from Hyperbots-led Purchase Order Automation
Tangible ROI:
80% reduction in operational costs.
Faster approval cycles.
Fewer manual errors.
Intangible ROI:
Improved vendor trust.
Stronger compliance posture.
Better financial forecasting.
Smarter Purchase Order Automation with Hyperbots
Modern enterprises cannot afford inefficiencies in procurement. The purchase order process, once slow and error-prone, is now being reimagined through AI-first automation. Hyperbots’ Procurement Co-pilot and supporting AI agents create a seamless, compliant, and scalable procurement ecosystem.
👉 Explore Hyperbots Procurement Co-pilot or schedule a custom demo to see how AI can transform your purchase order process.
FAQs on the Purchase Order Process
Q1: What is the purchase order process in procurement?
A: It is the structured workflow from requisition to PO creation, dispatch, fulfillment, and closure.
Q2: How does the purchase order process work in enterprises?
A: It starts with requisition creation, approval, PO issuance, vendor delivery, invoicing, and closure.
Q3: What are the purchase order process steps?
A: Requisition → Approval → PO Creation → Dispatch → Receipt → Invoice Matching → Closure.
Q4: How can AI improve the purchase ordering process?
A: AI reduces manual tasks, accelerates approvals, ensures compliance, and provides real-time audit readiness.
Q5: What is the difference between requisition and order?
A: Requisition is an internal request; order is the formal vendor-facing document.
