Purchase Order Creation Process: A Complete Walkthrough for Finance Leaders
Step-by-step PO creation guide with workflows, best practices, and automation to simplify procurement and drive efficiency.

Executive Summary
The purchase order creation process is the backbone of effective procurement management and financial control. It transforms informal buying requests into documented, authorized commitments that protect organizations from unauthorized spending, vendor disputes, and compliance violations. For CFOs, controllers, and procurement leaders, understanding and optimizing this process is not merely operational housekeeping—it's a strategic imperative that directly impacts cash flow, supplier relationships, and audit readiness.
Yet many organizations struggle with inefficient PO creation workflows. Manual processes create bottlenecks, approval delays stall vendor relationships, and inconsistent documentation complicates financial reporting.
This comprehensive guide delivers a complete walkthrough of the purchase order creation process, from initial requisition through vendor acknowledgment and three-way matching. We'll explore each step in detail, examine best practices that leading organizations employ, identify common pitfalls that undermine efficiency, and demonstrate how modern automation platforms like Hyperbots are transforming PO creation from a manual burden into a streamlined, intelligent workflow.
Finance leaders who master the purchase order creation process gain critical advantages: faster procurement cycles, stronger financial controls, improved supplier relationships, and finance teams freed to focus on strategic analysis rather than administrative tasks. Whether you're implementing structured PO workflows for the first time or optimizing existing processes, this guide provides actionable insights to transform how your organization creates purchase orders.
What Is Purchase Order Creation?
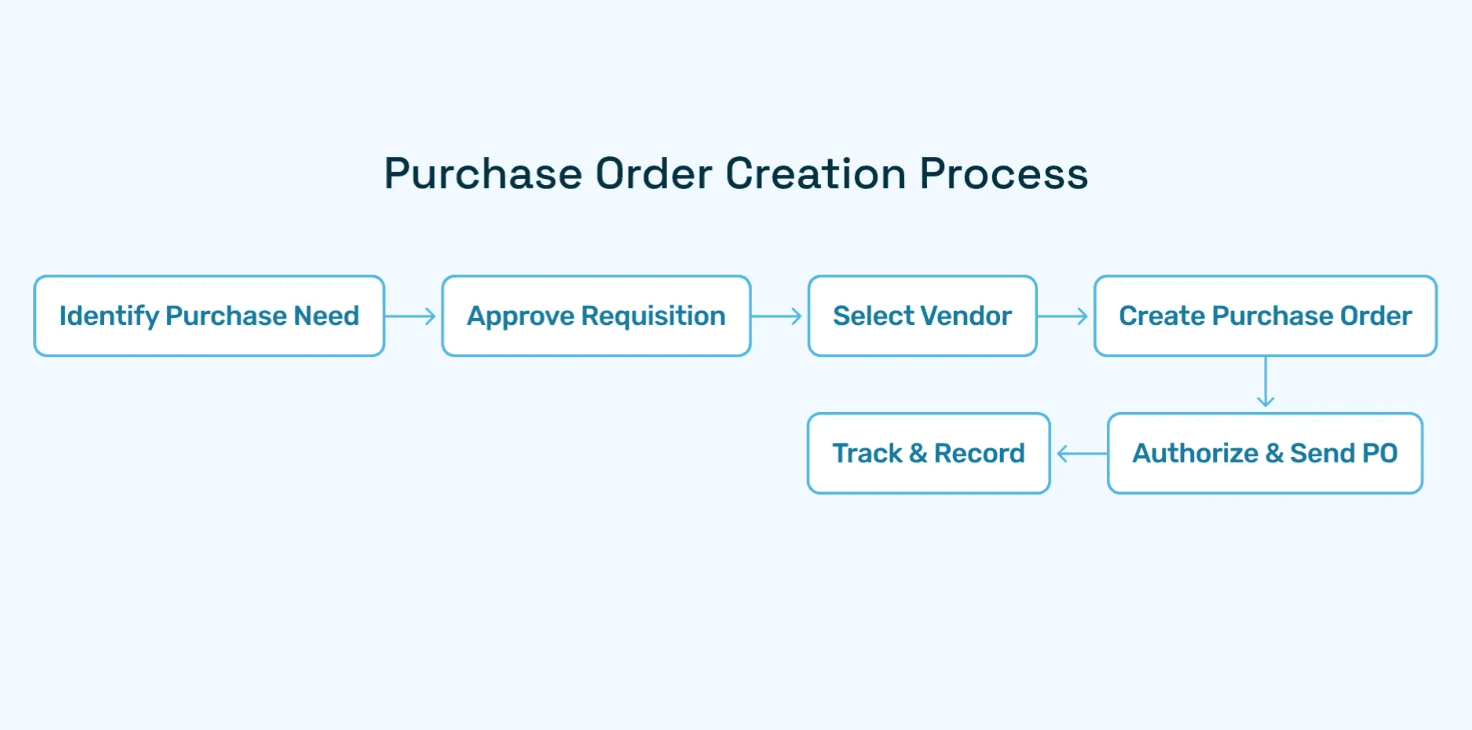
Purchase order creation is the systematic process of converting a business need for goods or services into a formal, documented commitment to a supplier. It encompasses the entire workflow from the moment someone identifies a purchase requirement through the transmission of an authorized purchase order to the vendor. This process sits at the critical intersection of procurement governance, financial control, and operational execution.
At its core, the PO creation process serves multiple essential functions:
Authorization and Control: It transforms informal requests into formally authorized commitments, ensuring that every purchase has appropriate approval before resources are committed. This prevents unauthorized spending and maintains budget discipline across the organization.
Documentation and Audit Trail: The creation process generates comprehensive documentation showing what was purchased, why, by whom, and under what authority. This audit trail supports financial reporting, tax compliance, and regulatory requirements.
Vendor Communication: A properly created PO provides suppliers with clear, unambiguous instructions about what to deliver, when, where, and under what terms. This clarity prevents disputes and strengthens vendor relationships.
Financial Planning: PO creation marks the moment when budget becomes committed spend. Tracking POs enables more accurate cash flow forecasting and working capital management than simply monitoring invoices and payments.
Risk Mitigation: Documented PO creation processes with appropriate controls reduce fraud risk, prevent duplicate payments, and ensure compliance with procurement policies and legal requirements.
Why must organizations document and standardize the PO creation process rather than relying on ad hoc buying? Informal procurement approaches create substantial risks:
Maverick Spending: Without structured creation processes, employees make unauthorized purchases outside negotiated contracts, losing volume discounts and negotiated terms
Budget Overruns: Undocumented commitments leave finance blind to outstanding obligations, making budget management reactive rather than proactive
Vendor Disputes: Unclear or inconsistent purchase terms lead to disagreements about pricing, delivery, or specifications
Compliance Failures: Regulatory frameworks like SOX require documented authorization of expenditures; informal processes create compliance gaps
Financial Reporting Issues: Without proper PO creation, accruals for period-end closes are guesswork rather than fact-based
Key Stakeholders in PO Creation
Effective purchase order creation involves coordination across multiple stakeholders, each playing distinct roles:
Procurement Team: The procurement function typically owns the PO creation process, ensuring consistency, compliance, and optimal terms. Procurement responsibilities include:
Maintaining relationships with approved vendors
Negotiating contracts and framework agreements
Creating POs based on requisitions or direct vendor engagement
Ensuring PO terms align with contracts and organizational policies
Managing supplier communications and dispute resolution
In organizations with centralized procurement, all POs flow through this team. In decentralized models, procurement establishes standards and provides oversight while departments create their own POs.
Finance Team (Controllers, CFO): Finance leadership establishes the control framework within which PO creation operates. Finance responsibilities include:
Setting approval thresholds and authorization hierarchies
Establishing budget controls and monitoring commitments vs. budget
Defining chart of accounts and cost allocation requirements
Ensuring PO processes support financial reporting and compliance
Analyzing procurement spend and identifying optimization opportunities
Controllers often establish specific requirements for PO documentation to support month-end closes and audit preparation.
Departmental Requestors: Business users who need goods or services initiate the PO creation process through requisitions. Their responsibilities include:
Clearly specifying requirements (quantities, specifications, timing)
Providing budget justification and account coding
Obtaining departmental approval before submitting requisitions
Confirming receipt of goods or services for three-way matching
The quality of information provided by requestors directly impacts PO accuracy and processing speed.
Vendors and Suppliers: Suppliers are critical stakeholders whose needs must be considered in PO creation design:
They require clear, complete information to fulfill orders accurately
They need reasonable lead times between PO receipt and delivery deadlines
They benefit from consistent PO formats that are easy to process
They require timely communication about changes or cancellations
Strong PO creation processes strengthen supplier relationships by providing professionalism and clarity, potentially yielding better terms and priority treatment.
Approvers (Managers, Directors, Executives): Various levels of management approve POs based on amount thresholds and budget responsibility:
They verify purchases are necessary and align with business objectives
They confirm budget availability and proper account coding
They ensure compliance with procurement policies
They authorize the financial commitment on behalf of the organization
Approval bottlenecks often represent the largest impediment to efficient PO creation, making workflow design critical.
Modern AI copilots like Hyperbots Procurement Copilot facilitate seamless stakeholder alignment by automatically routing information to appropriate parties, flagging issues requiring attention, and coordinating approvals without manual intervention. This eliminates the communication overhead that traditionally slows PO creation.
Why Standardized PO Creation Workflows Matter
Organizations operating with inconsistent, ad hoc PO creation processes face substantial costs and risks that compound as they scale. Standardization transforms PO creation from a source of friction into a competitive advantage.
Impact of Inconsistent Workflows
Procurement Delays: When each department or person creates POs differently, the process lacks predictability. Requestors don't know what information to provide, procurement teams spend time requesting clarifications, and approvers are unsure what they're approving. These inefficiencies stretch procurement cycles from days to weeks, frustrating both internal stakeholders and suppliers.
Vendor Disputes: Inconsistent POs create ambiguity that leads to disputes. When delivery terms are unclear, pricing isn't properly specified, or specifications are vague, suppliers may deliver something different than expected. The resulting back-and-forth consumes time for both procurement and AP teams while damaging supplier relationships.
Budget Overruns: Without standardized workflows, budget checks may be inconsistent or skipped entirely. Departments discover they've overspent only when invoices arrive, forcing difficult decisions about payment delays or budget transfers. Finance loses the ability to manage budgets proactively.
Compliance Failures: Regulatory frameworks require documented authorization of expenditures with appropriate segregation of duties. Inconsistent workflows make it difficult to demonstrate these controls during audits, potentially resulting in compliance findings or qualifications.
Reporting Challenges: When PO data is captured inconsistently, spend analysis becomes nearly impossible. Finance cannot answer basic questions like "How much are we spending with this supplier?" or "What are our outstanding commitments?" without extensive manual data gathering.
Benefits of Standardized PO Creation
Organizations that implement standardized, documented PO creation workflows realize substantial benefits:
Faster Cycle Times: When everyone follows the same process with clear steps and requirements, POs move through the workflow predictably and quickly. Best practice organizations reduce PO cycle time drastically, through standardization alone, before even considering automation.
Better Spend Visibility: Consistent data capture enables real-time spend dashboards showing commitments by supplier, category, department, and time period. CFOs can see total organizational spend at a glance rather than waiting for month-end consolidation.
Audit Readiness: Standardized processes create consistent audit trails that simplify audit preparation. When auditors request PO documentation, finance can produce it immediately rather than hunting through emails and filing cabinets.
Supplier Satisfaction: Professional, consistent PO processes signal organizational maturity to suppliers. Clear POs with complete information enable accurate fulfillment. Timely transmission shows respect for supplier planning. These factors strengthen relationships and may yield better pricing and terms.
Employee Empowerment: Clear, standardized processes reduce the learning curve for new employees and clarify expectations for everyone. Requestors know exactly what information to provide, reducing back-and-forth and enabling self-service.
Scalability: Standardized workflows scale efficiently as organizations grow. What works for 100 monthly POs continues working for 1,000 monthly POs without proportional staffing increases.
Best Practices for Purchase Order Creation
Leading organizations implement specific practices that optimize PO creation while strengthening controls and compliance.
Establish Clear Approval Hierarchies
Ambiguous approval requirements create bottlenecks and compliance gaps. Best practice organizations:
Define Dollar-Based Thresholds: Establish clear authorization levels tied to purchase amounts:
Document who can approve what amounts
Ensure thresholds align with organizational delegation of authority policies
Consider different thresholds for different categories (operating expenses vs. capital)
Review and adjust thresholds periodically as inflation or organization changes occur
Specify Approval Routing Rules: Beyond dollar amounts, routing may depend on:
Purchase category (IT equipment, professional services, marketing, etc.)
Vendor status (preferred suppliers vs. new vendors)
Budget availability (in-budget vs. over-budget purchases)
Risk assessment (high-risk purchases require additional review)
Provide Clear Guidance: Approvers need documented criteria for evaluation:
What should they verify before approving?
What red flags should trigger rejection?
When should they escalate rather than approve directly?
What's their accountability if they approve improper purchases?
Enable Delegation: Provide mechanisms for approvers to designate substitutes during vacation or heavy workload periods, preventing bottlenecks when key approvers are unavailable.
Track Approval Metrics: Monitor approval cycle times by approver to identify systematic bottlenecks and address them through training, delegation, or threshold adjustment.
Use Pre-Approved Supplier Lists
Maintaining curated lists of approved, validated suppliers accelerates PO creation while reducing risk:
Supplier Qualification: Before adding suppliers to approved lists:
Verify business registration and legal status
Confirm financial stability and business continuity
Evaluate quality management systems and certifications
Assess compliance with industry standards or regulations
Verify insurance coverage appropriate to purchase types
Check references from other customers
Preferred Supplier Programs: For strategic categories, establish preferred supplier relationships:
Negotiate framework agreements with pre-set pricing
Establish performance expectations and service levels
Simplify PO creation through standing terms
Enable volume consolidation for better pricing
Build relationships that provide competitive advantage
Supplier Master Data Quality: Maintain clean, complete vendor master data:
Standard naming conventions to prevent duplicates
Complete contact information and remittance details
Tax identification numbers and exemption certificates
Contract references and effective dates
Performance ratings and risk assessments
New Supplier Workflow: When purchases require new suppliers:
Establish clear justification requirements
Define approval thresholds for new vendor additions
Implement validation and due diligence processes
Capture complete supplier information before first PO
Pre-approved supplier lists enable requestors to select vendors confidently while ensuring POs reference validated, complete supplier data.
Automate Data Validation
Manual data validation is time-consuming and inconsistent. Automated validation catches errors before POs advance:
Mandatory Field Validation: System should prevent PO submission without:
Complete supplier information
Detailed item descriptions
Valid account codes
Delivery dates and locations
All pricing fields completed
Format Validation: Verify data format correctness:
Dates in proper format
Numeric fields contain only numbers
Email addresses are properly formatted
Tax IDs match expected patterns
Business Rule Validation: Check logical consistency:
Delivery dates are in the future
Unit prices are within expected ranges for items
PO total matches sum of line items
Account codes exist in chart of accounts
Budget codes are active and valid
Contract Compliance Validation: When contracts exist:
Verify pricing matches contract terms
Confirm supplier is the contracted vendor for this category
Check if purchase is within contract scope
Validate payment terms match contract
Duplicate Detection: Flag potential duplicate POs:
Similar items to same supplier in recent timeframe
Identical or very similar line item descriptions
Multiple POs with same reference numbers
Hyperbots implements comprehensive validation rules that adapt to organizational requirements, catching errors that would otherwise cause downstream problems while learning from patterns to improve validation over time.
Maintain Digital Audit Trails
Complete, immutable audit trails transform audit preparation from a burden into a routine reporting task:
Time-Stamped Activity Logs: Capture every action with:
Who performed the action (user ID and name)
What action occurred (created, modified, approved, transmitted)
When it occurred (date and time stamp)
What changed (before and after values for modifications)
Why it occurred (comments or justification if provided)
Approval Chain Documentation: Record complete approval history:
Who was requested to approve
When approval request was sent
When approval occurred
Method of approval (electronic signature, email, mobile app)
Any comments provided by approvers
Change History: Document all modifications to POs:
Original values and changed values for every field modified
Who authorized the change
Date of change
Reason for change if provided
Whether supplier was notified of change
Document Attachments: Link supporting documentation:
Original requisition
Quotes or proposals
Contract references
Specifications or drawings
Email correspondence
Supplier acknowledgments
Receipt documentation
Invoices
Access Logging: Track who accessed PO information:
Who viewed which POs
What reports were generated
Any exports or downloads of PO data
These comprehensive audit trails should be immutable—no one, including system administrators, should be able to modify or delete historical records. This ensures audit trail integrity and supports forensic investigation if needed.
Integrate PO Creation with ERP/Finance Systems
Seamless integration between PO systems and financial platforms eliminates duplicate data entry and ensures consistent, real-time visibility:
Bidirectional Data Flow:
Vendor master data from ERP flows to PO system
Chart of accounts and cost centers sync automatically
PO data flows back to ERP for commitment accounting
Budget balances accessible in real-time during PO creation
Goods receipts in ERP trigger PO status updates
Commitment Accounting: When POs are created:
Encumber budgets automatically to prevent overspending
Update available balance calculations in real-time
Support period-end accrual generation
Enable cash flow forecasting from outstanding POs
Unified Reporting: Integration enables consolidated reporting:
Combine requisition, PO, receipt, invoice, and payment data
Analyze complete cycle times and bottlenecks
Track from commitment through cash disbursement
Support vendor performance scorecards
Eliminate Reconciliation: With tight integration, reconciliation between systems becomes unnecessary—data exists in one logical system even if physically distributed across platforms.
Modern integration platforms provide pre-built connectors for major ERP systems. Hyperbots integrates natively with QuickBooks, NetSuite, SAP, Microsoft Dynamics, and other leading platforms, with bidirectional sync ensuring data consistency without custom development.
Compliance and Risk Mitigation
Embedded compliance controls transform the PO creation process into a risk management tool:
Segregation of Duties: Enforce through system controls:
Requestors cannot approve their own requisitions
PO creators cannot also be approvers for those POs
Receiving personnel are independent from purchasing
AP processors don't also create POs
Fraud Detection: Monitor for fraud indicators:
Frequent purchases just under approval thresholds (split purchase fraud)
POs to new vendors with limited due diligence
Unusual pricing compared to historical patterns
Concentration of purchases with specific suppliers
POs to vendors sharing addresses with employees
SOX Compliance: For public companies, PO processes must support SOX requirements:
Documented policies and procedures
Consistent application of approval controls
Complete audit trails
Regular control testing and monitoring
Evidence of management review
IFRS Compliance: International accounting standards require:
Recognition of purchase commitments
Proper period allocation of multi-period POs
Fair value measurement for certain commitments
Disclosure of material purchase obligations
Industry-Specific Compliance: Certain industries face additional requirements:
Government contractors must comply with FAR requirements
Healthcare organizations need compliance with procurement regulations
Financial services face heightened vendor due diligence requirements
Organizations implementing these best practices report 50–60% reduction in compliance findings during audits and dramatically improved confidence in procurement controls.
Common Mistakes in PO Creation
Even organizations with good intentions often fall into predictable traps that undermine PO effectiveness. Recognizing these mistakes enables proactive prevention.
Creating POs After Invoice Receipt
One of the most common and problematic mistakes is creating POs retroactively after invoices arrive or goods have already been delivered. This "PO after the fact" problem:
Undermines Financial Controls: The entire purpose of PO processes is authorizing purchases before commitments are made. Retroactive POs bypass these controls entirely, creating unauthorized spending.
Eliminates Budget Protection: Budget checks conducted after goods are delivered cannot prevent overspending, the commitment has already occurred.
Causes Three-Way Matching Failures: When POs are backdated to match invoices, the three-way matching becomes meaningless validation theater rather than genuine control.
Violates Audit Requirements: Auditors quickly identify backdated POs through date analysis. This pattern indicates control weaknesses and may result in audit findings or material weaknesses.
Damages Supplier Relationships: Requesting retroactive POs signals disorganization and lack of financial discipline. Suppliers may become concerned about payment reliability.
Root Causes:
Urgent purchases where "proper process takes too long"
Shadow IT spending where departments buy without procurement involvement
Verbal commitments made to vendors before formal authorization
Lack of understanding about PO requirements
Insufficient resources to process POs timely
Prevention:
Establish expedited approval paths for truly urgent purchases
Educate stakeholders that vendor commitments require POs first
Implement consequences for unauthorized commitments
Ensure PO creation is fast enough to support business needs
Monitor for backdated POs and address root causes
Skipping Budget Checks
Creating POs without verifying budget availability leads to overspending that becomes apparent only when invoices arrive, too late for prevention:
Budget Overrun Discovery Too Late: When budget checks occur at invoice payment rather than PO creation, departments discover overspending after goods are delivered and must be paid for.
Limited Remediation Options: Once goods are received, options are limited: pay from overspent budget, request emergency budget transfers, or delay payment (damaging supplier relationships).
Lost Forecasting Accuracy: Without budget checks at PO creation, finance lacks visibility into commitments. Budget reports show remaining balance rather than truly available balance.
Weakened Cost Control: Knowing that budget checks won't prevent purchases, departments may become less disciplined about spending control.
Root Causes:
PO systems not integrated with budget/ERP systems
Budget data not accessible in real-time
Complex budget structures making checks difficult
Pressure to expedite purchases overriding controls
Belief that "we'll find budget somewhere"
Prevention:
Implement real-time budget checks before PO approval
Calculate available budget as (allocated - committed POs - actual spend)
Block PO approval when budget insufficient (with override capability for exceptional cases)
Provide budget owners with dashboard visibility
Generate alerts when budgets approach limits
Poor Vendor Communication
Unclear, incomplete, or untimely communication with suppliers creates fulfillment problems:
Insufficient PO Detail: Vague item descriptions, missing specifications, or incomplete delivery instructions cause suppliers to deliver wrong items, quantities, or configurations.
Late PO Transmission: Creating approved POs but delaying transmission to suppliers prevents them from planning fulfillment properly, leading to late deliveries.
No Acknowledgment Follow-Up: Failing to confirm supplier received and accepted POs leads to situations where buyers assume orders are in process while suppliers haven't even seen the PO.
Poor Change Communication: Modifying POs without clearly communicating changes to suppliers results in deliveries based on outdated PO versions.
Missing Context: POs that don't explain project context, criticality, or special requirements leave suppliers unable to prioritize or accommodate special needs.
Root Causes:
Treating POs as internal documents rather than supplier communication tools
Manual processes where PO transmission is separate step easily forgotten
Lack of supplier portal or automated transmission
Insufficient detail in original requisitions carrying through to POs
No process for tracking supplier acknowledgment
Prevention:
Design PO templates with suppliers in mind- clear, complete, actionable
Automate PO transmission immediately upon final approval
Implement supplier acknowledgment tracking with follow-up workflow
Establish direct communication channels for PO questions
Provide context and contact information on POs
Reliance on Spreadsheets or Email
Managing PO creation through Excel spreadsheets or email creates numerous problems:
No Version Control: Multiple PO versions circulate via email with no clarity about which is current. Suppliers may work from outdated versions while buyers reference different versions.
Lost Information: PO requests in email threads get buried. Approval emails aren't connected to PO documents. Receipt confirmations exist separately from POs.
No Workflow Enforcement: Spreadsheets can't enforce approval routing, prevent unauthorized modifications, or ensure process consistency.
Manual Data Entry: Information is typed multiple times—from email to spreadsheet to accounting system—introducing errors at each step.
Limited Visibility: No one can answer "what POs are pending approval?" or "what did we order from this supplier last quarter?" without extensive manual searching.
No Audit Trail: Email and spreadsheet approaches don't create tamper-proof audit logs. Historical records can be modified or deleted without detection.
Security Risks: Spreadsheets shared via email lack access controls. Sensitive vendor or pricing information may be exposed to unauthorized individuals.
Root Causes:
"Spreadsheets are free and everyone knows how to use them"
Resistance to adopting new technology
Lack of budget for proper procurement systems
IT resource constraints preventing implementation
Small organizations thinking they don't need formal systems
Prevention:
Adopt cloud-based procurement platforms with reasonable pricing
Demonstrate ROI of automation vs. manual spreadsheet costs
Start with simple systems and add sophistication over time
Leverage modern solutions with fast, low-cost implementation
Hyperbots provides enterprise-grade capabilities at accessible price points, with implementation measured in weeks rather than months. Organizations transitioning from spreadsheets to Hyperbots typically achieve ROI within the first quarter through elimination of manual processing costs and error reduction.
How Hyperbots Transforms Purchase Order Creation
While improving processes and adopting best practices helps, transformational change requires intelligent automation that fundamentally reimagines how PO creation works. Hyperbots AI Procurement Copilot represents this new generation of procurement technology.
Procurement Copilot Core Capabilities
Auto-Generation of POs from Multiple Sources:
Rather than requiring manual PO creation, Hyperbots automatically generates draft POs from various triggers:
Requisition Conversion: Purchase requisitions submitted through any channel (email, Slack, Teams, web forms) are automatically converted to draft POs with all information pre-populated
Contract-Based Generation: For purchases covered by existing contracts, Hyperbots extracts pricing, terms, and specifications from contract documents (even PDFs) and generates POs automatically
Recurring Order Prediction: Machine learning analyzes historical purchase patterns and proactively generates POs for recurring needs before inventory runs low or contracts expire
Consumption Triggers: Integration with inventory management systems triggers automatic PO generation when reorder points are reached
This proactive PO generation eliminates manual creation effort by offering straight through processing while ensuring purchases occur on time without last-minute scrambling.
Intelligent Workflow Automation:
Hyperbots doesn't just digitize approval routing—it intelligently orchestrates the entire approval process:
Dynamic Routing: POs are automatically routed to appropriate approvers based on configurable rules considering amount, category, department, vendor type, and budget status
Parallel Processing: When multiple approvals are required, Hyperbots requests them simultaneously rather than sequentially, dramatically reducing cycle time
Smart Escalation: When approvals aren't completed within defined timeframes, the system automatically escalates to backup approvers or management
Context Provision: Approvers receive complete context—requisition justification, budget status, pricing comparisons, contract terms, prior purchase history—enabling informed decisions without research
Mobile-Optimized: One-click approval via email, Slack, Teams, or mobile app enables approval from anywhere
Delegation Management: Approvers easily designate substitutes during vacation or high-workload periods
The result: PO approval cycles compressed from days to hours, with approval rates improving because approvers have the information needed to make confident decisions.
AI-Powered Validation:
Hyperbots validates every PO against multiple criteria before allowing progression:
Completeness Checks: Verifies all mandatory fields are populated with properly formatted data
Pricing Validation: Compares PO pricing against contract terms, prior purchase history, and market benchmarks, flagging significant variances
Budget Verification: Checks budget availability in real-time against ERP systems, preventing over-budget POs
Duplicate Detection: Identifies potential duplicate POs based on supplier, items, amounts, and timing
Contract Compliance: Ensures PO terms align with existing contracts and preferred supplier agreements
Fraud Pattern Recognition: Detects suspicious patterns like split purchases, unusual supplier relationships, or pricing anomalies
When validation issues are detected, Hyperbots either resolves them autonomously (for routine issues within defined parameters) or escalates to appropriate personnel with full context and recommended resolutions.
Seamless ERP Integration:
Hyperbots integrates natively with leading ERP and accounting platforms without custom development:
QuickBooks: All versions including Online, Desktop, and Enterprise
NetSuite: Complete integration with procurement, financial, and inventory modules
SAP: S/4HANA and ECC versions with real-time data sync
Microsoft Dynamics 365: Finance, Business Central, and NAV versions
Oracle ERP Cloud: Full financial and procurement integration
Sage Intacct: Multi-entity support with dimensional accounting
Integration is bidirectional and real-time:
Vendor master data syncs automatically
Chart of accounts and cost centers stay current
Budget balances are accessible during PO creation
PO commitments update ERP immediately
Goods receipts flow back to update PO status
Invoice matching occurs across systems seamlessly
Hyperbots supports dual-write mode during system transitions, ensuring no data loss when organizations migrate between ERP platforms—a critical capability for companies undergoing digital transformation.
Intelligent Auto-Population:
Hyperbots minimizes manual data entry by extracting and populating information from multiple sources:
Contract Extraction: Natural language processing extracts pricing, terms, and specifications from contract PDFs, even when they're unstructured documents
Vendor Portal Integration: Pulls current pricing and product information directly from supplier catalogs and portals
Historical Learning: Analyzes prior invoices and POs to predict costs and populate details for repeat purchases
Requisition Import: Extracts structured and unstructured data from requisitions submitted via email, Slack, or other channels
One-Click Cloning: Creates new POs by copying similar historical POs, modifying only what's different
For repeat purchases, users simply select the item from history and confirm—the system handles all data population. For new purchases, intelligent suggestions based on category and supplier reduce typing to a minimum.
Differentiation from Competitors
The procurement technology market includes numerous solutions, but Hyperbots stands apart through several fundamental differences:
End-to-End Automation vs. Template-Based Tools:
Many procurement platforms offer digital forms—essentially electronic versions of paper POs. Users still manually complete all fields, route for approval, and handle exceptions. Hyperbots goes far beyond this by:
Automating PO generation rather than just digitizing templates
Using AI to predict needs before users request them
Autonomously resolving routine exceptions rather than flagging everything for manual review
Learning from each transaction to improve future automation
Handling unstructured inputs (emails, PDFs, conversations) not just structured forms
Fast Go-Live Timeline:
Traditional procurement implementations require 6-12 months with extensive configuration, data migration, change management, and user training. Hyperbots deploys in 3-4 weeks:
Pre-configured workflows based on industry best practices
Automated data migration from existing systems
AI learns organizational patterns during initial use
Intuitive interface requiring minimal training
Phased rollout option (pilot then expand)
Expert implementation support included
Organizations achieve ROI in the first quarter rather than waiting years for payback. This fast deployment is possible because Hyperbots leverages AI to adapt to organizational requirements rather than requiring extensive manual configuration.
Integrated Ecosystem vs. Point Solutions:
Most procurement vendors offer standalone PO systems that must integrate with separate invoice, payment, and expense management solutions. Integration gaps create manual handoffs and data synchronization issues.
Hyperbots provides an integrated ecosystem where Procurement Copilot works seamlessly with:
Invoice Processing Copilot: Automatically matches invoices against POs, resolves discrepancies, routes exceptions
Payments Copilot: Schedules and executes payments based on PO terms, optimizes for early payment discounts
Sales Tax Copilot: Ensures proper tax treatment, handles exemption certificates, supports compliance
This ecosystem eliminates gaps and manual processes that plague multi-vendor stacks. Data flows seamlessly from requisition through payment without re-keying or reconciliation.
Continuous Intelligence:
Hyperbots doesn't just process POs, it continuously analyzes procurement data to surface insights and recommendations:
Identifies consolidation opportunities where purchases could combine for volume discounts
Flags suppliers with performance issues (late deliveries, quality problems, price increases)
Recommends optimal reorder points based on consumption patterns
Highlights compliance risks before they become violations
Benchmarks organizational spend against industry standards
Predicts future spending trends for better budget planning
These insights transform procurement from transactional function to strategic capability that actively drives value.
Exception Handling Intelligence:
When issues arise—pricing mismatches, missing approvals, budget overruns—traditional systems halt and request human intervention. Hyperbots takes a different approach:
AI agents analyze exceptions to determine severity and appropriate resolution
Routine issues within defined parameters are resolved autonomously
Complex exceptions are routed to appropriate personnel with full context and recommended actions
Resolution patterns are learned to handle similar future cases automatically
All exception handling is fully logged for audit purposes
Enterprise-Grade Security:
Hyperbots maintains SOC 2 Type 2 and ISO 27001 certification, ensuring:
End-to-end encryption of data in transit and at rest
Role-based access controls with multi-factor authentication
Regular third-party security audits and penetration testing
Comprehensive disaster recovery and business continuity
Compliance with GDPR, CCPA, and other privacy regulations
Options for private cloud or on-premises deployment for highly regulated industries
For enterprises with stringent security requirements, Hyperbots provides the governance and controls necessary for procurement systems handling sensitive vendor and financial data.
ROI of Automating PO Creation
The financial case for automating purchase order creation is compelling across direct costs, cycle time improvements, and strategic benefits.
Direct Cost Reduction
Industry research consistently shows manual PO creation costs between $506 and $527 per purchase order when accounting for all direct and indirect costs:
Labor time for PO creation (research, data entry, formatting)
Approval routing and follow-up
Supplier communication and coordination
Error correction and dispute resolution
Reconciliation during invoice processing
Overhead allocation
For an organization processing 10,000 POs annually, this represents over $5 million in annual processing costs.
Beyond direct processing costs, organizations realize:
Headcount Optimization: Finance teams scale without proportional staffing increases; existing personnel focus on analysis rather than transaction processing
Error Cost Reduction: Fewer duplicate payments, pricing disputes, and late payment penalties
Discount Capture: Faster cycle times enable capturing early payment discounts worth 1-2% of spend
Expedite Fee Elimination: Timely PO processing avoids rush shipping and expedite charges
Compliance and Risk Mitigation
The risk reduction value of automated PO creation is harder to quantify but potentially more valuable than direct cost savings:
Audit Cost Reduction: Organizations with automated PO systems and strong audit trails spend 40-50% less time on audit preparation. What once required weeks of gathering documentation now takes days or hours. Responding to auditor requests happens in minutes rather than days.
Fraud Prevention: Automated segregation of duties and approval enforcement prevents the majority of procurement fraud schemes. Given that median procurement fraud losses exceed $200,000 per incident, prevention delivers substantial value. Automated duplicate detection alone can save organizations hundreds of thousands annually.
Regulatory Compliance: Automated audit trails and embedded controls reduce regulatory compliance violations and associated penalties. For public companies, strong SOX controls reduce audit fees and improve stakeholder confidence.
Contract Compliance: Automated validation against contract terms ensures negotiated pricing is actually realized—often recovering 3-5% of contract spend through enforcement that manual processes miss.
Budget Discipline: Real-time budget checks prevent overspending that creates period-end crises, budget transfer requests, and strained departmental relationships.
Strategic Benefits
Beyond tactical efficiency, automated PO creation enables strategic capabilities:
Spend Visibility: Real-time dashboards show commitments by supplier, category, department, and project—enabling data-driven procurement strategies. CFOs can identify consolidation opportunities, negotiate based on actual volume, and manage working capital proactively.
Supplier Performance Management: Automated tracking of PO-to-delivery cycles, quality issues, and pricing trends supports objective supplier evaluation and optimization. Underperforming suppliers are identified quickly, enabling proactive management.
Budget Management: Real-time visibility into commitments vs. budget enables proactive management rather than reactive crisis response. Departments see available balance (not just spent to date), preventing late-period budget surprises.
Scalability: Automated processes support business growth without proportional procurement team expansion.
Working Capital Optimization: Better visibility and control over commitments enables strategic working capital management. Organizations can time payments to optimize cash position while maintaining supplier relationships.
FAQs on Purchase Order Creation
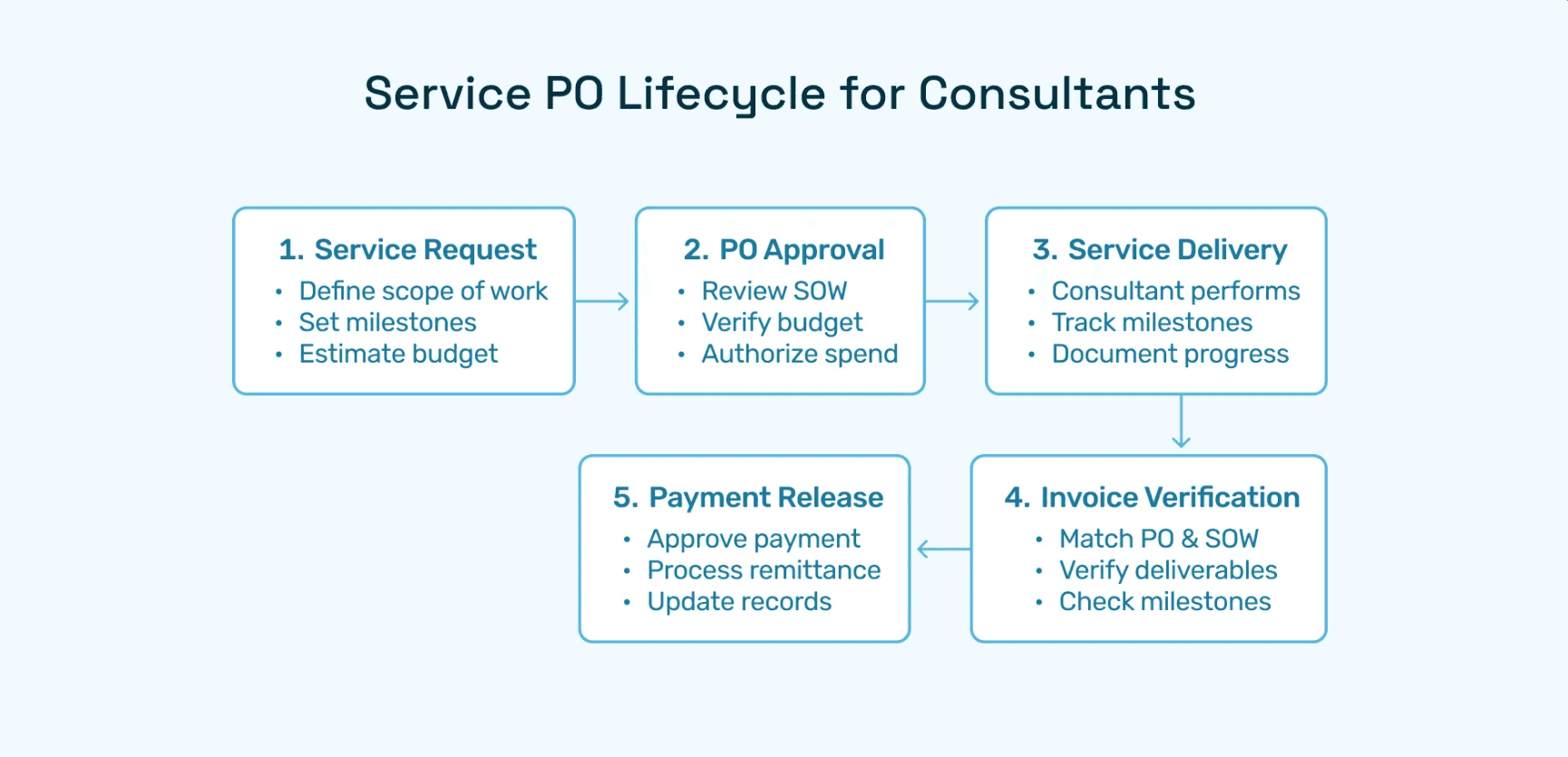
1. What's the difference between purchase order creation and requisition?
A purchase requisition is an internal request for goods or services submitted by an employee or department. It represents the identification of a need but isn't a commitment to a supplier. Purchase order creation is the subsequent process of converting an approved requisition into a formal, legally binding document transmitted to a supplier. The requisition asks "can we buy this?" while the PO tells the supplier "we are buying this under these terms." Requisitions go through internal approval; POs go to external vendors.
2. Can small businesses benefit from structured PO workflows?
Absolutely. While large enterprises have complex PO requirements, small businesses gain significant benefits from structured workflows:
Control spending and prevent unauthorized purchases
Maintain professional relationships with suppliers through clear documentation
Prepare for growth by establishing scalable processes early
Simplify tax preparation and audit readiness
Enable delegation as the business expands beyond founder-managed purchasing
Small businesses can start with simple workflows and templates, adding sophistication as they grow. Modern platforms like Hyperbots offer pricing and capabilities appropriate for companies of all sizes, from startups to Fortune 500 enterprises.
3. How long does it take to create a PO manually vs. automated?
Manual PO creation typically requires 30-45 minutes per PO when accounting for:
Gathering information from requisitions and quotes
Looking up vendor details
Entering data into templates or systems
Verifying pricing and terms
Obtaining approvals
Transmitting to suppliers
Complex POs with multiple line items or approvals can take 60-90 minutes. This doesn't include time spent correcting errors or resolving disputes caused by incomplete information.
4. What's included in a standard PO creation workflow?
A comprehensive PO creation workflow includes:
Requisition submission and initial review
Departmental approval of business need
Budget availability verification
Procurement review and supplier selection
PO drafting with all required fields
Multi-level approval routing based on amount and category
Final validation before transmission
Electronic transmission to supplier
Supplier acknowledgment capture
Receipt documentation upon delivery
Three-way matching with invoice
PO closure and archival
Organizations may adapt this framework based on size and complexity, but these core steps ensure proper control and documentation.
5. How do digital tools ensure compliance in PO creation?
Digital PO systems enforce compliance through multiple mechanisms:
Embedded Controls: Systems prevent actions that violate policies (e.g., can't approve own PO, can't exceed budget without override)
Automated Routing: Approval hierarchies are system-enforced rather than policy-dependent
Immutable Audit Trails: Complete activity logs that can't be modified or deleted
Real-Time Validation: Checks against contracts, budgets, and policies before PO approval
Segregation of Duties: Role-based permissions prevent conflicts of interest
Exception Monitoring: Automated alerts for unusual patterns or policy violations
Reporting: Compliance dashboards show control effectiveness and exceptions
These automated controls are more reliable than manual policy compliance because they can't be bypassed or forgotten.
6. Is a PO legally binding once created?
A PO becomes legally binding when the supplier accepts it, typically through formal acknowledgment or by beginning fulfillment. The PO represents an offer to purchase under stated terms. Supplier acceptance creates a binding contract.
However, legal enforceability depends on several factors:
The PO must be issued by someone with authority to bind the organization
Terms must be clear and complete
Both parties must agree to all material terms
The PO must comply with applicable laws and regulations
Many organizations include standard terms and conditions making clear that POs are governed by those terms, providing additional legal protection. Once binding, either party faces potential legal consequences for failure to perform.
Organizations should ensure PO creation workflows include proper authorization to avoid situations where unauthorized individuals create binding commitments.
7. Can AI really reduce errors in PO creation?
Yes, demonstrably. AI reduces PO errors through several mechanisms:
Automated Data Extraction: Natural language processing extracts information from contracts, quotes, and requisitions more accurately than manual typing
Validation Logic: AI checks completeness, format, and business rules that humans might miss
Pattern Recognition: Machine learning identifies anomalies based on historical patterns (unusual pricing, suspicious vendors, potential duplicates)
Continuous Learning: Systems improve over time by learning from corrections and feedback
Elimination of Re-Entry: Data flows automatically between systems without manual transcription
Organizations implementing AI-driven PO creation report error rate reductions from 15-20% (manual) to under 2% (automated). The remaining errors are typically edge cases requiring human judgment rather than data entry mistakes.
The key is that AI doesn't just digitize manual processes—it fundamentally reimagines how work gets done, eliminating error-prone steps entirely.
The Future of PO Creation Workflows
The evolution of purchase order creation is accelerating rapidly. What once required days of manual effort now happens in hours with intelligent automation. But the transformation is just beginning.
The next generation of PO creation will leverage emerging technologies:
Predictive Procurement: Rather than waiting for requisitions, AI will predict purchase needs based on consumption patterns, project timelines, inventory levels, and seasonal trends. Systems will generate draft POs proactively, asking "you'll likely need this—should I order it?" instead of waiting for shortages to trigger requests.
Autonomous Negotiation: AI agents will engage suppliers in preliminary negotiations within defined parameters—requesting competitive bids, comparing offers, clarifying terms, and identifying optimal pricing. Procurement professionals approve final terms rather than conducting all negotiations manually.
Blockchain-Enabled POs: Distributed ledger technology will create shared, immutable PO records between buyers and suppliers. This eliminates disputes about what was ordered, reduces fraud, and enables instant payment settlement when delivery conditions are met.
IoT Integration: Connected devices will automatically trigger PO creation when inventory reaches reorder points, equipment requires maintenance parts, or consumption rates change. Smart warehouses will manage their own procurement within approved parameters.
Natural Language Interfaces: Users will create POs through conversational interfaces: "Order 50 boxes of printer paper from Office Depot for delivery next week" becomes a complete PO without forms or data entry. AI handles all details based on organizational policies and historical patterns.
Advanced Analytics: Machine learning models will continuously optimize procurement decisions—identifying consolidation opportunities, predicting supplier risks, recommending strategic sourcing approaches, and forecasting spend with increasing accuracy.
For CFOs and finance leaders, the strategic imperative is clear: organizations treating PO creation as administrative paperwork will fall behind competitors who recognize it as a strategic capability. Purchase orders generate valuable data, enforce critical controls, and enable operational efficiency. When managed intelligently, they become competitive advantages rather than compliance burdens.