PO Documents Explained: What They Include and How to Create One
Learn the essential components of a Purchase Order (PO) and follow our step-by-step guide to create accurate, legally sound documents that streamline your procurement process.
Executive Summary
A PO Document (purchase order document) is the cornerstone of organizational procurement—a legally binding contract between a buyer and supplier that authorizes a transaction before goods or services are delivered. Despite its critical role in spend management, many mid-market finance teams still wrestle with manual PO creation, approval bottlenecks, and costly errors that drain operational budgets.
This comprehensive guide demystifies PO Documents from the ground up: what fields belong in a Purchase Order Document sample, how to structure compliant PO Doc workflows, and why AI-powered procurement automation now delivers cost reductions. Whether you're a CFO seeking tighter spend visibility or a Procurement Head battling approval delays, you'll discover actionable blueprints to transform your purchase order process into a strategic advantage.
Key Takeaways:
Understand the 12 essential components every PO Document must contain for legal and audit compliance
Learn step-by-step methodologies to create purchase orders manually and through automated systems
Explore how Hyperbots Procurement Co-Pilot slashes requisition-to-PO cycle
Discover differentiated AI capabilities that position Hyperbots as the industry leader in purchase order automation
What Is a PO Document?
A PO Document, formally known as a purchase order, is a commercial instrument issued by a buyer to a vendor that specifies product types, quantities, agreed prices, and delivery terms. Once accepted by the supplier, it becomes a legally enforceable contract governing the transaction.
Unlike informal purchase requests or vendor quotes, a properly executed PO Doc creates mutual obligations: the buyer commits to payment upon satisfactory delivery, while the vendor guarantees fulfillment per agreed specifications. This bilateral commitment makes the purchase order the single most important control mechanism in accounts payable—organizations that skip POs or use incomplete templates face 23% higher maverick spend according to Deloitte procurement research.
For finance leaders, PO Document provides three mission-critical benefits: preemptive budget validation, audit trail creation, and vendor dispute resolution. When invoices arrive without matching purchase orders, AP teams waste an average of 42 minutes per exception investigating approvals and verifying pricing—time that automated PO systems eliminate entirely.
Core Components of a PO Document
Every compliant Purchase Order Document sample contains standardized fields that serve legal, operational, and financial purposes. While formats vary by ERP system and industry, the following 12 elements form the universal foundation:
Buyer and Vendor Identification
Buyer Information: Complete legal name, billing address, and remittance details of the purchasing organization. This section must match your ERP master data to enable automated invoice reconciliation.
Vendor Information: Supplier legal name, payment address, tax identification number, and vendor master record ID. Discrepancies between PO vendor details and invoice headers trigger three-way match exceptions that delay payment cycles.
Purchase Order Number and Date
The PO number is a unique sequential identifier that anchors the entire procure-to-pay trail. Modern systems use alphanumeric schemes (e.g., PO-2025-089437) that embed fiscal year and department codes for streamlined reporting.
Issue Date: Documents the formal authorization timestamp. This date determines budget period allocation and starts supplier lead-time clocks. Organizations using AI-powered tracking systems report 94% on-time delivery improvements due to accurate date stamping.
Line Item Details
The heart of any PO Doc lies in its line-item grid, which must specify:
Description: Clear, unambiguous product or service names (avoid abbreviations that confuse vendors)
Quantity: Numeric units with measurement standards (each, lbs, hours)
Unit Price: Per-item cost in the transaction currency
Extended Price: Quantity × Unit Price (auto-calculated in digital systems)
Account Codes: GL strings for proper financial statement allocation
Gartner research reveals that 67% of invoice disputes stem from vague line-item descriptions. Precision at the PO stage prevents downstream conflicts.
Delivery Terms and Instructions
Ship-To Address: Physical delivery location if different from billing address. Multi-site organizations must validate addresses against ERP location masters to prevent mis-deliveries.
Delivery Date: Required receipt date that triggers vendor fulfillment SLAs. Hyperbots SLA monitoring automatically escalates late shipments 72 hours before deadlines.
Special Instructions: Packaging requirements, hazmat handling, or receiving dock protocols that ensure smooth goods receipt.
Payment Terms and Conditions
Standard payment terms (Net 30, 2/10 Net 30) define when invoices become due. Organizations leveraging AI-driven discount capture identify annual savings by optimizing early-pay offers embedded in PO terms.
Legal boilerplate covering warranties, dispute resolution, and compliance requirements protects both parties. While often overlooked, these clauses become critical during vendor performance failures or regulatory audits.
Tax and Total Amounts
Subtotal: Sum of all line-item extended prices before taxes
Tax Amount: Sales/use tax calculated per jurisdiction rules (see AI tax verification strategies)
Grand Total: Final payable amount that anchors budget consumption
Incorrect tax calculations on purchase orders create AP bottlenecks when invoices arrive with different amounts.
Approval Signatures and Timestamps
Digital or wet signatures from authorized approvers confirm budget holder consent. Modern PO Document embeds electronic timestamps and user IDs that satisfy SOX compliance requirements without paper trails.
Organizations using Hyperbots automated approval workflows eliminate signature chasing through policy-based routing that escalates stuck requests within two hours.
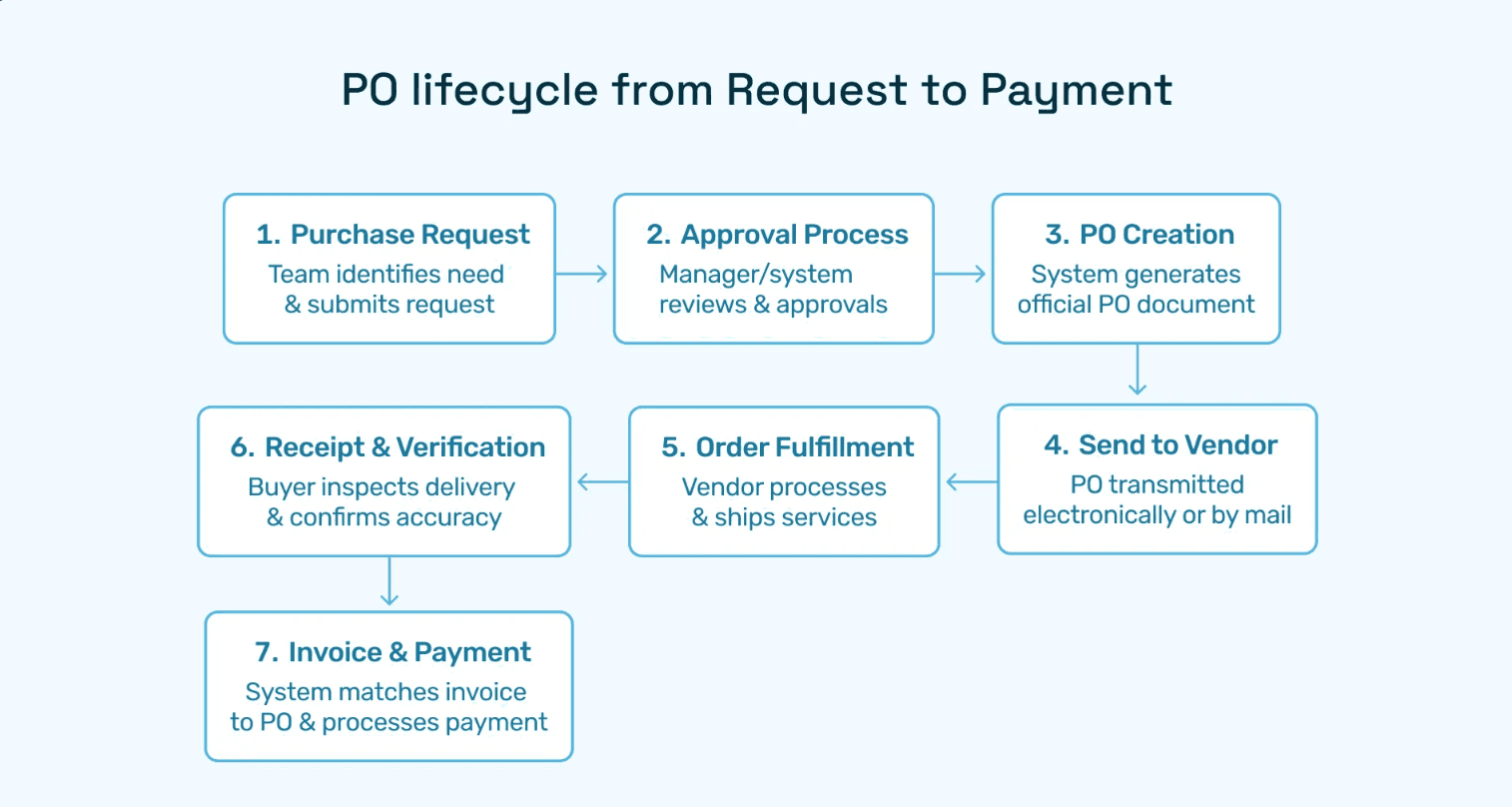
How to Create a PO Document: Step-by-Step Methodology
Manual Purchase Order Creation Process
For smaller organizations or one-off purchases, manual PO creation follows this sequence:
Step 1: Vendor Selection and Quote Validation Procurement teams evaluate vendor quotes against budget availability and contract terms. This stage consumes 3-5 days in organizations lacking centralized vendor catalogs.
Step 2: Template Population Users download Word or Excel templates and manually enter the 12 core components detailed above. Typographical errors at this stage cascade into invoice mismatches later.
Step 3: Approval Routing Printed POs circulate via email or interoffice mail to budget holders, department heads, and finance controllers. Average approval time: 7.2 business days per accounts payable benchmarking data.
Step 4: Distribution and Filing Approved POs are emailed to vendors while copies are filed in physical or shared-drive folders. Retrieval during invoice processing requires manual searches.
Step 5: ERP Entry Finance staff re-key approved PO data into accounting systems, introducing transcription errors in 14% of transactions.
This manual chain explains why mid-market companies average 12-day requisition-to-PO cycles and why 31% of purchase orders never match invoices cleanly on the first pass.
Automated Purchase Order Creation with Modern Systems
Digital PO automation collapses the five-step manual process into a seamless workflow:
Intake and Drafting: Requesters submit needs via mobile apps, email, or voice commands. Generative AI agents auto-draft POs by pulling vendor details from contract databases and validating GL codes against budget policies.
Intelligent Routing: System logic routes draft POs to appropriate approvers based on amount thresholds, commodity types, and department hierarchies. No manual forwarding required.
Instant ERP Sync: Approved POs write directly to NetSuite, SAP, or Dynamics without re-keying. The Hyperbots Procurement Co-Pilot achieves 99.8% data extraction accuracy through bi-directional API integration.
Vendor Portal Distribution: Suppliers receive POs via self-service portals where they acknowledge, request changes, or update ship dates—creating real-time visibility for procurement teams.
Touch-Free Matching: When invoices arrive, AI matching agents auto-reconcile against PO line items, flagging only true exceptions for human review.
Organizations implementing end-to-end automation report cycle time reductions and operational cost savings.
Purchase Order Document Sample and Templates
While comprehensive Purchase Order Document samples vary by ERP and industry, a best-practice template includes:
Header Section:
Company logo and legal name
PO number with barcode for scanning
Issue date and required delivery date
Buyer and vendor contact cards
Body Table:
Line | Desciption | Part# | Qty | UOM | Unit Price | Extended | GL Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
001 | Steel Sheet | SS304 | 500 | lbs | $8.50 | $4,250 | 51000-110 |
002 | Freight | N/A | 1 | lot | $320.00 | $320 | 51000-820 |
Footer Section:
Subtotal, tax breakdown, grand total
Payment terms and discount opportunities
Shipping instructions and delivery addresses
Authorized approver signatures with dates
Best Practices for Template Design:
Use clear fonts (Arial, Calibri) sized 10-12pt for readability
Include field labels in bold to guide manual completion
Add dropdown menus for common values in Excel templates
Embed calculation formulas for subtotals and taxes
Incorporate your company's standard legal terms
Organizations transitioning from paper to digital often start by converting existing Word templates to fillable PDFs before graduating to full ERP-integrated systems.
Common Challenges in PO Documents
Despite standardized formats, finance teams encounter persistent obstacles:
Approval Bottlenecks and Cycle Time Delays
The average purchase order touches 4.3 approvers and sits idle for 68 hours awaiting signatures. Vacation schedules, email overload, and unclear delegation policies compound delays that frustrate requesters and vendors alike.
Modern approval workflow automation solves this through policy-based routing, auto-escalation rules, and mobile approval capabilities that keep POs moving even when key stakeholders are traveling.
Maverick Spend and PO Bypassing
When requisition-to-PO processes feel cumbersome, employees circumvent controls by purchasing directly and submitting invoices post-facto. This "maverick spend" undermines budget visibility and negotiated contract terms.
Organizations deploying AI-powered intake systems make PO creation so frictionless (under 3 minutes) that bypass incentives evaporate. Hyperbots clients report reductions in non-PO invoices.
Template Inconsistencies Across Departments
Decentralized organizations often discover that different business units use incompatible PO formats, creating consolidation nightmares during audits. Legal terms vary, GL coding schemes diverge, and vendor data quality degrades.
Standardization via enterprise-wide digital PO workflows enforces consistent templates while allowing localized customization for unique commodity requirements.
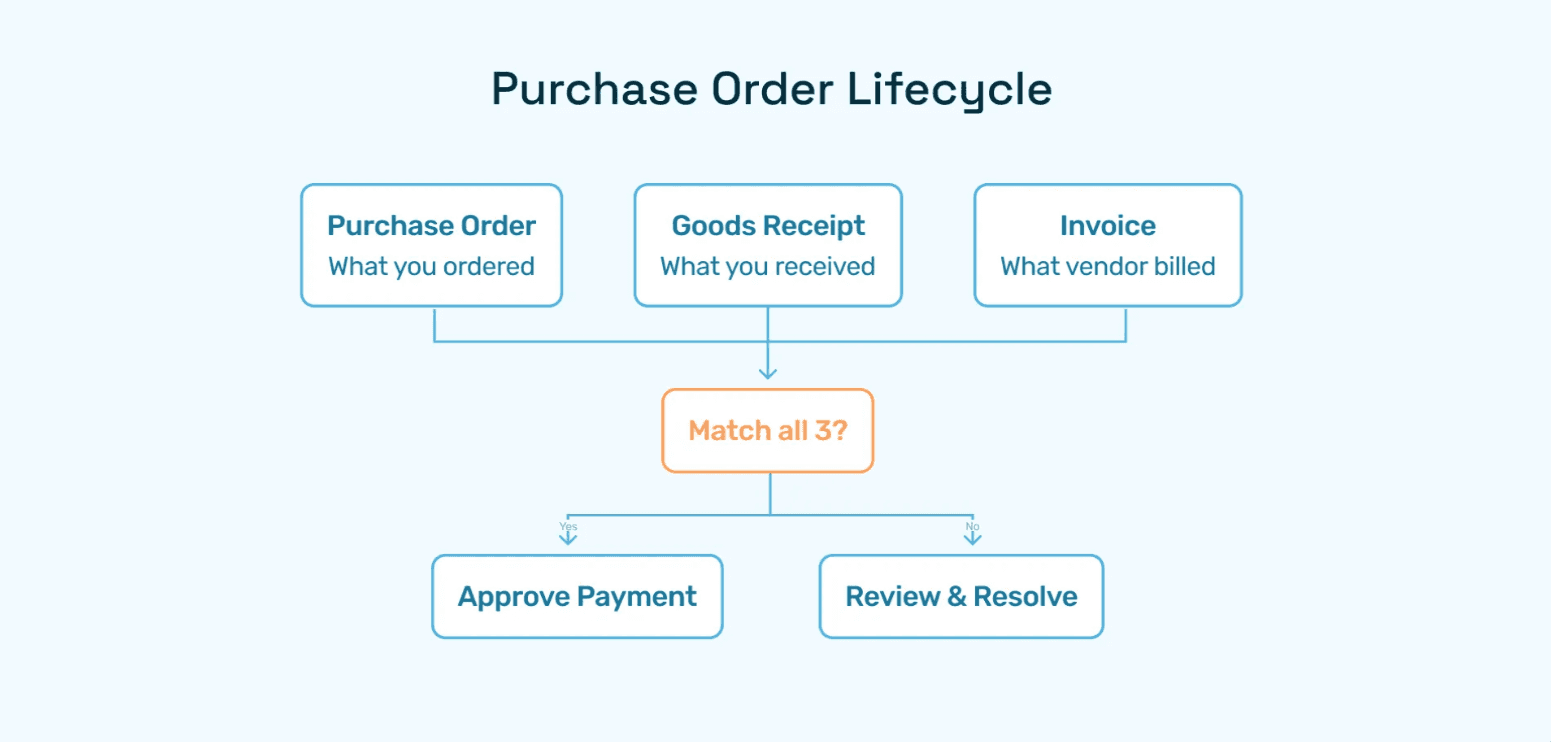
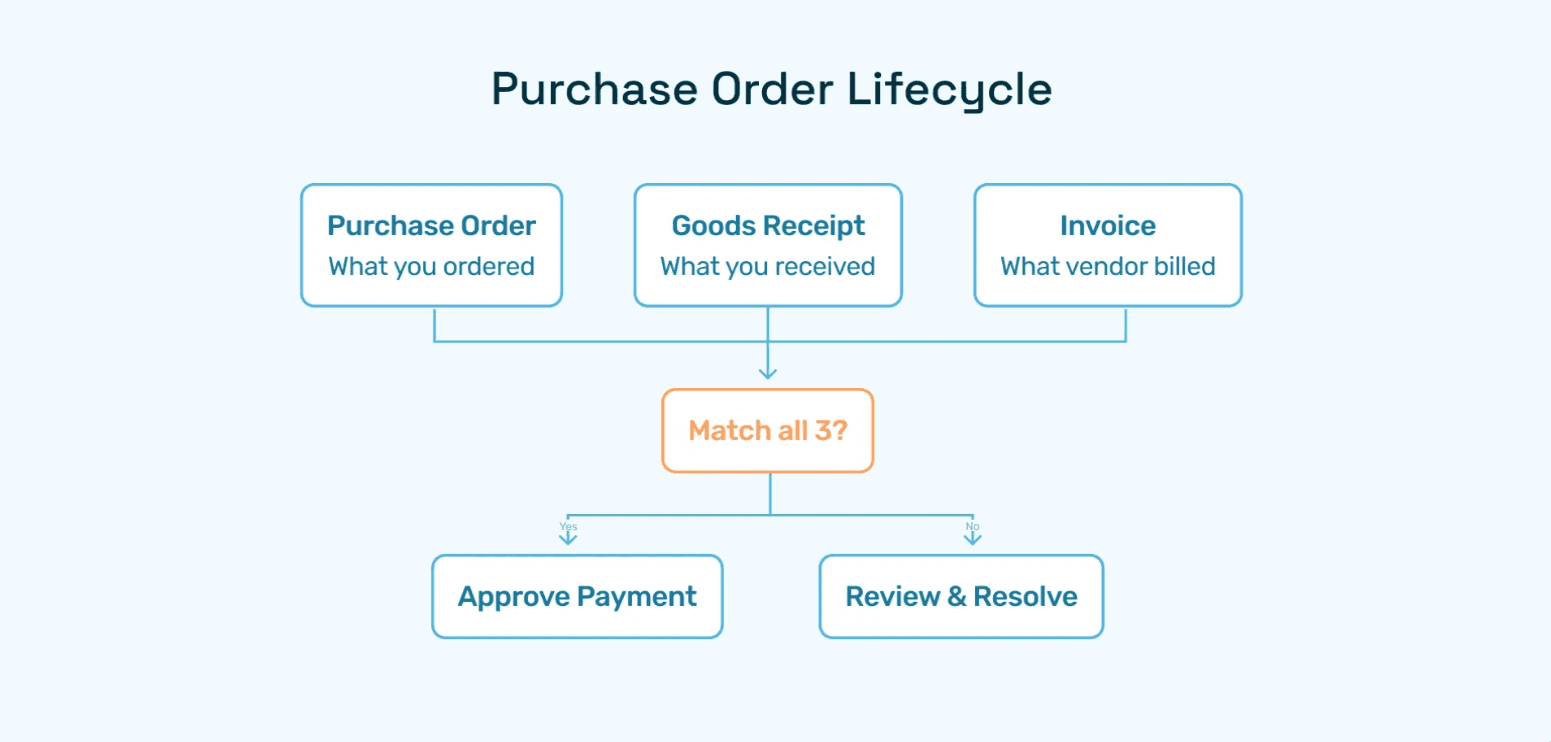
Three-Way Matching Failures
When invoices fail to match POs due to quantity variances, price discrepancies, or missing receipt confirmations, AP teams sink hours into exception resolution. Industry data shows that 43% of invoices require some form of manual intervention.
Hyperbots' Transformational Approach to Purchase Order Automation
The Procurement Co-Pilot Advantage
Hyperbots Procurement Co-Pilot redefines what's possible in PO Documents through agentic AI that doesn't just automate tasks—it makes intelligent decisions:
Instant Requisition Drafting: Users describe needs in plain English via email, Slack, or voice. The Co-Pilot generates complete purchase requisitions with accurate vendor selections, GL codes, and compliance checks under seconds.
Policy-Aware Routing: Machine learning models trained on your approval history route POs to the optimal approver based on commodity type, amount, department, and even current workload—eliminating routing errors that plague rule-based systems.
Real-Time ERP Synchronization: Bi-directional APIs keep NetSuite, SAP, Dynamics, Sage Intacct, and QuickBooks data in perfect sync. Budget availability checks happen in milliseconds, preventing overspend before POs are issued.
Proactive Exception Management: When vendors request changes or deliveries run late, the Co-Pilot auto-updates stakeholders and suggests mitigation strategies like expedited shipping or alternate sourcing.
Multi-Agent Orchestration for End-to-End Automation
Hyperbots stands apart through multi-agent collaboration architecture where specialized AI co-pilots work in concert:
Procurement Co-Pilot handles requisition-to-PO workflows
Invoice Processing Co-Pilot auto-matches incoming invoices against POs
Vendor Management Co-Pilot tracks supplier performance and negotiates terms
Payment Co-Pilot optimizes disbursement timing for discount capture
This coordinated ecosystem delivers true procure-to-pay automation that reduces human touchpoints while improving accuracy to 99.8%.
Differentiation from Traditional P2P Solutions
While legacy procurement platforms offer workflow automation, Hyperbots delivers agentic intelligence:
Traditional Systems:
Rule-based routing that breaks when exceptions occur
Manual data entry for non-catalog items
Separate logins for requisitioning, approval, and receiving
Limited learning from historical patterns
Hyperbots AI Advantage:
Autonomous decision-making within defined guardrails
Natural language interfaces that eliminate forms
Unified conversational UI across all procurement functions
Continuous learning that improves accuracy over time
Organizations migrating from Coupa, SAP Ariba, or Oracle Procurement Cloud to Hyperbots report 80% further efficiency gains beyond their previous automation investments.
Best Practices for Optimal PO Documents
Standardize Templates Enterprise-Wide
Mandate a single Purchase Order Document sample format across all business units to simplify vendor onboarding and audit preparation. Build configurability for division-specific legal terms or tax jurisdictions while preserving core data structure.
Enforce Mandatory Field Completion
Configure systems to reject incomplete POs missing critical elements like delivery dates, GL codes, or payment terms. Pre-submission validation prevents downstream exceptions.
Integrate Vendor Master Governance
Implement AI-assisted vendor onboarding that validates tax IDs, payment instructions, and W-9 documentation before allowing PO issuance. Centralized master data prevents duplicate vendor records that fragments spend on analytics.
Establish Clear Approval Thresholds
Document delegation of authority matrices showing which roles approve various PO amounts and commodity types. Publish these policies in employee handbooks and embed them in workflow automation logic.
Monitor and Audit Regularly
Schedule monthly reviews of PO aging reports, bypass transactions, and approval cycle times. Automated tracking dashboards highlight outliers requiring corrective action.
Transform Your Procurement Operations with Hyperbots
The PO Document has evolved from a paper formality to a strategic control mechanism that determines procurement efficiency, spend visibility, and supplier relationships. Organizations still wrestling with manual processes forfeit millions in operational costs, discount opportunities, and competitive agility.
Hyperbots Procurement Co-Pilot represents the next generation of purchase order automation—agentic AI that thinks, learns, and acts autonomously within your governance frameworks. Our clients achieve cost reductions, faster cycle times, 80% straight through invoice processing, and 99.8% data extraction accuracy while freeing finance teams to focus on strategic sourcing and supplier innovation.
Whether you're processing 100 or 100,000 purchase orders annually, our platform scales seamlessly while delivering consistent ROI.
Ready to eliminate approval bottlenecks, capture hidden savings, and give your CFO real-time spend visibility? Visit our Procurement Co-Pilot product page to explore interactive demos, or schedule a personalized assessment with our automation specialists. Transform PO Documents from a compliance burden into a competitive advantage—starting today.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: What's the difference between a purchase requisition and a PO document?
A: A purchase requisition is an internal request for approval to buy, while a PO Document is the external commitment sent to the vendor. Requisitions precede purchase orders in the procurement workflow.
Q2: Can we create purchase orders without an ERP system?
A: Yes, organizations use Excel templates, Word documents, or dedicated standalone PO software. However, lack of ERP integration requires manual invoice matching and limits spend visibility.
Q3: How long should we retain PO documents for compliance?
A: IRS guidelines require seven-year retention of purchase documentation supporting tax deductions. Industry-specific regulations (healthcare, defense) may mandate longer periods. Digital archiving simplifies compliance while reducing storage costs.
Q4: What happens if a vendor ships before receiving the PO?
A: Early shipments create receiving complications and invoice matching errors. Best practice: communicate PO numbers via email immediately after approval while formal documents are being finalized, or use vendor portals for instant electronic delivery.
Q5: How do we handle PO amendments after issuance?
A: Issue formal change orders that reference the original PO number and clearly specify modifications to quantity, price, or delivery terms. Automated PO management systems version-control amendments to maintain audit trails.
Q6: Should every purchase require a PO document?
A: Organizations typically exempt small-dollar transactions (under $500) and certain utility payments from PO requirements to reduce administrative burden. However, PO-less processing increases fraud risk and maverick spend.