How to Process a Purchase Order: Tasks, Roles, and Responsibilities in Modern Automation
Discover step-by-step purchase order processing, key job roles, and AI-driven automation for smarter procurement workflows.

Executive Summary
Procurement leaders and finance professionals know that processing a purchase order (PO) is the foundation of compliant, cost-effective operations. Traditionally, manual or spreadsheet-based workflows caused delays, errors, and limited visibility. Today, AI-powered platforms like Hyperbots automate approvals, standardize workflows, and embed compliance checks, shrinking cycle times and reducing mistakes. This shift allows finance teams to move beyond routine administration toward strategic analysis, including spend optimization, supplier performance, and cash flow forecasting. For CFOs and controllers, automated POs evolve into dynamic tools that enhance governance, mitigate risk, and drive smarter business decisions.
What Is a Purchase Order?
A purchase order (PO) is a formal document created by a buyer and issued to a supplier that specifies the goods or services being requested. It clearly outlines the items required, quantities, agreed prices, delivery schedules, and payment terms. In essence, a PO serves as a legally binding contract once the supplier accepts it, ensuring both parties share a common understanding of the transaction.
For finance and procurement teams, purchase orders are far more than just paperwork. They standardize how purchasing takes place across an organization, creating a structured framework that ensures spending is controlled, documented, and aligned with budgets. By requiring pre-approval before any commitment is made, POs help organizations avoid unauthorized purchases and keep costs in check.
Why Are Purchase Orders Important?
Authorized Spending: Every PO goes through an approval workflow, ensuring managers and finance teams validate the expense before it is incurred. This prevents overspending, duplicate orders, or purchases outside of policy.
Contractual Clarity: A purchase order captures the agreed details in writing—what is being purchased, at what price, and under what delivery conditions. This reduces disputes between buyers and suppliers and provides a contractual safeguard if issues arise.
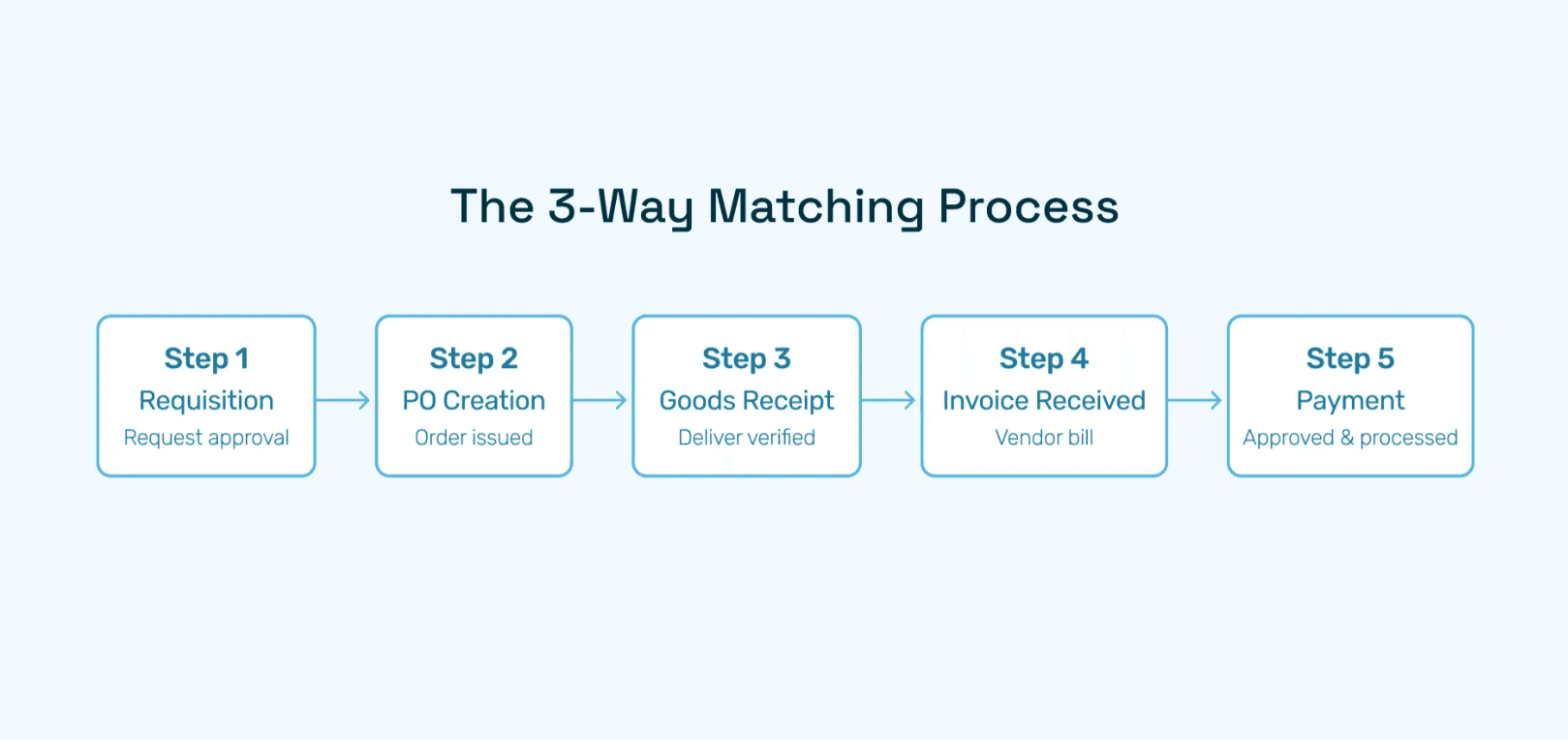
Three-Way Matching for Accuracy: Finance teams rely on purchase orders to match invoices and receipts against what was originally approved. This process, known as three-way matching, ensures that companies only pay for what was ordered and received, minimizing fraud and payment errors.
Improved Visibility and Control: With POs, procurement leaders gain better insight into purchasing patterns, supplier performance, and budget utilization. This transparency enables more accurate financial planning and stronger vendor negotiations.
POs in Modern Business
Traditionally, purchase orders were paper-based forms or manual spreadsheets, making the process slow and prone to error. Today, digital purchase order systems like those powered by automation and AI, streamline the entire workflow. From auto-generating POs to routing them for electronic approvals and syncing them with ERP systems, these platforms reduce manual effort while enhancing compliance.
Why Proper Purchase Order Processing Matters
Processing purchase orders properly is a financial safeguard that protects organizations from fraud, duplicate payments, and budget overruns. Every purchase order (PO) acts as a checkpoint, ensuring that each transaction is authorized, transparent, and traceable. When handled efficiently, POs reduce risk while creating valuable data for better decision-making. When mismanaged, they can result in compliance gaps, vendor disputes, or wasted cash flow.
For CFOs, controllers, and procurement leaders, the purchase order process is therefore central to financial governance. Done right, it ensures money is spent wisely, employees follow approved channels, and suppliers are paid correctly. Done poorly, it can lead to bottlenecks, errors, and missed opportunities for cost savings.
The Risks of Poorly Managed PO Processes
Fraud and Duplicate Payments
Without clear checks in place, fraudulent invoices or duplicate bills can slip through. If a PO isn’t matched against an invoice and a receipt, finance teams may pay for goods never received or services never rendered.Budget Overruns
Purchases made outside of approved PO workflows often exceed budget limits. Lack of oversight makes it difficult for finance teams to forecast spending and track commitments accurately.Audit and Compliance Issues
Auditors rely on POs to verify that company funds were spent appropriately. If records are missing, incomplete, or inconsistent, audits become slower, more costly, and more likely to expose compliance gaps.
What Best-in-Class PO Workflows Deliver
Leading organizations are moving away from manual, paper-based PO systems toward automated, digital-first workflows. Best-in-class PO processing delivers measurable improvements across finance and procurement.
Faster Cycle Times and Reduced Admin Effort
Automated systems can generate purchase orders in minutes instead of days, cutting out manual data entry and routing delays. Employees no longer waste time chasing signatures or re-keying the same information into multiple systems.Elimination of Bottlenecks
Traditional workflows often stall when approvers are unavailable or documents get lost in email chains. Automated approval routing ensures that POs move seamlessly through the process, even across departments or geographies. This prevents slowdowns and keeps suppliers satisfied with timely commitments.Error-Free and Audit-Ready Records
Digital PO systems embed compliance rules and automatically match invoices, receipts, and orders. This makes audits faster, easier, and far less error-prone. Auditors gain instant access to a digital trail of who approved what, when, and why—reducing the burden on finance teams.Smarter Decision-Making with Data
Beyond efficiency, best-in-class PO systems generate insights. They provide real-time visibility into spend patterns, vendor performance, and budget adherence. Finance leaders can use this data to negotiate better supplier contracts, forecast cash flow more accurately, and identify opportunities for cost savings.
Moving from Administration to Strategy
Perhaps the most transformative benefit of modern PO workflows is the shift in how finance teams allocate their time. Instead of drowning in repetitive administrative tasks, staff can focus on higher-value analysis—such as identifying spend leakages, improving supplier relationships, and aligning procurement strategy with business growth goals.
Platforms like Hyperbots push this transformation further by embedding AI into the purchase order process. AI-powered automation can flag anomalies, predict approval delays, and even suggest optimal purchasing decisions. This turns the PO process from a compliance checkpoint into a strategic enabler for finance and procurement.
According to Deloitte’s procurement operations research, digital automation has a transformative impact on how purchase orders are managed. By digitizing workflows and eliminating manual touchpoints, organizations can cut average purchase order cycle times by as much as 50%. What once took days of back-and-forth emails, spreadsheet updates, and paper-based approvals can now be completed in hours with automated routing, electronic approvals, and seamless integration into ERP systems.

Processing Purchase Orders Job Description: Key Roles in the Workflow
Purchase orders (POs) form the backbone of effective procurement and finance operations. Processing them properly is essential not only for maintaining compliance and controlling costs but also for supporting strategic business decisions. For organizations—especially mid-sized businesses where budgets are tight and workflows must be efficient—clarity in job roles and responsibilities is critical to ensure smooth operations.
Common Purchase Order Responsibilities
Finance and procurement teams handle multiple tasks to ensure purchase orders are accurate, approved, and executed efficiently. Typical responsibilities include:
Accurately Prepare, Review, and Submit Purchase Requisitions/Orders
Employees tasked with PO processing are responsible for initiating and submitting requisitions that are complete, accurate, and policy-compliant. This involves:Verifying item descriptions, quantities, prices, and vendor information
Ensuring that budget codes, project references, or department allocations are correctly applied
Utilizing pre-configured templates or digital procurement tools to minimize manual errors
Accurate preparation of POs is foundational: a single mistake at this stage can cascade into delayed deliveries, misallocated budgets, or payment discrepancies.
Collaborate with Procurement and Finance to Resolve Discrepancies
Inevitably, discrepancies may arise between purchase requisitions, POs, invoices, or goods received. PO handlers must:Communicate promptly with procurement and finance teams to resolve mismatched quantities or pricing
Investigate and flag duplicate requests or policy violations
Coordinate with suppliers for corrections or clarifications
This collaborative effort ensures that the organization maintains strong supplier relationships while protecting internal financial controls.
Monitor Approval and Delivery Status
Beyond creation, POs require careful tracking throughout the workflow. Key tasks include:Following up on approvals from managers or finance personnel in multi-level workflows
Tracking delivery dates and partial shipments
Updating the system to reflect receipt of goods and services
Timely monitoring prevents bottlenecks, ensures accurate inventory or project tracking, and reduces the risk of late payments or disputes with vendors.
Maintain Audit-Ready Records
Compliance and audit readiness are crucial aspects of PO management. Employees must ensure:Every PO, invoice, and receipt is properly logged in the system
Approval histories and correspondence are documented
Exception handling, partial deliveries, and discrepancies are tracked
Digitally maintained, organized records reduce the burden of audits, simplify reconciliation, and strengthen governance.
Specialized Roles in the PO Workflow
To achieve best-in-class efficiency, organizations often divide PO responsibilities across specific roles:
Requisitioner: Identifies the need, fills in required details, and submits the purchase request. Accuracy at this stage is critical for downstream efficiency.
Approver/Manager: Validates requests against budgets, policy, and compliance requirements. Ensures that expenditures are justified and aligns with organizational priorities.
Procurement Specialist: Oversees supplier selection, verifies contracts, and confirms terms and conditions. Acts as the bridge between internal teams and external vendors.
Receiving/Inventory Team: Confirms goods or services are delivered in the correct quantity and quality, recording receipt against the PO.
Finance/Accounts Payable: Performs invoice matching, ensures compliance with payment terms, and posts transactions to the general ledger.
Skills and Competencies Required
Effective PO processing professionals require a mix of technical and soft skills:
Attention to Detail: Ensures accurate data entry, correct invoice matching, and error-free approvals.
Analytical Thinking: Identifies discrepancies, evaluates procurement options, and monitors spending patterns.
Communication Skills: Facilitates smooth collaboration between procurement, finance, and vendors.
Technological Proficiency: Uses ERP systems, digital procurement platforms, and AI-powered automation tools efficiently.
Compliance Awareness: Understands internal policies, regulatory requirements, and audit standards.
Why Clear Roles Matter
Clearly defined PO responsibilities prevent bottlenecks, minimize errors, and improve organizational efficiency. Employees understand their part in the workflow, accountability is reinforced, and approval and payment delays are drastically reduced. Digital platforms amplify these benefits, automating repetitive tasks while allowing staff to focus on strategic insights such as spend analysis, supplier performance evaluation, and procurement optimization.
In a nutshell, processing purchase orders is a structured workflow that requires precision, collaboration, and accountability. Ultimately by defining key roles, assigning responsibilities, and leveraging digital tools, organizations can ensure compliance, streamline procurement, reduce errors, and free up staff to focus on higher-value financial and operational analysis. A well-managed PO workflow supports both day-to-day operations and long-term strategic decision-making, making it a cornerstone of efficient, modern finance and procurement management.
Sample Job Description: Purchase Order Processor
A Purchase Order (PO) Processor plays a critical role in ensuring that procurement and finance workflows run smoothly and efficiently. This position bridges the gap between internal teams and external suppliers, guaranteeing that orders are accurate, approved, and executed on time.
Core Duties
Accept, Review, and Validate PO Requests: Review purchase requisitions submitted by internal clients to ensure completeness, accuracy, and compliance with budget and company policies. Verify quantities, item descriptions, vendor details, and required delivery dates before initiating the approval process.
Route POs for Approval and Resolve Holds: Send POs through multi-level approval workflows and promptly address any issues or holds with requesters or managers. This ensures timely authorization and avoids delays in procurement.
Issue POs to Suppliers and Confirm Acknowledgment: Generate and dispatch approved purchase orders to suppliers through email, vendor portals, or integrated ERP systems. Follow up to confirm order acceptance and expected delivery timelines.
Support Accounts Payable (AP): Collaborate with the AP team to match POs against invoices and receipts. Investigate and resolve discrepancies, ensuring accurate and timely payment processing.
Collaborate with Vendors and Internal Teams: Maintain regular communication with suppliers, procurement, and department leads to address issues, clarify requirements, and optimize the procurement process.
Skills Required
Procurement System Proficiency: Comfortable using procurement platforms, ERP systems, or AI-powered automation tools for purchase order management.
Attention to Detail: Ensures that all POs are accurate and compliant, reducing errors and mitigating risk.
Communication & Stakeholder Management: Strong ability to coordinate with internal teams, managers, and external vendors effectively.
Analytical & Data Entry Skills: Proficient in Excel or ERP data management; capable of adapting to automated PO workflows and leveraging technology for efficiency.
The PO Processor role is administrative AND strategic. Ensuring accuracy, compliance, and timely execution is crucial and the processor has to contribute to cost control, operational efficiency, and supplier satisfaction. Modern organizations increasingly rely on automation to streamline these tasks, allowing PO Processors to focus on higher-value analysis, collaboration, and continuous process improvement.
Advanced Roles via Automation
AI-powered procurement platforms are transforming the traditional Purchase Order (PO) Processor role from administrative tasks into strategic, high-value responsibilities. Automation allows teams to focus on analysis, compliance, and operational optimization rather than manual processing.
Key ways automation enhances the PO processor role:
Exception Management:
Automatically flag blocked invoices, mismatched receipts, or policy violations
Prioritize high-impact issues for faster resolution
Reduce manual investigation time and improve accuracy
Supplier Analytics:
Aggregate data across POs, invoices, and supplier performance
Monitor delivery reliability, pricing trends, and contract compliance
Identify opportunities for supplier negotiation and process optimization
Compliance Monitoring:
Leverage dashboards and real-time reports for instant visibility
Track approval cycle times, budget adherence, and policy compliance
Ensure audit readiness with minimal manual effort
Driving Digital Transformation:
Reduce repetitive, low-value manual tasks through AI automation
Free up time for strategic initiatives like spend analysis and cross-department collaboration
Align day-to-day procurement activities with broader business goals
Benefits of AI-enhanced PO processing:
Faster resolution of discrepancies and exceptions
Improved supplier relationships and performance insights
Enhanced governance and audit readiness
Strategic focus for finance and procurement teams
Data-driven decision-making capabilities
Adopting AI-powered tools, organizations can shift the PO processor role from transactional execution to strategic stewardship of procurement operations. Teams are empowered to act proactively, optimize workflows, and contribute to cost savings, compliance, and overall business growth.
Automation transforms PO processors into strategic partners, providing higher efficiency, actionable insights, and a direct impact on organizational success.
Risks and Downsides of Manual vs. Automated PO Processing
While purchase order (PO) processing is essential for controlling costs and maintaining compliance, the approach organizations take can dramatically affect efficiency, accuracy, and financial oversight. Manual PO processing, in particular, carries a number of risks that can impact both day-to-day operations and long-term strategic outcomes.
Manual Risks
Errors in Coding, Quantity, and Price:
Manual entry increases the likelihood of mistakes in key fields such as account codes, item quantities, or unit prices. These errors can lead to incorrect payments, misallocated budgets, and disputes with suppliers. Even small mistakes can compound across multiple orders, creating significant operational and financial headaches.Delays in Approvals and Payment:
Paper-based or spreadsheet workflows require human routing and follow-up. Approvers may be unavailable, documents can get lost, and requests may sit in inboxes for days. Such delays can slow procurement, disrupt supply chains, and negatively affect vendor relationships.Fraud and Duplicate Payments:
Without automated checks, organizations are more vulnerable to fraudulent invoices or duplicate payments. Manual reconciliation often fails to catch subtle discrepancies, leaving the company exposed to financial risk and compliance issues.Lack of Real-Time Spend Visibility:
Manual processes make it difficult to track approved and pending purchases in real time. Finance teams may struggle to see where money is committed, forecast cash flow accurately, or identify overspending trends. This opacity reduces decision-making agility and limits opportunities for strategic cost management.
Industry Insights: Deloitte states that non-automated PO workflows are most vulnerable during audits.
Automated PO processing
By contrast, automated PO processing mitigates these risks by:
Validating entries in real time
Routing approvals instantly
Flagging duplicates and exceptions
Providing dashboards with live spend visibility
Hyperbots Platform: Revolutionizing How to Process Purchase Orders
The Hyperbots platform is redefining how organizations manage purchase orders, moving beyond traditional administrative workflows to a fully automated, intelligent, and collaborative procurement process. By leveraging AI-powered automation, Hyperbots helps finance and procurement teams save time, reduce errors, and focus on strategic value creation.
The Hyperbots Advantage
Automated PR-to-PO, Validation, and Approval:
Hyperbots’ Procurement Co-Pilot automates the entire journey from purchase requisition to purchase order. Requisitions are automatically validated against budgets, compliance rules, and vendor policies. Approval workflows are routed instantly to the right managers or finance personnel. This end-to-end automation can shrink PO cycle times by up to 80%, freeing teams from repetitive administrative work and accelerating procurement.Human-in-the-Loop for Exceptions:
While automation handles routine transactions, Hyperbots’ Human-in-the-Loop system ensures complex or unusual cases are flagged for human review. This balances efficiency with accuracy, allowing finance and procurement professionals to focus on high-impact decisions while maintaining governance over exceptions and policy violations.Vendor and AP Collaboration:
With the Vendor Management Co-Pilot, Hyperbots facilitates seamless collaboration between organizations, suppliers, and accounts payable teams. Vendors can receive POs automatically, confirm deliveries, submit invoices, and communicate updates—all within the platform. AP teams can match invoices to POs and receipts efficiently, reducing errors, disputes, and payment delays.Comprehensive Real-Time Analytics and Audit Trails:
Hyperbots provides dashboards and intelligence elements that offer a real-time view of procurement operations. Teams can track approvals, monitor budget adherence, analyze supplier performance, and maintain audit-ready records. Automated logging ensures compliance while giving finance leaders actionable insights to optimize spend and improve operational efficiency.Deep ERP Integrations:
Hyperbots integrates seamlessly with existing ERP systems, enabling accurate GL coding, automated payments, and compliance tracking. Transactions flow automatically into financial ledgers, reducing manual entry errors and providing a single source of truth across procurement and finance.
A combination of AI-driven automation, intelligent human oversight, and deep system integration, Hyperbots transforms purchase order processing from a time-consuming administrative task into a value-generating workflow. Organizations can now process POs faster, ensure compliance, collaborate effectively with vendors, and gain actionable insights—all while reducing operational risk and administrative burden.
ROI and Benefits of Hyperbots' Automated PO Processing
When finance leaders evaluate purchase order automation, the first question is simple: what’s the ROI? With Hyperbots, the answer is both measurable and transformative. The platform delivers savings you can quantify in hard dollars, along with intangible benefits that reshape how procurement and finance teams work.
Implementing Hyperbots' Procurement copilot deliver significant ROI and transforms procurement operations by providing:
Over 80% reduction in PO creation & dispatch time
5 minute PR creation time
At least a 10% reduction in cash outflows
Accurate and timely automatic communication with vendors
100% automation of forms and other information verification
Granular and customized workflow for each process
Improved vendor relationships due to predictable approval timelines.
By leveraging AI-driven PO tracking, companies not only achieve quantifiable cost savings but also strengthen operational resilience and supplier collaboration. Hyperbots’ integrated platform ensures that these benefits scale across departments, projects, and business units, turning procurement into a high-value function rather than a bottleneck.
Industry Insights: Accenture advocates that multi-entity, global vendors gain the biggest ROI from digital procurement.
The dual impact of automated PO processing is measurable cost savings and error reduction, alongside intangible benefits like compliance, audit readiness, operational visibility, and employee empowerment. Together, these factors translate into higher efficiency, lower risk, and stronger strategic contributions from procurement and finance teams.
FAQs
Q1. How to process a purchase order from start to finish?
Start with a purchase requisition, validate and route approvals, auto-generate and share the PO, confirm receipt and quality, match invoice to delivery and PO, and push for payment using automated software.
Q2. What’s in a processing purchase orders job description today?
Prepare and review PRs, manage approval workflow, issue POs, collaborate with AP/vendors, monitor execution, and resolve exceptions—preferably leveraging AI tools.
Q3. How do you manage if a user is already processing purchase order tasks?
Modern systems like Hyperbots handle concurrent users, locking step-wise changes to avoid duplicates and offering real-time status visibility to every role.
Q4. What is the ROI of automating PO processing?
Time savings of 60–80%, reduced errors, and lower headcount for admin work, plus improved policy compliance and audit readiness.