The CFO’s Guide to Strategic Transformation through Purchase Order Automation
Beyond Cost Cutting: How CFOs Can Leverage PO Automation to Drive Financial Visibility, Ensure Compliance, and Transform Procurement from a Cost Center into a Strategic Growth Driver.

Introduction: The Modern CFO's Imperative
In today's rapidly evolving business landscape, CFOs are no longer just financial stewards—they're strategic architects driving organizational transformation. The role has expanded far beyond traditional financial reporting and budgeting to encompass digital transformation, operational excellence, and strategic value creation across the entire enterprise.
One of the most impactful yet often overlooked opportunities for strategic value creation lies in purchase order automation. While procurement may seem like an operational concern, the financial implications are profound: working capital optimization, cost reduction, risk mitigation, and enhanced strategic visibility into spending patterns.
This comprehensive guide explores how forward-thinking CFOs are leveraging automated PO systems to unlock operational efficiency, enhance compliance, and drive measurable business outcomes. Whether you're considering your first automation initiative or looking to optimize existing systems, this guide provides the strategic framework and practical insights needed to drive successful transformation.
The Strategic Case for Purchase Order Automation
The Hidden Costs of Manual Procurement
Traditional purchase order processes are plagued with inefficiencies that extend far beyond the obvious time delays. Manual data entry errors lead to payment discrepancies, approval bottlenecks create supplier relationship friction, limited visibility hampers strategic decision-making, and compliance gaps expose organizations to regulatory and fraud risks.
Consider the typical manual PO process: requisition forms circulate via email, approvers are unavailable causing delays, data is manually entered into multiple systems, matching invoices to POs requires manual comparison, and exceptions consume disproportionate staff time. Each of these steps represents not just inefficiency, but opportunity cost—resources that could be deployed on higher-value strategic activities.
For CFOs seeking to optimize working capital, reduce operational costs, and strengthen internal controls, purchase order automation represents a strategic lever that delivers both immediate and long-term value. The question is no longer whether to automate, but how to do so strategically to maximize business impact.
The AI Revolution in Purchase Order Processing
Modern AI-powered purchase order processing is revolutionizing how organizations manage procurement workflows. Artificial intelligence brings capabilities that go far beyond simple automation of repetitive tasks.
AI-driven systems can intelligently extract data from purchase requisitions regardless of format, predict potential bottlenecks before they occur, recommend optimal approval workflows based on historical patterns, identify anomalies that may indicate errors or fraud, and continuously learn and improve from each transaction processed.
By automating routine tasks and leveraging intelligent algorithms, companies can process orders faster, more accurately, and with greater strategic insight than ever before. The technology has matured to the point where implementation timelines have shortened dramatically and ROI can often be achieved within the first year.
Building the Business Case: Measuring ROI and Success Metrics
Establishing Your Measurement Framework
Before embarking on any automation initiative, CFOs must establish clear metrics and expected outcomes. A robust measurement framework serves multiple purposes: it justifies the initial investment, tracks implementation progress, identifies optimization opportunities, demonstrates value to stakeholders, and guides continuous improvement efforts.
Understanding the financial impact of procurement automation requires a structured approach to measurement and evaluation. The most successful implementations begin with baseline measurements of current-state performance, followed by clearly defined targets for improvement.
Key Performance Indicators for Procurement Automation
Key metrics and KPIs for measuring ROI in procurement automation should encompass both efficiency and effectiveness dimensions.
Efficiency Metrics:
Cycle Time Reduction: Measure the time from requisition submission to PO issuance. Leading organizations achieve 60-80% reductions in cycle time through automation.
Cost Per Transaction: Calculate the fully-loaded cost of processing each purchase order, including labor, technology, and overhead. Automation typically reduces per-transaction costs by 40-70%.
Processing Capacity: Track how many POs your team can handle without adding headcount. Automation dramatically increases throughput without proportional cost increases.
Effectiveness Metrics:
Error Rate Improvements: Monitor data entry errors, duplicate orders, and matching exceptions. Automated systems typically achieve 95%+ accuracy rates.
Compliance Adherence: Track policy violations, approval bypasses, and audit findings. Automated workflows enforce compliance by design.
Supplier Satisfaction Scores: Measure supplier feedback on your procurement processes. Faster, more reliable PO processing improves supplier relationships and may unlock better terms.
Strategic Metrics:
Contract Compliance: Monitor purchases made against established contracts versus maverick spending.
Spend Visibility: Measure your ability to analyze spending patterns and identify optimization opportunities.
Working Capital Optimization: Track improvements in payment timing and early payment discount capture.
When building your business case, consider both tangible benefits (cost savings, reduced headcount requirements, fewer errors) and intangible advantages (improved supplier relationships, enhanced decision-making capabilities, greater employee satisfaction). The most compelling business cases quantify both dimensions and demonstrate how automation enables strategic initiatives that would otherwise be impossible.
Risk Mitigation: Compliance and Fraud Prevention
The CFO's Risk Management Imperative
For CFOs, risk management is paramount. In an era of increasing regulatory scrutiny, supply chain complexity, and sophisticated fraud schemes, purchase order automation offers significant advantages in both regulatory compliance and fraud prevention—two critical concerns that keep finance leaders awake at night.
The financial and reputational costs of compliance failures or fraud incidents can be devastating. Regulatory fines, audit failures, supplier disputes, and internal control weaknesses all represent existential risks that demand proactive mitigation strategies.
Ensuring Regulatory Compliance
Automated systems create comprehensive audit trails, enforce approval workflows, and ensure policy adherence across all procurement activities. Unlike manual processes that rely on individual diligence and are prone to shortcuts, automated systems enforce compliance consistently without exception.
How automated POs ensure regulatory compliance demonstrates the power of technology in maintaining consistent compliance with industry regulations, tax requirements, and internal policies. The system becomes your always-on compliance officer, never taking shortcuts and never forgetting a control.
Key Automated Compliance Features:
Mandatory Field Validation: System won't allow incomplete or incorrect data to proceed, ensuring data quality and completeness from the start.
Automated Policy Enforcement: Spending limits, approval hierarchies, and vendor restrictions are enforced systematically, eliminating the possibility of circumvention.
Real-Time Alerts: Stakeholders receive immediate notifications of threshold violations, policy exceptions, or unusual patterns requiring attention.
Comprehensive Documentation: Every action is logged with user identification, timestamp, and rationale, creating an immutable audit trail for regulatory reviews.
Segregation of Duties: System controls prevent the same individual from both creating and approving orders, a fundamental internal control requirement.
The compliance benefits extend beyond avoiding penalties. Organizations with robust automated controls often negotiate better insurance rates, face less intensive audits, and enjoy stronger reputations with regulators and stakeholders.
Minimizing Fraud Risk
Procurement fraud represents a significant financial risk for organizations of all sizes. The Association of Certified Fraud Examiners estimates that organizations lose 5% of revenue to fraud annually. Common procurement fraud schemes include duplicate payments, fictitious vendors, unauthorized purchases, kickback arrangements, and invoice manipulation.
Minimizing fraud risk with purchase order automation should be a top priority for every CFO. Automated systems implement multiple fraud prevention mechanisms that work in concert to detect and prevent fraudulent activities.
Advanced Fraud Prevention Capabilities:
Three-Way Matching: Automated reconciliation of purchase orders, receiving documents, and invoices identifies discrepancies that may indicate fraud or error.
Duplicate Detection Algorithms: Sophisticated algorithms identify potential duplicate payments based on multiple data points, not just invoice numbers.
Vendor Validation Protocols: Automated verification of vendor information against external databases prevents payment to fictitious entities.
Anomaly Detection: Machine learning models identify unusual patterns such as unusually high prices, suspicious vendor relationships, or abnormal purchasing behaviors.
Spend Analytics: Continuous monitoring of spending patterns reveals statistical outliers that warrant investigation.
The beauty of automated fraud prevention is that it operates continuously and consistently. While manual controls depend on individual vigilance that can be overwhelmed or circumvented, automated systems never tire, never miss patterns, and never look the other way.
Technical Implementation: Integration and Infrastructure
Building the Right Foundation
Successful automation requires seamless integration with existing financial systems and a robust technical architecture that can scale with your organization's growth. The technical foundation of your procurement automation strategy will determine its long-term success, adaptability, and total cost of ownership.
Many automation initiatives fail not because of the technology itself, but because of poor integration planning, inadequate change management, or inflexible architectures that can't adapt to evolving business needs. CFOs must ensure their technology teams approach implementation strategically, with an eye toward both immediate needs and future flexibility.
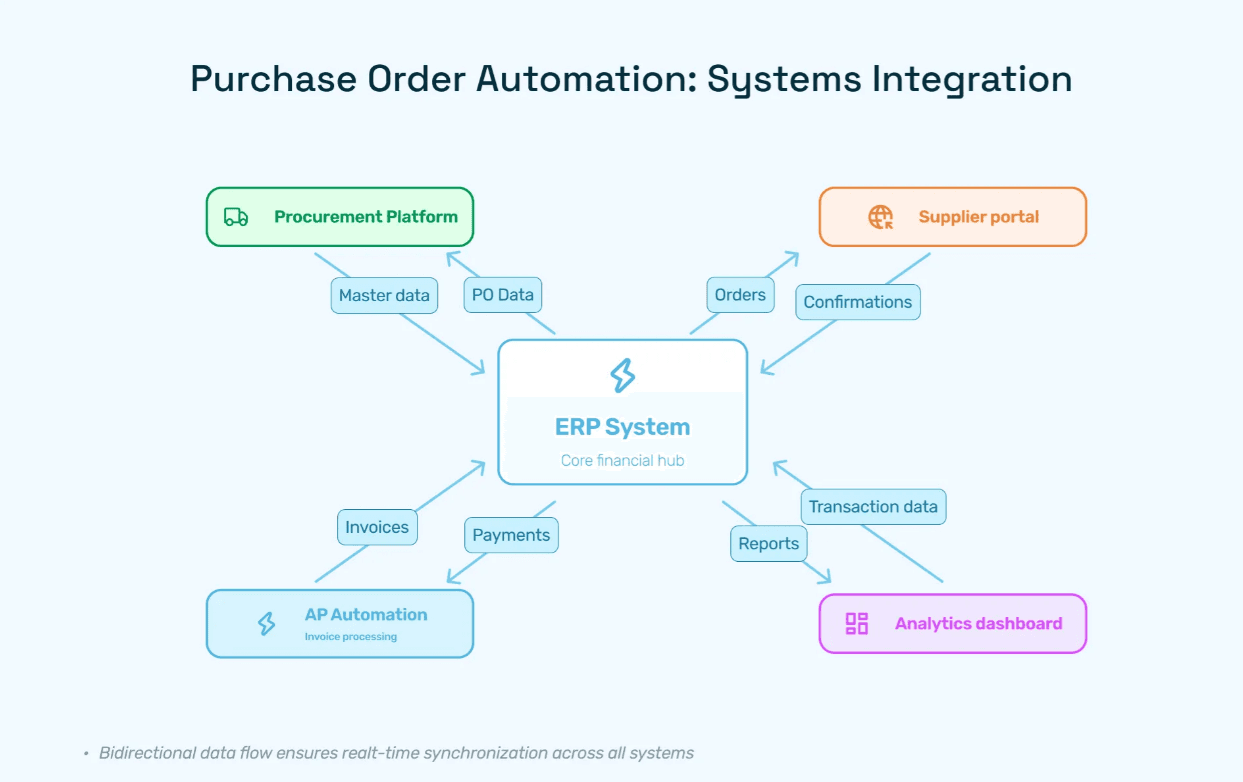
ERP Integration: The Critical Connection
Most organizations already have significant investments in ERP systems—SAP, Oracle, Microsoft Dynamics, NetSuite, or industry-specific platforms. These systems serve as the financial system of record and contain critical master data for vendors, general ledger accounts, cost centers, and more.
The key to successful automation is ensuring your new procurement solution works harmoniously with your existing infrastructure. A poorly integrated system creates data silos, requires duplicate entry, and ultimately undermines the efficiency gains automation promises.
Integrating purchase order automation with ERP systems requires careful planning across multiple dimensions: data mapping and transformation, authentication and security protocols, real-time versus batch synchronization, error handling and exception management, and master data governance.
Critical Integration Considerations:
Bidirectional Data Flow: Ensure vendor master data, GL codes, and cost centers flow from ERP to procurement system, while PO data, commitments, and accruals flow back to the ERP.
Real-Time Visibility: Modern integrations provide real-time or near-real-time synchronization, ensuring all systems reflect current state and enabling timely decision-making.
Data Consistency: Implement validation rules that ensure data meets both systems' requirements, preventing failed transactions and data quality issues.
Change Management: Recognize that integration isn't just technical—it requires process alignment and stakeholder coordination across finance, procurement, and IT.
Modern integration approaches leverage APIs, middleware platforms like MuleSoft or Dell Boomi, and cloud-based connectors to create seamless data flows between systems. The best implementations are invisible to users—they simply see one cohesive system rather than multiple disconnected applications.
Proper integration ensures data consistency, eliminates duplicate entry, provides real-time visibility across the entire procure-to-pay process, and maximizes user adoption by providing a seamless experience.
API-First Architecture: Building for the Future
As organizations adopt increasingly complex technology ecosystems—best-of-breed applications, cloud services, mobile apps, and emerging technologies—the flexibility of your procurement platform becomes critical. An API-first approach provides the agility needed to adapt to changing business requirements and integrate with emerging technologies.
API-first procurement automation platforms offer superior flexibility, faster implementation timelines, and easier customization compared to traditional monolithic systems. This architectural approach enables CFOs to build best-of-breed technology stacks tailored to their specific organizational needs.
Advantages of API-First Architecture:
Faster Integration: Pre-built APIs dramatically reduce integration timelines from months to weeks or even days.
Greater Flexibility: Connect with any system that supports modern API standards, not just pre-built connectors.
Future-Proofing: Easily add new capabilities or swap out components as technology evolves without wholesale system replacement.
Innovation Enablement: Experiment with emerging technologies like AI, blockchain, or IoT without disrupting core systems.
Lower Total Cost of Ownership: Reduce custom development and ongoing maintenance costs through standardized interfaces.
For CFOs thinking strategically about technology investments, API-first architecture represents a shift from rigid, monolithic systems to flexible, composable architectures that can evolve with the business. This approach protects technology investments while enabling continuous innovation.
Industry-Specific Applications
Tailoring Automation to Your Sector
While the benefits of purchase order automation are universal—efficiency, accuracy, compliance, visibility—implementation approaches and priorities vary significantly across industries. Understanding sector-specific considerations ensures your automation strategy addresses the unique challenges of your business and delivers maximum value.
Industry-specific factors include regulatory requirements, supply chain complexity, product characteristics, competitive dynamics, and organizational culture. The most successful automation initiatives recognize these differences and tailor their approach accordingly.
Manufacturing Sector: Managing Complexity at Scale
Manufacturing organizations face unique procurement challenges that make automation particularly valuable. Complex bill-of-materials management requires coordinating hundreds or thousands of components. Just-in-time inventory requirements demand precise timing and reliability. Intricate supplier networks span multiple tiers and geographies. Production schedule volatility creates demand fluctuations that ripple through the supply chain.
Purchase order automation in manufacturing addresses these challenges through specialized capabilities designed for manufacturing complexity.
Manufacturing-Specific Automation Benefits:
BOM Integration: Automated conversion of production schedules and BOMs into component-level purchase requisitions, ensuring nothing is forgotten.
Supplier Collaboration: Direct integration with supplier systems enables real-time inventory visibility, automated replenishment, and collaborative planning.
Quality Management: Link PO specifications with incoming inspection requirements and automatically route non-conforming materials.
Engineering Change Management: Propagate design changes through the procurement system to ensure suppliers are producing to current specifications.
Total Cost Visibility: Track not just purchase price but landed costs including freight, duties, quality costs, and working capital implications.
For manufacturing CFOs, procurement automation isn't just about efficiency—it's about production reliability, inventory optimization, and ultimately, customer satisfaction. Delays or errors in procurement can halt production lines, miss customer commitments, and damage hard-won reputations.
Healthcare Sector: Balancing Cost, Compliance, and Patient Care
Healthcare organizations operate in one of the most highly regulated industries while facing intense pressure to control costs. The procurement challenges are unique: life-critical supplies requiring absolute reliability, stringent FDA and regulatory requirements, complex Group Purchasing Organization (GPO) contracts, high-value capital equipment, and diverse stakeholder needs from clinical to administrative staff.
How healthcare companies use automated POs demonstrates the transformative impact of automation in this critical sector.
Healthcare-Specific Automation Capabilities:
Regulatory Compliance: Automated tracking of FDA approvals, lot numbers, expiration dates, and recall management ensures patient safety and regulatory compliance.
Clinical Integration: Connect procurement with clinical systems so physicians can order directly from approved formularies and preference cards.
Contract Optimization: Automatically route purchases to preferred vendors and GPO contracts, capturing maximum savings while tracking contract compliance.
Supply Chain Visibility: Real-time visibility into inventory levels, par locations, and usage patterns enables better planning and cost management.
Emergency Procurement: Streamlined expedited approval workflows for urgent clinical needs without compromising necessary controls.
Healthcare CFOs must balance competing priorities: reducing supply costs (often the second-largest expense after labor), ensuring clinical quality and patient safety, maintaining regulatory compliance, and supporting clinician productivity and satisfaction. Purchase order automation provides the control and visibility needed to optimize across all these dimensions simultaneously.
The stakes in healthcare procurement are higher than in most industries—the right supplies in the right place at the right time can literally be a matter of life and death. Automation removes human error and delays from this critical process.
Implementation Roadmap: From Strategy to Success
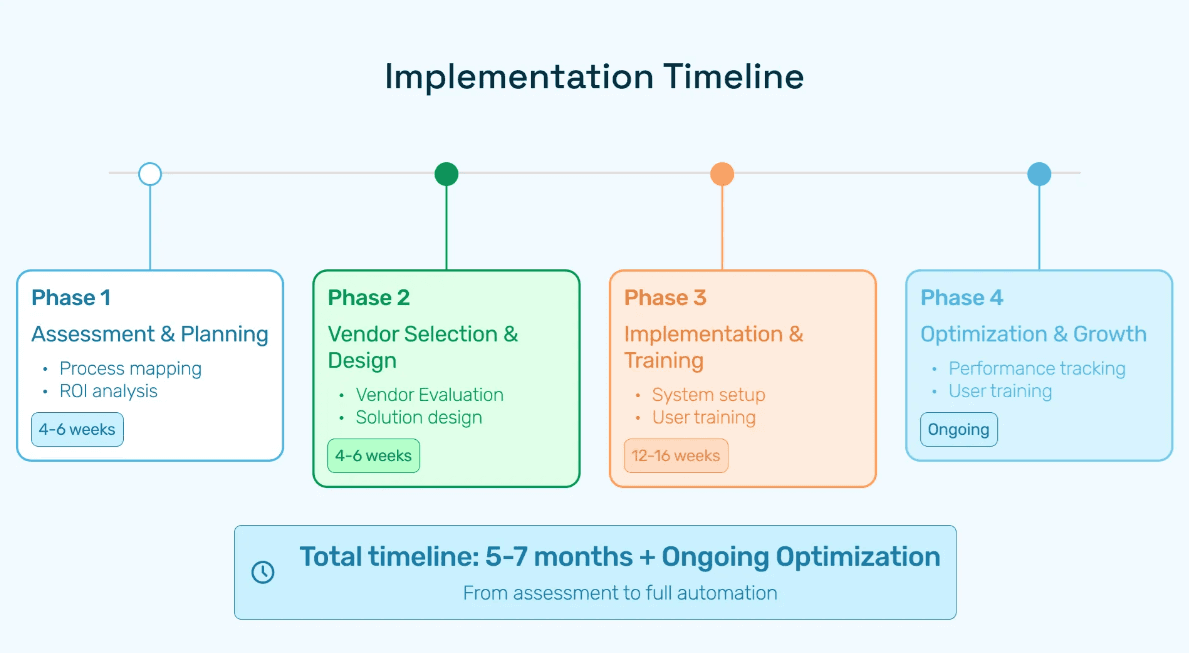
Phase 1: Assessment and Planning
Successful automation begins with thorough assessment of current state, clear articulation of desired outcomes, and realistic planning for the journey ahead. This foundational phase determines whether your initiative delivers transformational value or becomes another disappointing technology investment.
Key Activities:
Process Documentation: Map current procurement workflows including all touchpoints, approval paths, exceptions, and pain points.
Stakeholder Engagement: Interview users across procurement, finance, operations, and business units to understand diverse needs and concerns.
Data Readiness Assessment: Evaluate the quality and completeness of master data that will feed your automated system.
Technology Landscape Review: Document current systems, integration points, and technical constraints.
ROI Modeling: Develop detailed financial projections based on realistic assumptions and industry benchmarks.
Phase 2: Vendor Selection and Design
Choosing the right technology partner and designing your solution architecture are critical decisions with long-term implications. Look beyond sales presentations to understand true capabilities, implementation approaches, and post-implementation support.
Selection Criteria:
Functional Fit: Does the solution handle your specific requirements without excessive customization?
Integration Capabilities: Can it integrate seamlessly with your existing systems using modern, standards-based approaches?
User Experience: Will your team actually want to use this system, or will adoption be a constant battle?
Scalability: Can the platform grow with your organization in transaction volume, complexity, and geographic scope?
Vendor Stability: Is this a vendor that will be supporting and enhancing the platform for years to come?
Phase 3: Implementation and Change Management
Technology implementation is only half the battle—successful adoption requires equal attention to change management, training, and organizational alignment.
Implementation Best Practices:
Phased Rollout: Start with a pilot in one business unit or category to prove value and refine before enterprise rollout.
Executive Sponsorship: Ensure visible, active support from finance leadership to signal importance and overcome resistance.
Comprehensive Training: Invest in role-based training that shows users not just how but why the new process benefits them.
Communication: Regular updates on progress, wins, and lessons learned maintain momentum and engagement.
Quick Wins: Identify and publicize early successes to build confidence and demonstrate value.
Phase 4: Optimization and Continuous Improvement
Automation is not a "set it and forget it" initiative. The most successful organizations continuously analyze performance, identify optimization opportunities, and evolve their processes to capture incremental value.
Optimization Focus Areas:
Workflow Refinement: Analyze approval patterns and cycle times to identify bottlenecks and streamline further.
Supplier Enablement: Work with key suppliers to connect their systems directly, enabling automated ordering and advanced collaboration.
Analytics and Insights: Leverage the rich data generated by automated systems to drive strategic sourcing decisions.
Policy Updates: Use exception reporting to identify policies that may need updating based on business changes.
Technology Evolution: Stay current with new features and capabilities released by your vendor to capture ongoing value.
The Strategic Advantage: Beyond Cost Savings
While cost reduction and efficiency gains typically justify automation investments, forward-thinking CFOs recognize that the strategic advantages extend far beyond these immediate benefits.
Enhanced Strategic Visibility
Automated systems generate rich data on spending patterns, supplier performance, category trends, and organizational behaviors. This data becomes a strategic asset enabling better decision-making across multiple dimensions: supplier rationalization and negotiation strategies, make-versus-buy decisions, working capital optimization, and risk identification and mitigation.
Organizational Agility
Automated processes are easier to change than manual ones. When business conditions shift—new markets, acquisitions, regulatory changes, or operational pivots—automated systems can be reconfigured quickly while manual processes require extensive retraining and behavioral change.
Talent Optimization
By automating routine transactional work, you free your finance and procurement teams to focus on strategic activities: supplier relationship management, category strategy development, contract negotiation, and process innovation. This shift not only delivers more value but also improves employee satisfaction and retention by providing more engaging work.
Competitive Advantage
In industries with thin margins or rapid change, procurement excellence can be a genuine competitive differentiator. Faster cycle times enable quicker response to market opportunities. Better supplier relationships unlock preferential treatment during shortages. Superior data and analytics enable smarter sourcing decisions. Lower procurement costs drop directly to the bottom line or fund investment in growth.
Conclusion: The CFO's Call to Action
Purchase order automation represents one of the highest-ROI transformation opportunities available to CFOs today. The technology is mature, implementation risks are manageable, and the benefits are substantial and measurable. Organizations that embrace procurement automation gain immediate efficiency and cost benefits while building strategic capabilities for the future.
The question for CFOs is not whether to automate purchase orders, but how quickly you can capture these benefits relative to your competitors. In an era where every efficiency gain matters and where strategic agility separates winners from losers, procurement automation has moved from "nice to have" to strategic imperative.
This guide has provided a comprehensive framework for approaching purchase order automation strategically—from building the business case through implementation to continuous optimization. The organizations that will benefit most are those that view automation not as a tactical IT project but as a strategic transformation initiative sponsored by finance leadership.
The journey begins with a clear-eyed assessment of where you are today, a compelling vision of where automation can take you, and the commitment to see the transformation through. The CFOs who act decisively will position their organizations for sustained competitive advantage in an increasingly digital and fast-paced business environment.
The time to begin your transformation is now. The strategic value is waiting to be unlocked.

