The Playbook for Operational Excellence in Purchase Order Automation: Cost Savings, Adoption, and Workflow Design
Discover how purchase order automation can transform procurement from a manual, error-prone process into a strategic, cost-saving, and scalable operational function.
I. The New Era of Procurement Efficiency
In today’s fast-paced business environment, organizations are increasingly turning to purchase order (PO) automation to streamline procurement and finance operations. Traditional manual purchase order processes are plagued by inefficiencies such as human error, delayed approvals, duplicate purchases, and compliance risks. Automated systems, by contrast, provide real-time tracking, standardized processes, and actionable insights, transforming procurement from a reactive function into a strategic driver of business performance.
Why Organizations are Moving from Manual to Automated PO Systems
Manual PO processing often requires numerous touchpoints, from creating requisitions to tracking approvals, generating purchase orders, and reconciling payments. These multi-step processes consume time, increase error rates, and create bottlenecks. Organizations adopting automated purchase order systems experience streamlined workflows, faster approvals, and accurate record-keeping.
Link Between Cost Savings, ROI, and User Adoption
The effectiveness of any PO automation initiative hinges on three pillars:
Cost Savings: Reducing labor, errors, and maverick spending.
ROI: Measuring tangible and intangible returns relative to implementation costs.
User Adoption: Ensuring procurement staff, approvers, and suppliers embrace the system fully.
Quick Benchmark: Companies adopting PO automation report 60–75% reduction in process costs within months.
Understanding Purchase Order Automation
Purchase Order (PO) automation represents a strategic shift in procurement operations, moving organizations from manual, error-prone processes to a streamlined, technology-driven system. By digitizing and automating the entire PO lifecycle, organizations can not only accelerate procurement but also achieve greater control, compliance, and visibility over spending. In essence, PO automation transforms what was once a back-office administrative function into a strategic enabler of operational efficiency and financial governance.
What PO Automation Covers
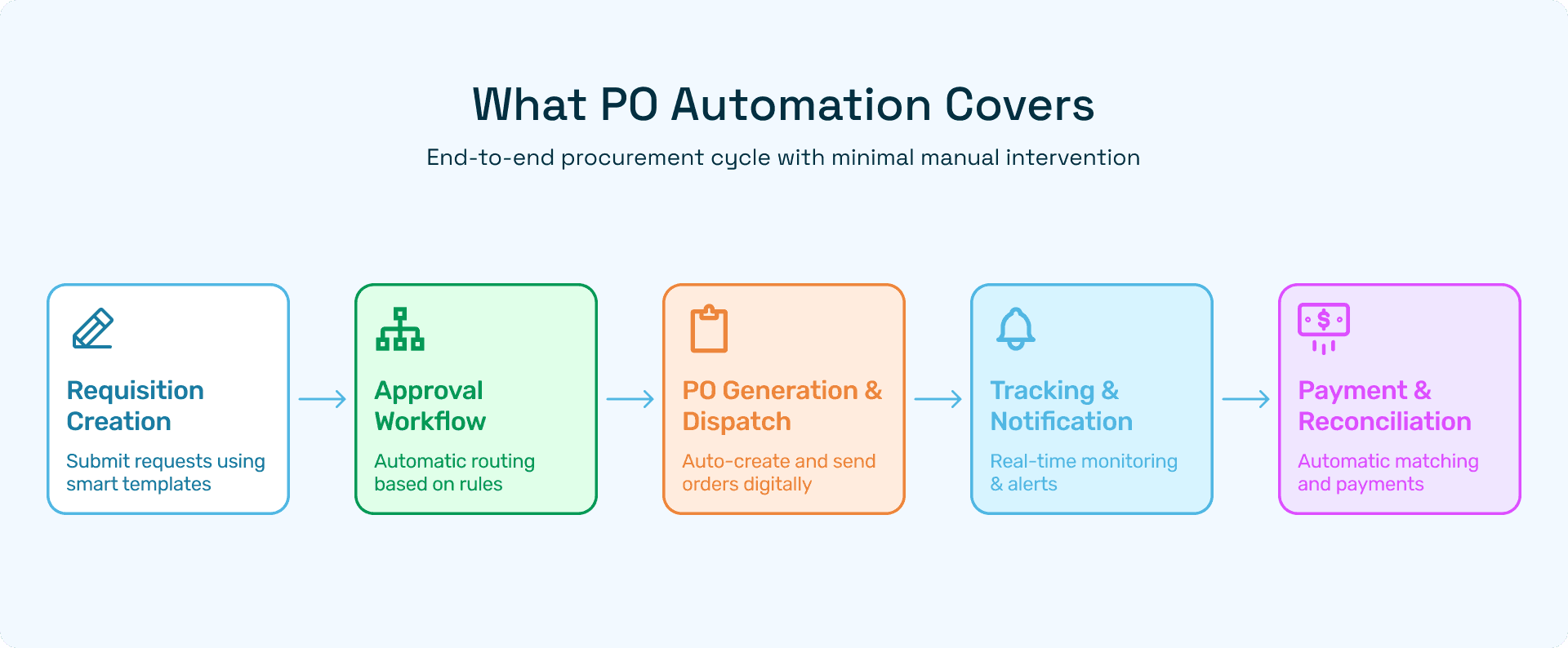
PO automation encompasses the end-to-end procurement cycle, providing a cohesive framework that integrates request initiation, approvals, order issuance, and payment. Each stage is carefully orchestrated to reduce manual intervention, minimize errors, and provide real-time insights.
1. Requisition Creation
The process begins with requisition creation, where staff members submit purchase requests using standardized templates. Modern PO automation tools allow employees to:
Select items from pre-approved catalogs with vendor and pricing details already integrated.
Attach supporting documents like quotes, specifications, or business justifications.
Auto-fill relevant fields such as cost center, department, and project codes, reducing repetitive data entry.
This step not only accelerates request submission but also enforces consistency in documentation, ensuring that all necessary information is captured upfront.
2. Approval Workflow
Once a requisition is submitted, it enters a rule-based approval workflow. Automated systems route requests based on predefined criteria, such as:
Purchase amount thresholds
Department or project codes
Budget availability
Advanced systems can even incorporate dynamic approvals, where unusual requests are flagged for managerial review, or split approvals are required for multi-department purchases. This approach ensures that approvals are consistent, timely, and fully aligned with corporate policies.
3. PO Generation & Dispatch
After approval, the system automatically generates the purchase order in a standardized format. Key features include:
Auto-populated supplier and item details
Pre-defined terms and conditions
Tax and compliance calculations
The PO can then be dispatched digitally via email, supplier portals, or EDI (Electronic Data Interchange), reducing delays and eliminating reliance on manual mail or fax. Suppliers receive accurate and complete orders, which minimizes back-and-forth communications and accelerates order fulfillment.
4. Tracking & Notifications
One of the most powerful aspects of PO automation is real-time tracking. Both procurement teams and suppliers can monitor order status, including:
Pending approvals
Order dispatch
Expected delivery dates
Invoice receipt and payment
Automated alerts notify stakeholders of exceptions, delays, or required actions, enabling proactive problem resolution. This visibility reduces miscommunication, ensures timely deliveries, and strengthens supplier relationships.
5. Payment & Reconciliation
Integration with accounting and ERP systems enables automatic matching of POs, invoices, and payments. Key benefits include:
Reducing manual reconciliation errors
Ensuring on-time vendor payments
Maintaining an auditable trail for financial compliance
By connecting procurement with finance seamlessly, organizations can improve cash flow management and strengthen internal controls over spending.
Key Goals of PO Automation
The adoption of PO automation drives multiple strategic objectives that extend beyond mere operational efficiency:
1. Efficiency
Automated workflows minimize manual effort and shorten procurement cycle times. By eliminating repetitive tasks such as paper approvals, email follow-ups, and data entry, organizations can redirect human effort to higher-value activities like strategic sourcing or vendor management.
2. Accuracy
PO automation reduces errors in:
Data entry
Coding (GL or cost center allocation)
Calculations, including taxes and discounts
This not only prevents costly mistakes but also enhances the reliability of financial reporting.
3. Compliance
Automated systems enforce corporate purchasing policies, ensuring that all procurement adheres to:
Budget limits
Preferred supplier lists
Approval hierarchies
Regulatory requirements
Non-compliant requests can be automatically flagged, preventing unauthorized purchases and reinforcing governance.
4. Transparency
Every transaction within an automated system is recorded digitally, creating a fully auditable trail. Procurement teams, finance departments, and auditors can easily access:
Who requested a purchase
Who approved it
When it was dispatched and paid
This transparency strengthens accountability, simplifies audits, and provides actionable insights for future decision-making.
Differentiating from Generic Procurement Digitization
It’s important to distinguish true PO automation from generic digitization:
Generic digitization often focuses on storing documents electronically or scanning invoices. While this reduces paper clutter, it does not fundamentally improve process efficiency or enforce compliance.
PO automation, in contrast, integrates workflows, approvals, compliance rules, and analytics into a single, intelligent system. It proactively guides procurement decisions, prevents errors, and provides real-time insights into spending patterns and supplier performance.
In short, while digitization replaces paper with pixels, PO automation redefines how purchasing happens, delivering measurable operational, financial, and strategic benefits.
III. Cost Savings from Purchase Order Automation
Implementing purchase order (PO) automation delivers tangible financial benefits across both direct and indirect cost dimensions. By digitizing the entire procurement lifecycle, organizations not only reduce operational inefficiencies but also unlock opportunities for strategic savings. These savings extend beyond mere labor reduction, encompassing error prevention, supplier optimization, cash flow management, and improved operational agility.
A. Direct Cost Savings
Direct cost savings are the most immediately measurable benefits of PO automation, directly impacting procurement and finance teams’ budgets.
1. Labor Cost Reduction
Manual PO processing requires significant human effort, from creating requisitions and routing approvals to tracking orders and reconciling invoices. Automating these tasks provides measurable reductions in labor hours:
Requisition creation: Automated templates and catalogs reduce the time staff spend filling forms and researching vendor details.
Approval routing: Rule-based workflows eliminate the need for managers to manually review and forward requests.
PO generation & dispatch: Automated PO creation ensures correct formatting and delivery without manual intervention.
Tracking & follow-ups: System alerts replace time-consuming email threads or phone calls to check order status.
For instance, finance teams handling hundreds of POs weekly can save 20–30 hours per week, which translates into reduced overtime costs or the ability to redeploy staff to higher-value activities such as vendor analysis, cost optimization, or strategic sourcing.
2. Lower Error Correction and Maverick Spending
Errors in PO processing—such as incorrect cost center coding, duplicate orders, or unauthorized purchases—can lead to significant financial leakage. PO automation mitigates these risks by:
Validating entries against pre-approved supplier lists, budgets, and contracts.
Automatically flagging inconsistencies or deviations from company policy.
Reducing duplicate orders by detecting identical requisitions before PO generation.
By enforcing compliance, organizations prevent maverick spending, which research shows can represent 5–10% of total procurement budgets. The cost savings from avoided errors are compounded by reduced time spent correcting mistakes and reconciling accounts.
3. Better Supplier Pricing
PO automation ensures strict adherence to negotiated contract terms and preferred pricing. Embedded rules trigger automatic application of volume discounts, promotional rates, or tiered pricing, ensuring that organizations fully capitalize on negotiated supplier agreements. This not only drives cost savings per transaction but also strengthens supplier relationships by increasing the predictability and reliability of business volumes.
B. Indirect Cost Benefits
While direct savings are easy to quantify, PO automation also generates indirect benefits that can significantly impact overall procurement performance.
1. Faster Cycle Times
Automated workflows accelerate approvals, order creation, and dispatch, often reducing the average procurement cycle from several days to mere hours. Faster cycle times:
Prevent the need for rush orders, which often incur higher freight charges or premium pricing.
Enable organizations to respond more quickly to operational needs, reducing downtime and production delays.
Allow teams to process a higher volume of orders without additional resources, increasing operational scalability.
2. Improved Vendor Relationships
Timely, accurate POs and payments enhance supplier trust and foster stronger partnerships. Benefits include:
Reduced disputes over misaligned orders, pricing, or payment delays.
Greater supplier willingness to provide priority service or flexible terms.
Improved long-term collaboration, which can lead to joint cost-saving initiatives, such as consignment stock, bulk-order discounts, or vendor-managed inventory.
3. Enhanced Cash Flow Management
PO automation provides real-time visibility into pending approvals, outstanding orders, and upcoming payments, allowing finance teams to:
Optimize working capital by timing payments strategically.
Avoid unnecessary late fees or interest charges.
Plan procurement budgets more accurately, enabling more efficient allocation of cash to other strategic initiatives.
C. Quantifying Cost Impact
To measure the tangible benefits of PO automation, organizations can track several key performance metrics:
Metric | Before Automation | After Automation | Improvement |
Cost per PO | $25 | $7 | 72% reduction |
Average approval time | 5 days | 1 day | 80% faster |
Duplicate PO rate | 6% | 1% | 83% reduction |
Error correction rate | 4% | 0.5% | 88% reduction |
Supplier compliance | 75% | 95% | 20% improvement |
By monitoring these metrics, companies can quantify ROI and justify further investments in procurement automation technology.
D. Real-world Example
Consider a mid-sized manufacturing firm that implemented a PO automation solution:
Processing costs were reduced by 65%, freeing significant staff bandwidth for strategic projects.
Approval cycles decreased from 4 days to under 24 hours, enabling faster production planning and order fulfillment.
Supplier compliance improved by 20%, ensuring that all purchases were within contract terms and negotiated rates.
Maverick spending dropped by 50%, translating into thousands of dollars saved annually and fewer audit exceptions.
This case demonstrates that PO automation not only delivers cost savings but also strengthens operational efficiency, supplier collaboration, and financial control.
E. Strategic Implications
Beyond immediate savings, organizations can leverage PO automation for long-term advantages:
Data collected through automated systems enables spend analytics, helping procurement teams identify trends, negotiate better deals, and forecast future demand.
Automation creates standardized, repeatable processes that can scale with business growth.
By reducing friction in procurement, organizations can reallocate resources to higher-value activities, such as strategic sourcing, supplier risk management, and sustainability initiatives.
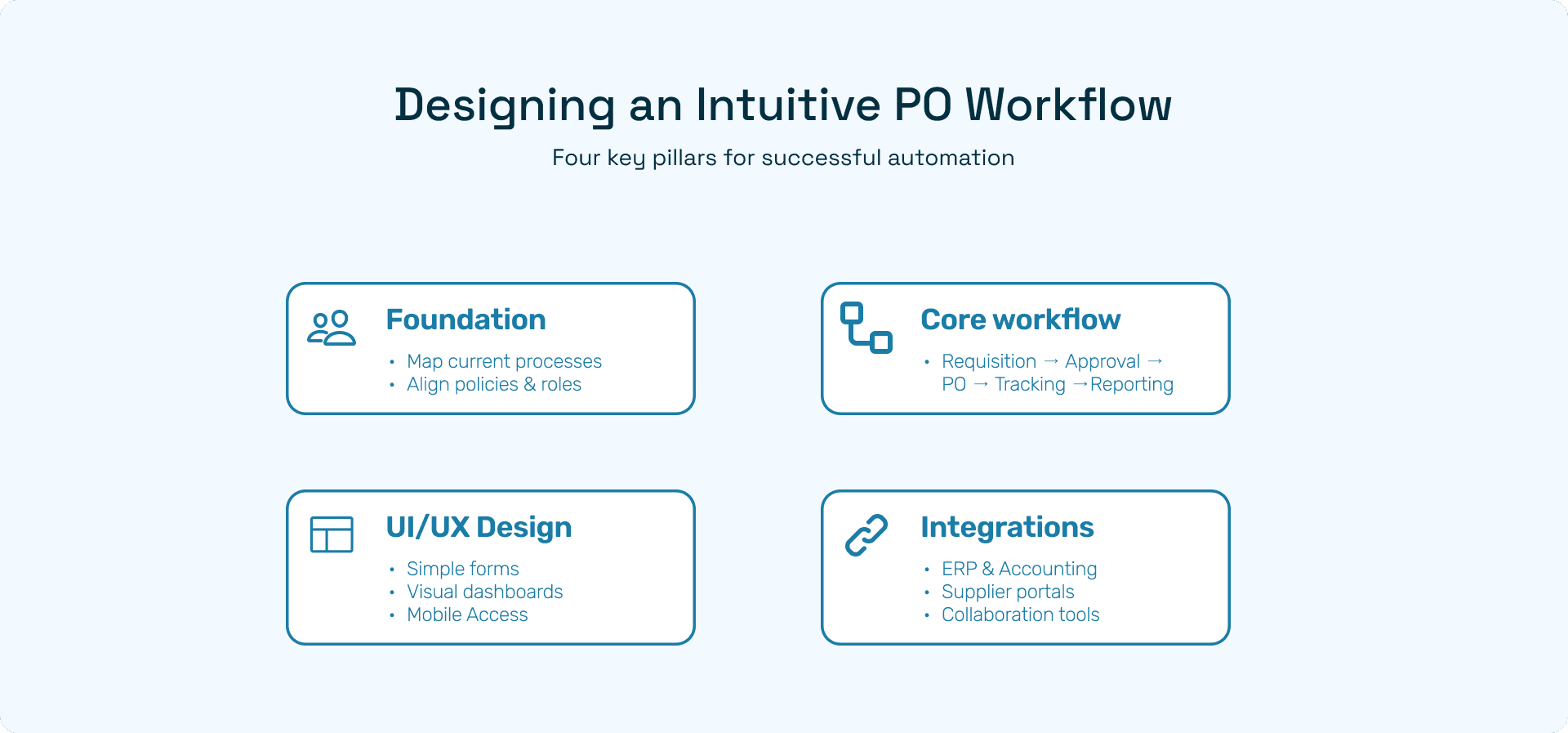
Designing an Intuitive Purchase Order Automation Workflow
A well-designed purchase order (PO) automation workflow is critical to maximizing efficiency, compliance, and user adoption. A thoughtfully crafted workflow ensures that procurement processes are seamless, errors are minimized, approvals are timely, and stakeholders—from requesters to approvers and finance teams—can collaborate effectively. Designing such a workflow requires careful consideration of people, processes, technology, user experience, and system integrations.
A. The Foundation: People, Process, and Technology
Successful PO automation begins with a strong foundation that balances organizational roles, established processes, and the enabling technology. Without this, even the most sophisticated system may fail to deliver measurable benefits.
1. Mapping Current Procurement Flow
Before automating, organizations should conduct a comprehensive assessment of existing procurement processes:
Identify friction points: Map out areas where tasks are delayed, approvals get stuck, or users frequently encounter issues. Examples include repetitive data entry, unclear approval paths, or miscommunication with suppliers.
Document repetitive tasks: Highlight tasks that are highly manual and time-consuming, such as PO creation, coding, or tracking invoice payments. These are prime candidates for automation.
Analyze approval bottlenecks: Determine which stages in the workflow consistently delay procurement. For instance, multi-level approvals may be unnecessarily sequential, or managers may lack visibility into pending requests.
A clear understanding of the current state provides a roadmap for streamlining processes and designing an automation workflow that genuinely improves efficiency.
2. Aligning Workflow with Policies and Roles
A robust workflow aligns with organizational policies and clearly defines user responsibilities:
Policy adherence: Each step should enforce corporate rules, including budget limits, preferred supplier use, and contract compliance.
Role clarity: Assign responsibilities to ensure accountability. Requesters, approvers, finance teams, and procurement staff should all know their obligations.
Escalation procedures: Include rules for automatic escalation if approvals are delayed or requests exceed thresholds, ensuring uninterrupted workflow.
By aligning processes with policies and roles, organizations prevent compliance gaps and reduce the risk of maverick spending.
B. Core Workflow Components
A comprehensive PO automation workflow typically consists of the following key components:
1. Requisition Creation
Requisition creation is the first interaction users have with the system, making it a critical touchpoint:
Predefined templates: Standardize data entry to reduce errors and omissions. Templates can include item descriptions, quantities, cost centers, and delivery details.
Autofill fields: Use existing data from ERP or vendor catalogs to populate frequently used fields automatically.
Catalog selection: Provide access to pre-approved supplier catalogs, ensuring pricing and contract terms are applied consistently.
Effective requisition design reduces errors, accelerates submissions, and enhances user satisfaction.
2. Approval Routing
Approvals are central to procurement governance:
Rule-based approvals: Automatically route requisitions based on factors such as amount, department, or project.
Escalations and reminders: Trigger alerts for overdue approvals or complex requests requiring higher-level authorization.
Parallel approvals: Allow simultaneous approvals for multi-department purchases to shorten cycle times.
Automated routing ensures consistency, prevents bottlenecks, and enforces compliance.
3. PO Generation & Dispatch
Once approvals are complete, the system generates and dispatches POs:
Integration with ERP/accounting tools: Automatically populate relevant accounting codes, project allocations, and GL entries.
Digital dispatch: Send POs via email, supplier portals, or electronic data interchange (EDI) for fast, error-free delivery.
Standardized formatting: Ensure POs contain all necessary information, including terms, tax, and delivery instructions.
This stage reduces manual processing errors and accelerates supplier fulfillment.
4. Tracking & Notifications
Real-time visibility is crucial for both procurement teams and suppliers:
Order tracking: Monitor status at each stage, including approval, dispatch, and expected delivery.
SLA tracking: Ensure timelines are met for approvals, dispatch, and delivery.
Automated notifications: Alert stakeholders to pending actions, delays, or exceptions.
Proactive tracking minimizes delays, improves supplier relationships, and allows teams to respond quickly to disruptions.
5. Audit & Reporting
Transparency and compliance are achieved through robust reporting:
Audit trails: Capture all transactions, approvals, and changes in the system.
Analytics dashboards: Provide actionable insights into spending patterns, cycle times, supplier performance, and compliance metrics.
Regulatory compliance: Ensure adherence to industry-specific reporting and financial standards.
A strong audit and reporting layer allows finance and procurement teams to measure effectiveness, identify improvement areas, and support audits with ease.
C. UI/UX Design Principles
Even the most sophisticated PO automation system can fail if the user interface is unintuitive. Applying thoughtful design principles ensures adoption and efficiency:
Simplify forms: Reduce unnecessary fields and enable autofill wherever possible.
Guided workflows: Use step-by-step instructions or prompts to guide users through requisition submission, approvals, and PO creation.
Visual dashboards: Provide at-a-glance status views for pending approvals, order tracking, and performance metrics.
Mobile access: Enable remote approvals and requisition creation to support distributed teams.
Intuitive navigation: Organize menus, buttons, and actions logically, minimizing the learning curve for users.
A well-designed UI/UX reduces errors, increases productivity, and encourages adoption across all user groups.
D. Integrations
PO automation workflows achieve maximum value when integrated with other enterprise systems:
Accounting platforms: Seamlessly connect to tools like QuickBooks, Xero, or SAP for accurate financial coding and reconciliation.
ERP systems: Ensure POs, requisitions, and approvals sync automatically with production, inventory, and project management modules.
Supplier portals & e-invoicing systems: Enable automated order confirmation, invoice matching, and payment processing.
Collaboration tools: Integration with Slack, Teams, or email ensures notifications reach the right stakeholders instantly.
By connecting to the broader enterprise ecosystem, automation eliminates redundant data entry, ensures accuracy, and provides real-time insights across procurement and finance operations.
E. Key Takeaways
Designing an intuitive PO automation workflow is more than implementing software—it requires:
Mapping and understanding existing processes to identify friction points.
Aligning workflows with organizational policies and roles for compliance.
Incorporating user-friendly UI/UX principles to enhance adoption.
Integrating seamlessly with enterprise systems to maintain accuracy and visibility.
A thoughtfully designed workflow not only accelerates procurement but also strengthens governance, reduces errors, and delivers measurable ROI.
How to Drive User Adoption of Purchase Order Automation
Even the most advanced PO automation system can fail to deliver its full potential if users do not adopt it effectively. Driving user adoption requires a strategic approach that addresses human, technological, and organizational factors. Successful adoption ensures that teams embrace the system, adhere to policies, and ultimately achieve efficiency, compliance, and measurable ROI.
A. Common Barriers to Adoption
Understanding the obstacles to adoption is the first step toward designing strategies that encourage engagement. Common barriers include:
Resistance to Change
Employees often feel comfortable with existing manual processes, even if they are inefficient. Resistance can manifest as reluctance to use new software, preference for old habits like spreadsheets or emails, or skepticism about system benefits. Without addressing this mindset, automation initiatives risk underutilization.Complex Interfaces
If the user interface is unintuitive, overly complicated, or inconsistent, users may struggle to navigate the system. Complex forms, multiple clicks to complete tasks, or unclear approval flows can frustrate staff and reduce compliance.Inadequate Training or Unclear Benefits
Employees are more likely to resist tools they do not understand. A lack of comprehensive, role-based training or unclear communication of the system’s advantages can leave users unsure of how to use it effectively. Without clarity on the “why” and the “how,” adoption slows.
B. Change Management Strategies
Overcoming adoption barriers requires a structured change management approach that combines communication, training, and engagement:
Involve Stakeholders Early and Run Pilot Programs
Engage key stakeholders—including procurement, finance, IT, and department heads—from the start.
Pilot programs with small groups allow teams to experience the system firsthand, identify pain points, and provide feedback before full-scale rollout.
Early involvement fosters ownership and reduces resistance by showing that user input shapes the workflow.
Communicate Clear Benefits to Each User Group
Tailor communication to address the unique concerns and priorities of each role:
Requesters: Faster requisitions, fewer errors.
Approvers: Streamlined approvals, clear visibility of pending tasks.
Finance teams: Accurate coding, reduced reconciliation effort, better reporting.
Highlight tangible outcomes such as saved time, fewer errors, and enhanced collaboration. Clear messaging helps users understand “what’s in it for me.”
Provide Role-Based Training and Ongoing Support
Offer structured training sessions customized for different roles and levels of system interaction.
Use a mix of modalities: live workshops, video tutorials, FAQs, and user manuals.
Establish ongoing support channels (helpdesk, chat support, or dedicated super users) to quickly resolve issues and maintain user confidence.
C. Incentivizing Adoption
Behavioral reinforcement is key to sustaining adoption and ensuring long-term compliance:
Tie KPIs to System Usage and Compliance
Include system adoption metrics in individual and departmental KPIs. Examples:
Percentage of requisitions submitted via the automated system.
On-time approvals completed through the workflow.
Reduction in manual corrections or errors.
Linking performance goals to system usage encourages consistent engagement and accountability.
Celebrate Quick Wins and Share Success Stories
Publicize examples of how the system saved time, reduced errors, or improved supplier relationships.
Highlight individuals or teams who demonstrate best practices. Recognition builds positive momentum and encourages peer adoption.
Establish Continuous Feedback Loops for Workflow Improvements
Solicit user feedback regularly to understand pain points and areas for improvement.
Implement iterative updates to workflows based on user input, showing that the system evolves to meet their needs.
Encourage collaboration between IT, procurement, and end-users to foster a culture of continuous improvement.
D. Additional Best Practices
To further reinforce adoption, organizations can:
Gamify adoption: Introduce friendly competitions or badges for consistent system usage.
Simplify access: Ensure single sign-on (SSO) and mobile-friendly interfaces to make the system convenient.
Monitor metrics: Track adoption trends over time and intervene early if usage drops in specific departments or roles.
Communicate leadership support: Executive sponsorship signals the system’s importance and encourages buy-in at all levels.
E. Key Takeaways
Driving user adoption of PO automation is a multi-faceted effort that combines change management, training, incentives, and continuous improvement. Organizations that invest in understanding barriers, communicating clear benefits, and actively engaging users see higher compliance rates, faster adoption, and ultimately, better returns on their automation investment. A well-adopted system translates into streamlined procurement, cost savings, enhanced compliance, and improved operational efficiency.
Case Example: Success Snapshot
To illustrate the tangible benefits of purchase order (PO) automation, consider the example of a mid-sized manufacturing firm that transformed its procurement operations through a combination of technology, process optimization, and change management.
A. Company Profile
Industry: Manufacturing
Size: Mid-sized, approximately 500 employees
Operations: Multi-department procurement spanning production, maintenance, and administrative functions
Like many organizations of this scale, the company faced operational inefficiencies due to manual PO processes, which slowed approvals, increased costs, and reduced overall compliance with corporate procurement policies.
B. Challenges
Before implementing PO automation, the organization faced several key challenges:
High Processing Costs
Manual data entry, approvals, and order tracking consumed significant staff hours.
Finance and procurement teams struggled to keep up with hundreds of weekly POs, creating overtime and increased labor costs.
Approval Delays
Multi-level approval workflows were slow, often taking four or more days to complete.
Bottlenecks occurred when managers were unavailable, leading to production delays and rushed orders with higher costs.
Low Compliance and Visibility
A lack of system enforcement allowed maverick spending and off-contract purchases.
Inconsistent data coding led to errors in accounting and reporting, creating challenges during audits.
Limited User Engagement
Staff were hesitant to adopt new tools due to unfamiliarity with digital workflows.
Training was inconsistent, leaving users reliant on outdated manual methods.
C. Solution Implementation
The company addressed these challenges by implementing an AI-powered PO automation system. Key elements of the solution included:
Intuitive Workflows
Requisition creation was simplified using pre-defined templates, autofill fields, and catalog selection to minimize errors.
Approval routing was automated based on rules and thresholds, with escalations for overdue requests.
Real-time tracking and notifications ensured visibility at every step.
ERP & Accounting Integration
Automated POs synced with the company’s ERP and accounting systems, reducing manual data entry and ensuring accurate coding.
Supplier catalogs and contract pricing were integrated into the system to enforce compliance and optimize costs.
Change Management & Training
Role-based training programs empowered employees with hands-on experience tailored to their responsibilities.
Pilot programs and continuous feedback loops allowed iterative workflow improvements.
Success stories and quick wins were communicated across departments to encourage adoption.
D. Results and Measurable Impact
The implementation of PO automation delivered substantial, measurable benefits across multiple dimensions:
Metric | Before Automation | After Automation | Improvement |
Processing Cost per PO | $25 | $8 | 65% reduction |
Approval Cycle Time | 4 days | <1 day | 75% faster |
Compliance Rate | 75% | 95% | +20% |
User Adoption | ~50% | 95% active users within 3 months | +45% |
Additional Benefits:
Reduced labor effort freed finance and procurement staff to focus on strategic sourcing and supplier negotiations.
Faster approvals enabled more timely production planning and reduced rush-order costs.
Automated audit trails improved financial transparency, simplifying internal and external audits.
Strong adoption rates ensured long-term ROI and sustained process efficiency.
E. Key Takeaways
This case demonstrates that combining workflow optimization, automation, and effective change management can produce dramatic improvements in cost, efficiency, compliance, and user engagement. Key lessons include:
Automation Alone Isn’t Enough – Successful adoption requires intuitive workflows, training, and ongoing support.
Integration Drives Accuracy – Linking POs to ERP and accounting systems eliminates errors and enforces compliance.
User Engagement is Critical – Role-based training, pilot programs, and communication of benefits accelerate adoption.
ROI is Measurable Across Metrics – Cost per PO, cycle time, compliance rates, and user adoption are tangible indicators of success.
By strategically combining technology and process improvements, the company transformed procurement from a manual, error-prone function into a highly efficient, compliant, and user-friendly system—demonstrating that PO automation can deliver both operational and strategic value.
Conclusion: Building a Sustainable, Scalable Procurement Future
Maximizing the return on investment (ROI) from purchase order (PO) automation goes beyond simply implementing a software solution. True value arises when organizations approach automation as a strategic transformation, integrating people, processes, and technology to create a procurement ecosystem that is efficient, compliant, and scalable. By thoughtfully combining cost optimization, streamlined workflows, and user adoption strategies, companies can unlock lasting benefits that extend far beyond operational savings.
A. Automation as a Strategic Transformation
PO automation is not merely a digital replacement for paper-based processes—it is a foundation for strategic procurement management:
Efficiency and accuracy: Automation reduces repetitive manual tasks, accelerates approvals, and minimizes errors in data entry, coding, and invoice reconciliation.
Compliance and control: Embedded rules and approval workflows enforce corporate policies, prevent unauthorized spending, and strengthen governance.
Visibility and insights: Real-time dashboards and reporting tools provide actionable analytics, enabling proactive decision-making and better supplier management.
Approaching automation as a strategic initiative ensures that it supports broader organizational goals, such as cost control, operational agility, and supplier collaboration.
B. Key Takeaways for Sustained Success
To build a procurement function that is sustainable and scalable, organizations should focus on several critical areas:
Labor and Cost Savings
Automation directly reduces operational costs by eliminating repetitive tasks, lowering error correction time, and preventing maverick spending. These savings can be reinvested in strategic procurement activities, such as supplier negotiations, demand forecasting, or sustainability initiatives.ROI Tracking and Continuous Improvement
Implement KPI dashboards and performance metrics to measure the impact of PO automation on key procurement indicators, such as cost per PO, approval cycle times, compliance rates, and user adoption. Continuous monitoring enables teams to identify improvement areas, refine workflows, and optimize supplier relationships over time.Intuitive Workflow Design
A well-designed workflow ensures that the system is user-friendly, reduces bottlenecks, and supports organizational policies. Incorporating features such as automated approvals, catalog integration, real-time notifications, and audit trails increases efficiency while maintaining compliance.Proactive Change Management and User Adoption
Successful automation depends on people as much as technology. Clear communication of benefits, role-based training, pilot programs, and continuous feedback loops foster high adoption rates. When employees embrace the system, the organization achieves greater efficiency, accuracy, and ROI.
C. Scaling Procurement for the Future
PO automation lays the groundwork for a future-ready procurement function:
Scalability: Automated systems can handle growing transaction volumes without requiring proportional increases in staff.
Adaptability: Integrated workflows can quickly accommodate new policies, suppliers, or business models.
Strategic decision-making: Analytics derived from automated workflows provide insights into spending patterns, supplier performance, and cost optimization opportunities.
Supplier collaboration: Timely, accurate POs and payments foster stronger supplier partnerships, enabling joint initiatives like volume discounts, just-in-time inventory, or sustainability programs.
By aligning technology, people, and processes, organizations create a procurement system that not only supports current operations but also scales with business growth.
D. Final Thoughts
Purchase order automation represents a transformative opportunity for modern organizations. Beyond reducing labor and errors, it enhances compliance, strengthens supplier relationships, and empowers data-driven decision-making. However, the true power of automation is realized only when it is strategically implemented, thoughtfully adopted, and continuously optimized.
Organizations that invest in intuitive workflows, proactive change management, and robust KPI tracking can achieve sustainable, scalable procurement operations—transforming procurement from a transactional function into a strategic enabler of business growth.
Explore AI-powered solutions like Hyperbots Procurement Co-Pilot to simplify workflows, enhance ROI visibility, and accelerate adoption across finance and procurement teams.